Abstract
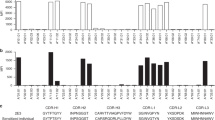
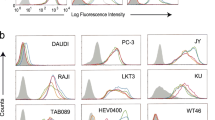
The regions of the HLA-A2 molecule controlling anti-A2 alloreactivity were explored using naturally occurring allelic variants of HLA-A, and a panel of transfectants expressing the products of A2.1 genes that had been mutated at multiple positions encoding residues in the α2 domain α-helix. As a means of detecting distant conformational effects, these altered A2.1 molecules were also examined serologically. Amino acid substitutions at the carboxy-terminal end of the α2 domain α-helix led to diminished staining with the monoclonal antibody (mAb) MA2.1. The epitope for this antibody has previously been mapped to the α1 domain α-helix (residues 62–65). This suggests that interdomain contacts may cause conformational alteration, and that mutants can have distant, as well as local effects. Of the 24 positions where substitutions were made, only six led to loss of the anti-A2 alloresponse by the three clones and three lines that were tested. In addition, the mutations that altered the MA2.1 epitope, located on the α1 domain α-helix, did not inhibit allorecognition. This suggests that a limited number of regions on the A2.1 molecule are responsible for allodeterminant expression. The most influential substitutions were those at positions 152, 154, 162, and 166. It is notable that three of these are predicted to be T-cell receptor (Tcr)-contacting residues, and one (152) to contribute to peptide binding. These results suggest that the specificity of alloreactive T cells is determined by exposed polymorphisms, directly contacted by the Tcr, and by concealed polymorphisms which influence peptide binding.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bernhard, E. J., Al-Xuan, T. Le, Yannelli, J. R., Holterman, M. J., Hogan, K. T., Parham, P., and Engelhard, V. H.: The ability of cytotoxic T cells to recognize HLA-A2.1 or HLA-B7 antigens expressed on murine cells correlates with their epitope specificity. J Immunol 139: 3614–3621, 1987
Bjorkman, B. J., Saper, M. A., Samraoui, B., Bennett, W. S., Strominger, J. L., and Wiley, D. C.: Structure of the human class I histocompatibility antigen, HLA-A2. Nature 329: 506–511, 1987
Braunstein, N. D. and Germain, R. N.: Allele-specific control of Ia molecule surface expression and conformation: Implications for a general model of Ia structure-function relationships. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84: 2921–2925, 1987
Calvo, V., Rojo, S., Lopez, D., Galocha, B., and Lopez De Castro, J. A.: Structure and diversity of HLA-B27 subtype polymorphism. J Immunol 144: 4038–4045, 1990
Darsley, M. J., Takahashi, H., Macchi, M. J., Frelinger, J. A., Ozato, K., and Appella, E.: New family of exon-shuffled recombinent genes reveals extensive interdomain interactions in class I histocompatibility antigens and identifies residues involved. J Exp Med 165: 211–222, 1987
Elliott, T. J. and Eisen, H. N.: Cytotoxic T lymphocytes recognize a reconstituted class I histocompatibility antigen (HLA-A2) as an allogeneic target molecule. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87: 5213–5217, 1990
Ferrier, P., Layet, C., Caillol, D. H., Jordan, B. R., and Lemonnier, F. A.: The association between murine β2-microglobulin and HLA-class I heavy chains results in serologically detectable conformational changes of both chains. J Immunol 135: 1281–1287, 1985
Healy, F., Sire, J., Gomard, E., Yssel, H., Jordan, B., and Levy, J.: A study of functionally active amino acids involved in the interaction of HLA-A2 or HLA-A3 molecules with cytolytic T lymphocytes. J Immunol 141: 2487–2496, 1988
Heath, W. R., Hurd, M. E., Carbone, F. R., and Sherman, L. A.: Peptide-dependent recognition of H-2Kb by alloreactive cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Nature 341: 749–752, 1989
Hogan, K. T., Clayberger, C., Al-Xuan, T. L., Walk, B. F., Ridge, J., Parham, P., Krensky, A. M., and Engelhard, V. H.: Cytotoxic T lymphocyte-defined epitope differences between HLA-A2.1 and HLA-A2.2 map to two distinct regions of the molecule. J Immunol 141: 4005–4011, 1988a
