Summary
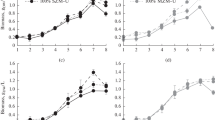
The effect of ammonium on growth and spiramycin biosynthesis in Streptomyces ambofaciens cultured on a chemically defined medium was studied. Spiramycin biosynthesis was better in the presence of valine and isoleucine than in the presence of ammonium. This production was reduced in the presence of excess ammonium (100 mm). The addition of catabolic intermediates of valine and isoleucine reserved the negative effect of ammonium. Valine dehydrogenase (VDH), the enzyme responsible for valine, leucine and isoleucine catabolism, was repressed when excess ammonium was present in the medium. This repression was approximately 25% when the ammonium concentration was increased from 50 to 100 mm. In addition to the repression of VDH biosynthesis, ammonium inhibited the activity of this enzyme. This inhibition was 45 and 65% in the presence of 50 and 100 mm ammonium, respectively.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Castro JM, Liras P, Cortes J, Martin JF (1985) Regulation of α-aminoadipylcysteïnyl-valine, isopenicillin N synthetase, isopenicillin isomerase and deacetoxycephalosporin C synthetase by nitrogen sources in Streptomyces lactamdurans. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 22:32–40
Flores ME, Sanchez S (1985) Nitrogen regulation of erythromycin formation in Streptomyces erythreus. FEMS Microbiol Lett 26:191–194
Lebrihi A, Germain P, Lefebvre G (1987) Phosphate repression of cephamycin and clavulanic acid production by Streptomyces clavuligerus. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 26:130–135
Lebrihi A, Lefebvre G, Germain P (1988) Carbon catabolite regulation of cephamycin C and expandase biosynthesis in Streptomyces clavuligerus. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 28:44–51
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr A, Randall RJ (1951) Proteïn measurements with the Folin-phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–273
Magasanik B (1982) Genetic control of nitrogen assimilation in bacteria. Annu Rev Genet 16:135–168
Omura S, Tanaka Y (1986) Biosynthesis of tylosin and its regulation by ammonium and phosphate. In: Kleinkauf H, Döhren HV, Dormauer H, Nesmann G (eds) Regulation of secondary metabolite formation. VCH publishers, Berlin, pp 306–332
Omura S, Tanaka Y, Tanaka H, Takahashi Y, Iwai Y (1980a) Stimulation of the production of macrolide antibiotics by magnesium phosphate and related insoluble materials. J Antibiot 33:1568–1569
Omura S, Tanaka Y, Kitao C, Tanaka H, Iwai Y (1980b) Stimulation of leucomycin production by magnesium phosphate and its relevance to nitrogen catabolite regulation. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 18:691–695
Omura S, Tanaka Y, Mamada H, Masuma R (1984) Effect of ammonium ion, inorganic phosphate and amino acids on the biosynthesis of protylonolide, a precursor of tylosin aglycone. J Antibiot 37:494–502
Schütte h, Hummel W, Tsai H, Kula M-R (1985) l-Leucine dehydrogenase from Bacillus cereus: production, large-scale purification and protein characterization. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 22:306–317
Shen Y-Q, Heim J, Solomon NA, Wolfe S, Demain AL (1984) Repression of \-lactam production in Cephalosporium acremonium by nitrogen sources. J Antibiot 37:503–511
Tanaka Y, Taki A, Masuma R, Omura S (1986) Mechanism of nitrogen regulation of protylonolide biosynthesis in Streptomyces fradiae. J Antibiot 39:813–821
Tyler B (1978) Regulation of the assimilation of nitrogen compounds. Annu Rev Biochem 47:1127–1162
Vancura A, Rezanka T, Marsalek J, Vancurova I, Kristan V, Basarova G (1987) Effect of ammonium ions on the composition of fatty acids in Streptomyces fradiae, producer to tylosin. FEMS Microbiol Lett 48:357–360
Vancura A, Rezanka T, Marsalek J, Melzoch K, Basarova G, Kristan V (1988) Metabolism of l-threonine and fatty acids and tylosin biosynthesis in Streptomyces fradiae. FEMS Microbiol Lett 49:411–415
Vu-Trong K, Gray PP (1987) Influence of ammonium on the biosynthesis of the macrolide antibiotic tylosin. Enzyme Microbiol Technol 9:590–593
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Correspondence to: A. Lebrihi
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lebrihi, A., Lamsaif, D., Lefebvre, G. et al. Effect of ammonium ions on spiramycin biosynthesis in Streptomyces ambofaciens . Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 37, 382–387 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00210997
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00210997