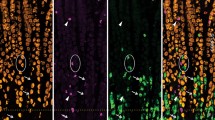
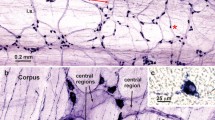
Summary
The distribution of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide-, substance P-, [met]enkephalin- and somatostatin-like immunoreactive nerves was studied in the caecum from foetal guinea-pigs of 6–9 weeks gestation (i.e., approximately 1–4 weeks before birth) and 4–5-day-old guinea-pigs. Peptide-immunoreactive nerves were first detected in the myenteric and submucous plexuses and circular muscle layer at 6 weeks of gestation and in the mucosa at 7 weeks of gestation. The density of fibres in these layers increased during prenatal development until, by 9 weeks of gestation, their distribution resembled that seen in the postnatal animals. This distribution was similar to that described previously in adult animals. A different pattern of development was observed in the caecal taenia coli muscle. Peptide-immunoreactive fibres were not detected until 8 weeks of gestation in this tissue layer, and were then only sparsely distributed. A dramatic increase in the number of labelled fibres, however, occurred between 8 and 9 weeks of gestation. Further, vasoactive intestinal polypeptide- and substance P-immunoreactive fibres were more numerous in the taeniae coli of 9-week-old embryos than in those of postnatal animals. Thus, the guinea-pig enteric nervous system, which in many respects is well-developed at the time of birth, may still be undergoing developmental changes at this time.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baluk PLJ (1982) The enteric nervous system: morphology and development in vivo and in vitro. PhD Thesis, University of London
Buchan AMJ, Byrant MG, Polak JM, Gregor M, Ghatei MA, Bloom SR (1981) Development of regulatory peptides in the human fetal intestine. In: Polak S, Bloom SR (eds) Gut hormones. Churchill Livingstone, Edinburgh, pp 119–124
Chayvialle J-A, Paulin C, Descos F, Dubois P-M (1983) Ontogeny of vasoactive intestinal peptide in the human fetal digestive tract. Regul Pept 5:245–256
Costa M, Furness JB (1982) Neuronal peptides in the intestine. Br Med Bull 38:247–252
Costa M, Furness JB, Gibbins IL (1986) Chemical coding of enteric neurons. In: Hökfelt T, Fuxe K, Pernow B (eds) Progress in brain research. Vol 68. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 217–239
Cuello AC, Galfré G, Milstein C (1979) Detection of substance P in the central nervous system by a monoclonal antibody. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 76:3532–3536
Epstein ML, Hudis J, Dahl JL (1983) The development of peptidergic neurons in the foregut of the chick. J Neurosci 3:2431–2447
Fontaine-Perus J, Chanconie M, Polak JM, Le Douarin NM (1981) Origin and development of VIP and substance P containing neurons in the embryonic avian gut. Histochemistry 71:313–323
Fontaine-Perus JC, Chanconie M, Le Douarin NM (1982) Differentiation of peptidergic neurones in quail-chick chimaeric embryos. Cell Differ 11:183–193
Furness JB, Costa M (1982) Identification of gastrointestinal neurotransmitters. Handbook of experimental pharmacology 59:383–460
Furness JB, Costa M (1987) The enteric nervous system. Churchill Livingstone, Edinburgh
Furness JB, Costa M, Walsh JH (1981) Evidence for and significance of the projection of VIP neurons from the myenteric plexus to the taenia coli in the guinea-pig. Gastroenterology 80:1557–1561
Gabella G (1981) On the musculature of the gastro-intestinal tract of the guinea-pig. Anat Embryol 163:135–156
Gershon MD, Rothman TP (1984) Experimental and genetic approaches to the study of the development of the enteric nervous system. Trends Neurosci 7:150–155
Gershon MD, Sherman D, Gintzler AR (1981) An ultrastructural analysis of the developing enteric nervous system of the guineapig small intestine. J Neurocytol 10:271–296
Gershon MD, Payette RF, Rothman TP (1983) Development of the enteric nervous system. Fed Proc 42:1620–1625
