Abstract
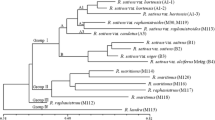
RAPD (random amplified polymorphic DNA) markers generated by 15 arbitrary decamers were used to determine the frequency of DNA polymorphism in 39 watermelon [Citrullus lanantus (Thunb.) Mansf.] germplasms. Of the 15 primers tested, all except 1 (primer 275) directed the amplification of polymorphic products. A total of 162 amplification products were generated across all 39 genotypes. Among the 162 fragments, 35 (21%) appeared to be reliable polymorphic markers. The mean value by marker difference in this comparison was 0.24, and the highest, 0.69. Eight RAPD markers could be utilized in the unique variety discrimination 8 watermelon genotypes. From the phenograms constructed by UPGMA based on the comparison of RAPD markers, four clusters were resolved. Each group was also characterized and identified with morphological and genetic characteristics for each genotype. The free sugars of the edible parts of watermelons were analyzed by HPLC (high-performance liquid chromatography). Results from the phylogenetic analysis of band sharing data were consistent with sweetness as measured by HPLC. In conclusion, RAPD assays can be used for providing alternative markers for identifying genotypes and quantitative characteristics in watermelon.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cenis JL (1992) Rapid extraction of fungal DNA for PCR amplification. Nucleic Acids Res 20:2308
Chaparro JX, Werner DJ, Malley DO, Sederof RR (1994) Targeted mapping and linkage analysis of morphological, isozyme, and RAPD markers in peach. Theor Appl Genet 87:805–815
Dich V, Schubert I (1993) Midiprep method for isolation of DNA from plants with a high content of polyphenolics. Nucleic Acids Res 21:3328
D'Ovidio R, Tanzarella OA, Porceddu E (1990) Rapid and efficient detection of genetic polymorphism in wheat through amplification by polymerase chain reaction. Plant Mol Biol 15:169–171
Dweikat I, Mackenzie S, Levy M, Ohm H (1993) Pedigree assessment using RAPD-DGGE in cereal crop species. Theor Appl Genet 85:497–505
Eisenberg S (1955) Use of sugars and other carbohydrates in the food industry. Adv Chem 12:12
Elmstrom GW, Davids PL, Munroe KA (1980) Sugars in maturing fruit of watermelon cultivars. Hortscience (Abstr) 15:277
Francisco-Ortega J, Newbury HJ, Ford-Lloyd BV (1993) Numerical analysis of RAPD data highlight the origin of cultivated tagasaste (Chamaecytisus proliferus ssp. Palmensis) in the Canary Islands. Theor Appl Genet 87:264–270
Kihara H (1951) Triploid watermelons. Proc Am Soc Hortic Sci 58:217–230
Martin JM, Blake TK, Hockett EA (1991) Diversity among North American spring barley cultivars based on coefficients of parent-age. Crop Sci 31:1131–1137
Murray JM, Thompson WF (1980) Rapid isolation of high molecular weight plant DNA. Nucleic Acids Res 8:4321–4325
Nei M, Li W (1979) Mathematical model for studying genetic variation in terms of restriction endonuclease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 76:5269–5273
Richmond ML, Brandao SCC, Gray JI, Markakis P, Stine CM (1981) Analysis of simple sugars and sorbitol in fruit by high performance liquid chromatography. J Agric Food Chem 29:4–7
Rohlf FJ (1990) NTSYS-pc Numerical taxonomy and multivariate analysis system, version 1.60. Applied Biostatistics, New York
Rowland LJ, Levi A (1994) RAPD-based genetic linkage map of blueberry derived from a cross between diploid species (Vaccinum darrowi and V. elliottii). Theor Appl Genet 87:863–868
Saghai-Maroof MA, Soliman KA, Jorgensen RA, Allard RW (1984) Ribosomal DNA spacer-length polymorphisms in barley: Mendelian inheritance, chromosomal location, and population dynamics. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 81:8014–8018
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning — a laboratory manual. 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, N.Y.
Shin JS, Chao S, Corpuz L, Blake T (1990) A partial map of the barley genome incorporating restriction fragment length polymorphism, polymerase chain reaction, isozyme, and morphological marker loci. Genome 33:803–810
Szmidt AE, Wang XR (1993) Molecular systematics and genetic differentiation of Pinus sylvestris L. and P. densiflora Sieb. et Zucc. Theor Appl Genet 86:159–165
Tao Y, Manners JM, Ludlow MM, Henzel RG (1983) DNA polymorphisms in grain sorghum (Sorghum bicolor L. Moench). Theor Appl Genet 86:679–688
Welsh J, McClelland M (1990) Fingerprinting genomes using PCR with arbitrary primers. Nucleic Acids Res 18:7213–7218
Wilkie SE, Isaac PG, Slater RG (1993) Random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) markers for genetic analysis in Allium. Theor Appl Genet 86:497–504
Williams JG, Kubelik AR, Livak KJ, Rafalski JA, Tingey SV (1990) DNA polymorphism amplified by arbitrary primers are useful as genetic markers. Nucleic Acids Res 18:6531–6535
Yang X, Quiros C (1993) Identification and classification of celery cultivars with RAPD markers. Theor Appl Genet 86:205–212
Yu L-X, Nguyen HT (1994) Genetic variation detected with RAPD markers among upland and lowland rice cultivars (Oriza saliva L.). Theor Appl Genet 87:668–672
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by J. W. Snape
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, S.J., Shin, J.S., Park, K.W. et al. Detection of genetic diversity using RAPD-PCR and sugar analysis in watermelon [Citrullus lanantus (Thunb.) Mansf.] germplasm. Theoret. Appl. Genetics 92, 719–725 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00226094
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00226094