Abstract
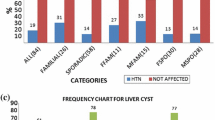
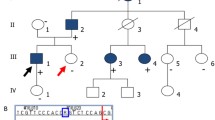
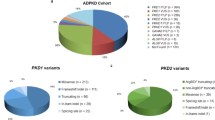
Linkage analysis was performed on 22 Bulgarian families with polycystic kidney disease (PKD) ascertained through the hemodialysis centers of two medical schools. A total of 128 affected and 59 unaffected individuals, and 54 spouses have been investigated using eight polymorphic markers linked to PKD1 and nine markers to PKD2. The results demonstrate locus heterogeneity with 0.67 as the maximum likelihood value of alpha, i.e., the proportion of families linked to PKD1. In five families, the results suggest linkage to PKD2, and observed recombinants place the gene between loci D4S1544 and D4S1542. In one family, two double recombinants for closely linked markers on chromosome 16 and on chromosome 4 give evidence for the lack of link-age to either PKD1 or PKD2, thus suggesting the involvement of a third locus. Analysis of clinical data in the PKD1 group versus the unlinked group shows no significant differences in the severity of the disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bachner L, Vinet MC, Lacave R, Babron MC, Rondeau E, Sraer JD, Chevet D, Kaplan JC (1990) Linkage study of a large family with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease with reduced expression. Absence of linkage to the PKD 1 locus. Hum Genet 85:221–227
Bear JC, McManamon P, Morgan J, Payne RH, Lewis H, Gault MH, Churchill DN (1984) Age at clinical onset and at ultrasonographic detection of adult polycystic kidney disease: data for genetic counselling. Am J Med Genet 18:45–53
Bear JC, Parfrey PS, Morgan JM, Martin CJ, Cramer BC (1992) Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease: new information for genetic counselling. Am J Med Genet 43:548–553
Breuning MH, Snijdewint FG, Smits JR, Dauwerse JG, Saris JJ, Ommen GJ van (1990a) A TaqI polymorphism identified by 26–6 (D16S125) proximal to the locus affecting adult polycystic kidney disease (PKD1) on chromosome 16. Nucleic Acids Res 18:3106
Breuning MH, Snijdewint FG, Dauwerse JG, Saris JJ, Bakker E, Pearson PL, Ommen GJ van (1990b) Two step procedure for early diagnosis of polycystic kidney disease with polymorphic DNA markers on both sides of the gene. J Med Genet 27:614–617
Dalgaard OZ (1957) Bilateral polycystic disease of the kidneys: a follow-up of two hundred and eighty four patients and their families. Acta Med Scand 328:1–255
Dalgaard OZ, Norby S (1989) Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease in the 1980's. Clin Genet 36:320–325
Davies F, Coles GA, Harper PS, Williams AJ, Evans C, Cochlin D (1991) Polycystic kidney disease re-evaluated: a population-based study. Q J Med 79:477–485
Fenton I, Sandkuijl LA (1992) MEGABASE/PKD: a genetic database for polycystic kidney disease. Contrib Nephrol 97:118–127
Fossdal R, Böthvarsson M, Asmundsson J, Peters D, Breuning MH, Jensson O (1993) Icelandic families with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease: families unlinked to chromosome 16p13.3 revealed by linkage analysis. Hum Genet 91:609–613
Gabow PA, Johnson AM, Kaehny WD, Kimberling WJ, Lezotte DC, Duley IT, Jones RH (1992) Factors affecting the progression of renal disease in autosomal-dominant polycystic kidney disease. Kidney Int 41:1311–1319
Germino GG, Barton NJ, Lamb J, Higgs DR, Harris P, Xiao GH, Scherer G, Nakamura Y, Reeders ST (1990) Identification of a locus which shows no genetic recombination with the autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease gene on chromosome 16. Am J Hum Genet 46:925–933
Germino GG, Weinstat-Saslow D, Himmelbauer H, Gillespie GA, Somlo S, Wirth B, Barton N, Harris KL, Frischauf AM, Reeders ST (1992) The gene for autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease lies in a 750-kb CpG-rich region. Genomics 13:144–151
Gyapay G, Morissette J, Vignal A, Dib C, Fizames C, Millasseau P, Marc S, Bernardi G, Lathrop M, Weissenbach J (1994) The 1993–94 Genethon human genetic linkage map. Nature Genet 7:246–339
Harris PC, Thomas S, Ratcliffe PJ, Breuning MH, Coto E, Lopez-Larrea C (1991) Rapid genetic analysis of families with polycystic kidney disease 1 by means of a microsatellite marker. Lancet 338:1484–1487
Hyland VJ, Suthers GK, Friend K, MacKinnon RN, Callen DF, Breuning MH, Keith T, Brown VA, Phipps P, Sutherland GR (1990) Probe, VK5B, is located in the same interval as the autosomal dominant adult polycystic kidney disease locus, PKD1. Hum Genet 84:286–288
