Summary
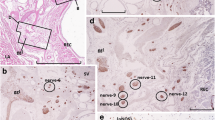
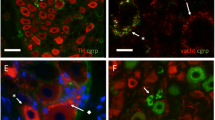
In male rats a large number of the postganglionic neurons which innervate the pelvic organs are located in the major pelvic ganglion. In the present study we have identified the location within this ganglion of neurons which project to either of three pelvic organs, the penis, colon or urinary bladder. Two fluorescent retrogradely-transported dyes, Fast Blue and Fluoro-Gold, were used. For most animals one dye was injected into the cavernous space of the penis, the wall of the distal colon or the wall of the urinary bladder. In a small number of animals two organs were injected, each with a different dye. One to six weeks after injection the major pelvic ganglia were fixed in buffered formaldehyde. The distribution of fluorescent dye-labelled cells was observed in whole mounts of complete ganglia and, in most cases, also in small accessory ganglia located between the ureter and the prostate. The studies showed a unique pattern of distribution for each organ-specific group of neurons. Most of the colon neurons are located in the major pelvic ganglion near the entrance of the pelvic nerve, whereas almost all of the penis neurons are near or within the penile nerve. Bladder neurons are relatively evenly distributed throughout the ganglion. These results demonstrate a distinct topographical organization of organ-specific neurons of the major pelvic ganglion of the male rat, a phenomenon which has also been observed in other peripheral ganglia.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baljét B, Drukker J (1980) The extrinsic innervation of the pelvic organ in the female rat. Acta Anat 107:241–267
Booth AM, Roppolo JR, de Groat WC (1986) Distribution of cells and fibers projecting to the penis of the cat. Proc Soc Neurosci
Bowers CW, Zigmond RE (1979) Localization of neurons in the rat superior cervical ganglion that project into different postganglionic trunks. J Comp Neurol 185:381–392
Chung SK, McKenna KE (1987) The autonomic innervation of the penis and clitoris of the rat. Proc Soc Neurosci
Costa M, Furness JB (1973) The origins of the adrenergic fibres which innervate the internal anal sphincter, the rectum, and other tissues of the pelvic region of the guinea-pig. Z Anat Entwickl-Gesch 140:129–142
Costa M, Furness JB, Gibbins IL (1986) Chemical coding of enteric neurons. Prog Brain Res 68:217–239
Dail WG, Evan AP, Eason HR (1975) The major pelvic ganglion in the pelvic plexus of the male rat: a histochemical and ultrastructural study. Cell Tissue Res 159:49–62
Dail WG, Moll MA, Weber K (1983) Localization of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide in penile erectile tissue and in the major pelvic ganglion of the rat. Neuroscience 10:1379–1386
Dail WG, Minorsky N, Moll MA, Manzanares K (1986) The hypogastric nerve pathway to penile erectile tissue: histochemical evidence supporting a vasodilator role. J Autonom Nerv Sys 15:341–349
Dail WG, Trujillo D, Walton G, de la Rosas D (1987) Autonomic composition of reproductive organs in the rat: analysis of the composition of the cavernous nerve. Proc Soc Neurosci
Gibbins IL, Furness JB, Costa M (1987) Pathway-specific patterns of the coexistence of substance P, calcitonin gene-related peptide, cholecystokinin and dynorphin in neurons of the dorsal root ganglia of the guinea-pig. Cell Tissue Res 248:417–437
Greenwood D, Coggeshall RE, Hulsebosch CE (1985) Sexual dimorphism in the numbers of neurons in the pelvic ganglia of adult rats. Brain Res 340:160–162
Langley JN, Anderson HK (1986) The innervation of the pelvic and adjoining viscera. VII. Anatomical observations. J Physiol 20:372–406
Langworthy OR (1965) Innervation of the pelvic organs of the rat. Invest Urol 2:491–511
Macrae IM, Furness JB, Costa M (1986) Distribution of subgroups of noradrenaline neurons in the coeliac ganglion of the guineapig. Cell Tissue Res 244:173–180
Purinton PT, Fletcher TF, Bradley WE (1973) Gross and light microscopic features of the pelvic plexus in the rat. Anat Rec 175:696–706
Shimizu T, Egan-Konopka LM, Ohta Y, Dun NJ (1982) Localization of postganglionic neurons to the male genital organs in the major pelvic ganglion of the rat. Tohoku J Exp Med 136:351–352
Steers WDS, Mallory B, de Groat WC (1988) Electrophysiological study of neural activity in penile nerve of the rat. Am J Physiol 254:R989-R1000
Tabatabei M, Booth AM, de Groat WC (1986) Morphological and electrophysiological properties of pelvic ganglion cells in the rat. Brain Res 382:61–70
Tanaka S, Zukeran C, Nakagawa S (1983) A macroscopical study of the somatic and visceral nerves innervating the male rat lowest digestive tract. Jpn J Anat 58:1–13
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Keast, J.R., Booth, A.M. & de Groat, W.C. Distribution of neurons in the major pelvic ganglion of the rat which supply the bladder, colon or penis. Cell Tissue Res. 256, 105–112 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00224723
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00224723