Gershon MD, Payette R, Teitelman G, Rothman TP (1984) Neuronal commitment and phenotypic expression by developing enteric neurons. In: Chan-Palay V, Palay SL (eds) Coexistence of neuroactive substances in neurons. John Wiley, New York, pp 181–204
Gintzler AR, Rothman TP, Gershon MD (1980) Ontogeny of opiate mechanisms in relation to the sequential development of neurons known to be components of the guinea-pig's enteric nervous system. Brain Res 189:31–48
Hills J (1984) Putative autonomic neurotransmitters and receptors. PhD Thesis, University of London
Hökfelt T, Kellerth JO, Nilsson G, Pernow B (1975) Experimental immunohistochemical studies on the localization and distribution of substance P in cat primary sensory neurons. Brain Res 100:235–252
Jessen KR, Saffrey MJ, Van Noorden S, Bloom SR, Polak JM, Burnstock G (1980) Immunohistochemical studies of the enteric nervous system in tissue culture and in situ: localization of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP), substance P and enkephalin immunoreactive nerves in the guinea-pig gut. Neuroscience 5:1717–1735
Kessler JA, Adler JE, Bell WO, Black IB (1983) Substance P and somatostatin metabolism in sympathetic and special sensory ganglia in vitro. Neuroscience 9:309–318
Leander S, Håkanson R, Sundler F (1981) Nerves containing substance P, vasoactive intestinal polypeptide, enkephalin or somatostatin in the guinea-pig taenia coli: distribution, ultrastructure and possible functions. Cell Tissue Res 215:21–39
Le Douarin N (1982) The neural crest. Development and cell biology. Vol 12. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Le Douarin NM, Teillet MA (1974) Experimental analysis of the migration and differentiation of neuroblasts of the autonomic nervous system and of neuroectodermal mesenchymal derivatives, using a biological cells marking technique. Dev Biol 41:162–184
Llewellyn-Smith IJ, Furness JB, Wilson AJ, Costa M (1983) Organisation and fine structure of enteric ganglia. In: Elvin L-G (ed) Autonomic ganglia. John Wiley, Chichester, pp 145–182
Rothman TP, Nilaver G, Gershon MD (1984) Colonization of the developing murine enteric nervous system and subsequent phenotypic expression by the precursors of peptidergic neurons. J Comp Neurol 225:13–23
Saffrey MJ, Polak JM, Burnstock G (1982) Distribution of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide-, substance P-, enkephalinand neurotensin-like immunoreactive nerves in the chicken gut during development. Neuroscience 7:279–293
Schultzberg M, Hökfelt T, Nilsson T, Terenius L, Rehfeld JF, Brown M, Goldstein M, Said S (1980) Distribution of peptideand catecholamine-containing neurons in the gastrointestinal tract of the rat and guinea-pig: immunohistochemical studies with antisera to substance-P, vasoactive intestinal polypeptide, enkephalins, somatostatin, gastrin/cholecystokinin, neurotensin and dopamine beta-hydroxylase. Neuroscience 5:689–744
Sisk DB (1976) Physiology of the guinea-pig. In: Wagner JE, Manning PJ (eds) The biology of the guinea-pig. Academic Press, New York, pp 79–90
Smith J, Cochard P, Le Douarin NM (1977) Development of choline acetyltransferase and cholinesterase activities in enteric ganglia derived from presumptive adrenergic and cholinergic levels of the neural crest. Cell Differ 6:199–216
Snipes RL (1982) Anatomy of the guinea-pig cecum. Anat Embryol 165:97–111
Sundler F, Alumets J, Håkanson R, Schaffalitzky De Muckadell OB (1979) Cellular localization and ontogeny of immunoreactive vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP) in the chicken gut. Cell Tissue Res 196:193–201
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saffrey, M.J., Burnstock, G. Distribution of peptide-immunoreactive nerves in the foetal and newborn guinea-pig caecum. Cell Tissue Res. 253, 105–114 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00221745
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00221745