Summary
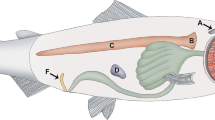
The distributions of peptide-containing nerves in the urinary bladder of the toad, Bufo marinus, were studied by means of fluorescence immunohistochemistry of whole-mount preparations. The bundles of smooth muscle in the bladder are well supplied by varicose nerve fibres displaying somatostatin-like immunoreactivity; these fibres probably arise from intrinsic perikarya. The urinary bladder also has a well-developed plexus of nerves containing substance P-like immunoreactive material; these elements probably represent sensory nerves of extrinsic origin. Nerve fibres showing immunoreactivity to vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP) or enkephalin are rare within the urinary bladder of the toad. It is considered unlikely that any of these peptides directly mediates the hyoscine-resistant excitatory response of the smooth muscle to nerve stimulation in the toad bladder.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alm P, Alumets J, Håkanson R, Sundler F (1977) Peptidergic (vasoactive intestinal polypeptide) nerves in the genitourinary tract. Neuroscience 2:751–754
Alm P, Alumets J, Brodin E, Håkanson R, Nilsson G, Sjöberg N-O, Sundler F (1978) Peptidergic (Substance P) nerves in the genito-urinary tract. Neuroscience 3:419–425
Alm P, Alumets J, Håkanson R, Owman C, Sjöberg N-O, Sundler F, Walles B (1980) Origin and distribution of VIP (vasoactive intestinal polypeptide)-nerves in the genito-urinary tract. Cell Tissue Res 205:337–347
Alm P, Alumets J, Håkanson R, Owman C, Sjöberg N-O, Stjernqvist M, Sundler F (1981) Enkephalin-immunoreactive nerve fibres in the feline genito-urinary tract. Histochem 72:351–355
Alumets J, Fahrenkrug J, Håkanson R, Schaffalitzky de Muckadell O, Sundler F, Uddman R (1979) A rich VIP nerve supply is characteristic of sphincters. Nature 280:155–156
Bolaffi JL, Reichlin S, Goodman DBP, Forrest JN (1980) Somatostatin: occurrence in urinary bladder epithelium and renal tubules of the toad, Bufo marinus. Science 210:644–646
Burnstock G, O'Shea J, Wood M (1963) Comparative physiology of the vertebrate autonomic nervous system. I. Innervation of the urinary bladder of the toad (Bufo marinus). J Exp Biol 40:403–419
Campbell G, Gibbins IL (1979) Non-adrenergic, non-cholinergic transmission in the autonomic nervous system: purinergic nerves. In: Kalsner S (ed) Trends in autonomic pharmacology, Vol 1. Urban and Schwarzenberg, Baltimore Munich, pp 103–144
Campbell G, Gibbins IL, Morris JL, Furness JB, Costa M, Oliver JR, Beardsley AM, Murphy R (1982) Somatostatin is contained in and released from cholinergic nerves in the heart of the toad, Bufo marinus. Neuroscience 7:2013–2023
Choo LK, Mitchelson F (1980) The effect of indomethacin and adenosine 5′-triphosphate on the excitatory innervation of the rat urinary bladder. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 58:1042–1048
Costa M, Buffa R, Furness JB, Solcia E (1980a) Immunohistochemical localization of polypeptides in peripheral autonomic nerves using whole mount preparations. Histochemistry 65:157–165
Costa M, Furness JB, Llewellyn-Smith IJ, Davies B, Oliver J (1980b) An immunohistochemical study of the projections of somatostatin-containing neurons in the guinea-pig intestine. Neuroscience 5:841–852
Erspamer V, Ronzoni G, Erspamer GF (1981) Effects of active peptides on the isolated muscle of the human urinary bladder. Invest Urol 18:302–304
Furness JB, Costa M (1975) The use of glyoxylic acid for the fluorescence histochemical demonstration of peripheral stores of noradrenaline and 5-hydroxytryptamine in whole mounts. Histochemistry 41:335–352
Furness JB, Costa M, Walsh JH (1981) Evidence for and significance of the projection of VIP neurons from the myenteric plexus to the taenia coli in the guinea-pig. Gastroenterol 80:1557–1567
Furness JB, Papka RE, Della NG, Costa M, Eskay RL (1982) Substance P-like immunoreactivity in nerves associated with the vascular system of guinea-pigs. Neuroscience 7:447–459
Gibbins IL (1982) Lack of correlation between ultrastructural and pharmacological types of non-adrenergic autonomic nerves. Cell Tissue Res 221:551–581
Hökfelt T, Elfvin L-G, Schultzberg M, Elde R, Goldstein M, Luft R (1977) Occurrence of somatostatin-like immunoreactivity in some peripheral sympathetic noradrenergic nerves. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 74:3587–3591
Hökfelt T, Schultzberg M, Elde R, Nilsson G, Terenius L, Said S, Goldstein M (1978) Peptide neurons in the peripheral tissues including the urinary tract: immunohistochemical studies. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol 43 Suppl 11:79–89
Husted S, Sjögren C, Andersson K-E (1981) SubstanceP and somatostatin and excitatory neurotransmission in rabbit urinary bladder. Arch Int Pharmacodyn 252:72–85
Johns A (1979) The effect of vasoactive intestinal peptide on the urinary bladder and taenia coli of the guinea-pig. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 57:106–108
Larsson L-I, Fahrenkrug J, Schaffalitzky de Muckadell OB (1977) Vasoactive intestinal polypeptide occurs in nerves of the female genito-urinary tract. Science 197:1374–1375
Leeman SE, Gamse R (1981) Substance P in sensory neurons. Trends in Pharmacol Sci 2:119–121
Lundberg JM, Änggård A, Fahrenkrug J (1982a) Complementary roles of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP) and acetylcholine for cat submandibular gland blood flow and secretion. III. Effects of local infusions. Acta Physiol Scand 114:329–337
Lundberg J, Hedlund B, Bartfai T (1982b) Vasoactive intestinal polypeptide enhances muscarinic ligand binding in cat submandibular salivary gland. Nature 295:147–149
McLean JR, Burnstock G (1966) Histochemical localization of catecholamines in the urinary bladder of the toad (Bufo marinus). J Histochem Cytochem 14:538–548
Morris JL, Gibbins IL, Clevers J (1981) Resistance of adrenergic neurotransmission in the toad heart to adrenoceptor blockade. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 317:331–338
Sjögren C, Andersson K-E, Husted S (1982) Contractile effects of some polypeptides on the isolated urinary bladder of the guinea-pig, rabbit and rat. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol 50:175–184
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Acknowledgements. I would like to thank Drs. M. Costa and J.B.Furness for the provision of characterised antisera and the use of laboratory facilities. I would also like to thank Professor G. Campbell and Dr.J.L. Morris for critical comments of the manuscript. This work was supported by a grant from the National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gibbins, I.L. Peptide-containing nerves in the urinary bladder of the toad, Bufo marinus . Cell Tissue Res. 229, 137–144 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00217886
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00217886