Kimberling WJ, Fain PR, Kenyon JB, Goldgar D, Sujansky E, Gabow PA (1988) Linkage heterogeneity of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. N Engl J Med 319:913–918
Kimberling WJ, Kumar S, Gabow PA, Kenyon JB, Connolly CJ, Somlo S (1993) Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease: localization of the second gene to chromosome 4q13–q23. Genomics 18:467–472
Lathrop GM, Lalouel JM (1984) Easy calculations of lod scores and genetic risks on small computers. Am J Hum Genet 36:460–465
Mandich P, Restagno G, Novelli G, Bellone E, Potenza L, Varetto O, Dallapiccola B, Carbonara A, Ajmar F (1990) Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease: a linkage evaluation of heterogeneity in Italy. Italian Collaborative Group on Polycystic Kidney Disease. Am J Med Genet 35:579–581
Mills KA, Buetow KH, Xu Y, Weber JL, Altherr MR, Wasmuth JJ, Murray JC (1992) Genetic and physical maps of human chromosome 4 based on dinucleotide repeats. Genomics 14:209–219
Norby S, Sorensen AW, Boesen P (1989) Non-allelic genetic heterogeneity of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease? Prog Clin Biol Res 305:83–88
Ott J (1991) Analysis of human genetic linkage, revised edn. Johns Hopkins University Press Baltimore London
Parfrey PS, Bear JC, Morgan J, Cramer BC, McManamon PJ, Gault MH, Churchill DN, Singh M, Hewitt R, Somlo S, et al (1990) The diagnosis and prognosis of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. N Engl J Med 323:1085–1090
Peters DJ, Sandkuijl LA (1992) Genetic heterogeneity of polycystic kidney disease in Europe. Contrib Nephrol 97:128–139
Peters DJ, Spruit L, Saris JJ, Ravine D, Sandkuijl LA, Fossdal R, Boersma J, van-Eijk R, Norby S, Constantinou-Deltas CD, et al (1993) Chromosome 4 localization of a second gene for autoomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Nature Genet 5: 359–362
Ravine D, Walker RG, Gibson RN, Forrest SM, Richards RI, Friend K, Sheffield LJ, Kincaid-Smith P, Danks DM (1992) Phenotype and genotype heterogeneity in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Lancet 340:1330–1333
Reeders ST, Breuning MH, Davies KE, Nicholls RD, Jarman AP, Higgs DR, Pearson PL, Weatherall DJ (1985) A highly polymorphic DNA marker linked to adult polycystic kidney disease on chromosome 16. Nature 317:542–544
Reeders ST, Breuning MH, Ryynanen MA, Wright AF, Davies KE, King AW, Watson ML, Weatherall DJ (1987) A study of genetic linkage heterogeneity in adult polycystic kidney disease. Hum Genet 76:348–351
Romeo G, Devoto M, Costa G, Roncuzzi L, Catizone L, Zucchelli P, Germino GG, Keith T, Weatherall DJ, Reeders ST (1988) A second genetic locus for autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Lancet 2:8–11
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 2nd edn. edition. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, NY
Shen Y, Holman K, Doggett NA, Callen DF, Sutherland GR, Richards RI (1994) Dinucleotide repeat polymorphisms at the D16S525, D16S359, D16S531 and D16S522 loci. Hum Mol Genet 3:210
Somlo S, Wirth B, Germino GG, Weinstat-Saslow D, Gillespie GA, Himmelbauer H, Steevens L, Coucke P, Willems P, Bachner L, et al (1992) Fine genetic localization of the gene for autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (PKD1) with respect to physically mapped markers. Genomics 13: 152–158
The European Polycystic Kidney Disease Consortium (1994) The polycystic kidney disease 1 gene encodes a 14 kb transcript and lies within a duplicated region on chromosome 16. Cell 77:881–894
Thompson AD, Shen Y, Holman K, Sutherland GR, Callen DF, Richards RI (1992) Isolation and characterisation of (AC)n microsatellite genetic markers from human chromosome 16. Genomics 13:402–408
Todorov V, Nacheva I (1991) Genealogic and genetic-mathematic analysis in adult polycystic kidney disease. Savremenna Medicina 4:13–16
Weissenbach J, Gyapay G, Dib C, Vignal A, Morissette J, Millasseau P, Vaysseix G, Lathrop M (1992) A second-generation linkage map of the human genome. Nature 359:794–801
Wolff E, Nakamura Y, O'Connell P, Leppert M, Lathrop GM, Lalouel JM, White R (1988) Isolation and mapping of a polymorphic DNA sequence (pEKMDA2-I) on chromosome 16 [D16S83]. Nucleic Acids Res 16:9885
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bogdanova, N., Dworniczak, B., Dragova, D. et al. Genetic heterogeneity of polycystic kidney disease in Bulgaria. Hum Genet 95, 645–650 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00209481
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00209481