Abstract
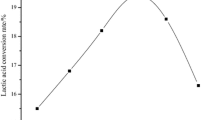
Production of l(+)-lactic acid by Rhizopus oryzae NRRL 395 was studied in solid medium on sugar-cane bagasse impregnated with a nutrient solution containing glucose and CaCO3. A comparative study was undertaken in submerged and solid-state cultures. The optimal concentrations in glucose were 120 g/l in liquid culture and 180 g/l in solid-state fermentation corresponding to production of l(+)-lactic acid of 93.8 and 137.0 g/l, respectively. The productivity was 1.38 g/l per hour in liquid medium and 1.43 g/l per hour in solid medium. However, the fermentation yield was about 77% whatever the medium. These figures are significant for l(+)-lactic acid production.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Butcha K (1983) Lactic acid. In: Rehm HJ, Reed G (eds) Biotechnology. A comprehensive treatise, vol 3. Biomass, microorganisms for special applications. Microbial products, Part I: Energy for renewable resources, Verlag Chemie, Weinheim, pp 410–417
Claes LE (1992) Mechanical characterization of biodegradables implants. Clin Mater 10:41–46
Cooke TF (1990) Biodegradability of polymers and fibers. A review of the literature. J Polym Eng 3:171–211
Giraud E, Lelong B, Raimbault M (1991) Influence of pH and initial lactate concentration on the growth of Lactobacillus plantarum. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 36:96–99
Hang YD, Hamamci H, Woodams EE (1989) Production of l(+)-lactic acid by Rhizopus oryzae immobilized in calcium alginate gels. Biotechnol Lett 11:119–120
Holland SJ, Tighe BJ, Gould PL (1986) Polymers for biodegradable medical devices: 1. The potential of polyesters as controlled macro-molecular release systems. J Controlled Release 4:155–180
Kandler O (1982) Gärungsmechanismen bei Milchsäurebakterien. Forum Mikrobiol 5:16
Lockwood LB (1975) Organic acid production of acids. In: Smith JE, Berry DR (eds) Filamentous fungi, vol 1. Industrial mycology, Edward Arnold, London, pp 140–157
Lockwood LB, Ward GE, May OE (1936) The physiology of Rhizopus oryzae. J Agric Res 53:849–857
Miller GL (1959) Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugars. Anal Chem 31:426–428
Narahara H, Koyama Y, Yoshida T (1982) Growth and enzyme production in a solid-state culture of Aspergillus oryzae. J Ferment Technol 60:311–319
Nielsen JJ, Veibel S (1967) The reactivity of lactic acid and some of its simple derivatives. Acta Polytech Scand 63:67–75
Oriol E, Schetino B, Viniegra-Gonzalez G, Raimbault M (1988) Solid state culture of Aspergillus niger on support. J Ferment Technol 66:57–62
Oriol E, Raimbault M, Roussos S, Viniegra-Gonzalez G (1988) Water and water activity in the solid state fermentation of cassava starch by Aspergillus niger. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 27:498–503
Raimbault M, Alazard D (1980) Culture method to study fungal growth in solid fermentation. Eur J Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 9:199–209
Soccol C (1992) Physiologie et métabolisme de Rhizopus en culture solide et submergée en relation avec la dégradation d'amidon cru et la production d'acide l(+) lactique. Thèse de Doctorat, Mention Génie enzymatique, Bioconversion et Microbiologie, Université de Technologie de Compiègne
Vert M (1991) Biodégradables: réalités et perspectives. Caoutchoucs et Plastiques 706:71–76
Vert M, Guerin P (1992) Des biosystèmes aux matériaux polymères: une utopie. Biofutur 113:52–57
Vert M, Li S, Garreau H (1991) More about the degradation of LA-GA-derived matrices in aqueous media. J Controlled Release 16:15–26
Vert M, Li SM, Spenlehauer G, Guerin P (1992) Bioresorbability and biocompatibility of aliphatic polyesters. J Mater Sci Mater Med 3:432–446
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Soccol, C.R., Marin, B., Raimbault, M. et al. Potential of solid state fermentation for production of L(+)-lactic acid by Rhizopus oryzae . Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 41, 286–290 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00221220
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00221220