Hogan, K. T., Clayberger, C., Bernhard, E. J., Walk, S. F., Ridge, J. P., Parham, P., Krensky, A. M., and Engelhard, V. H.: Identification by site-directed mutagenesis of amino-acid residues contributing to serological and cytotoxic T lymphocyte-defined epitope differences between HLA-A2.1 and HLA-A2.3. J Immunol 141: 2519–2525, 1988b
Hogan, K. T., Clayberger, C., Bernhard, E. J., Walk, S. F., Ridge, J. P., Parham, P., Krensky, A. M., and Engelhard, V. H.: A panel of unique HLA-A2 mutant molecules define epitopes recognized by HLA-A2-specific antibodies and cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J Immunol 142: 2097–2104, 1989
Kahn-Perles, B., Boyer, C., Arnold, B., Sanderson, A. R., Ferrier, P., and Lemonnier, F. A.: Acquisition of HLA-class I W6/32 defined antigenic determinant by heavy chain from different species following association with bovine β2-microglobulin. J Immunol 138: 2190–2196, 1987
Kanda, T., La Pan, K., Takahashi, H., Appella, E., and Frelinger, J. A.: The α1 and α2 domains of H-2 class I molecules interact to form unique epitopes. Immunogenetics 25: 110–115, 1987
Kisielow, P., Teh, H. S., Bluthmann, H., and von Boehmer, H.: Positive selection of antigen-specific T cells in thymus by restricting MHC molecules. Nature 335: 730–733, 1988
Lechler, R. I., Lombardi, G., Batchelor, J. R., Reinsmoen, N., and Bach, F. N.: The molecular basis of alloreactivity. Immunol Today 11: 83–88, 1990
Lombardi, G., Sidhu, S., Daly, M., Batchelor, J. R., Makgoba, W., and Lechler, R. I.: Are primary alloresponse truly primary? Int Immunol 2: 9–13, 1989a
Lombardi, G., Sidhu, S., Lamb, J. R., Batchelor, J. R., and Lechler, R. I.: Corecognition of endogenous antigens with HLA-DR1 by alloreactive human T cell clones. J Immunol 142: 753–759, 1989b
McMichael, A. J., Parham, P., Rust, N., and Brodsky, F. M.: A monoclonal antibody that recognizes an antigenic determinant shared by HLA-A2 and B17. Hum Immunol 1: 121–129, 1980
Matis, L. A., Sorger, S. B., McElligot, D. L., Fink, P. J., and Hedrick, S. M.: The molecular basis of alloreactivity in antigen-specific, major histocompatibility complex-restricted T cell clones. Cell 51: 59–69, 1987
Mattson, D. H., Shimojo, N., Cowan, E. P., Baskin, J. J., Turner, R. V., Shvetsky, B. D., Coligan, J. E., Maloy, W. L., and Biddison, W. E.: Differential effects of amino-acid substitutions in the β-sheet floor and α2-helix of HLA-A2 on recognition by alloreactive viral peptide-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J Immunol 143: 1101–1107, 1989
Matzinger, P. and Bevan, M. J.: Why do so many lymphocytes respond to major histocompatibility antigens. Cell Immunol 29: 1–5, 1977
Mentzer, S. J., Barbosa, J. A., Strominger, J. L., Biro, P. A., and Burakoff, S. J.: Species-restricted recognition of transfected HLA-A2 and HLA-B7 by human CTL clones. J Immunol 137: 408–413, 1986
Moots, R. J., Matsui, M., Pazminy, L., McMichael, A., and Frelinger, J.: A cluster of mutations in HLA-A2 α2-helix abolishes peptide recognition by T cells. Immunogenetics 34, this issue
Ohlen, C., Bastin, J., Ljunggren, H., Foster, L., Wolpert, E., Klein, G., Townsend, A. R. M., and Karre, K.: Resistance to H-2-restricted but not to allo-H2-specific graft and cytotoxic T lymphocyte responses in lymphoma mutant. J Immunol 145: 52, 1990
Santos-Aguado, J., Barbosa, J. A., Biro, A. P., and Strominger, J. L.: Molecular characterization of serological recognition sites in the human HLA-A2 molecule. J Immunol 141: 2811–2818, 1988
Santos-Aguado, J., Crimmins, A. V., Mentzer, S. J., Burakoff, S. J., and Strominger, J. L.: Alloreactivity studied with mutants of HLA-A2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86: 8936–8940, 1989
Storkus, W., Howell, D. N., Salter, R. D., Dawson, J. R., and Cresswell, P.: NK susceptibility varies inversely with target cell class I HLA antigen expression. J Immunol 138: 1657–1659, 1987
Zinkernagel, R. M.: Thymus and lymphohemopoietic cells: their role in T cell maturation, in selection of T cells H-2 restriction specificity, and H-2 linked Ir gene control. Immunol Rev 42: 224–270, 1978
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lombardi, G., Matsui, M., Moots, R. et al. Limited regions of the α2-domain α-helix control anti-A2 allorecognition: an analysis using a panel of A2 mutants. Immunogenetics 34, 149–156 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00205817
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00205817