Summary
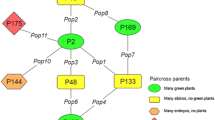
The use of haploidy to introgress recessive traits into Brassica napus canola is illustrated by describing the properties of doubled haploids obtained by microspore culture from crosses between a yellow-seeded rapeseed line (low erucic acid, high glucosinolate) and black-seeded canola. Of the 99 doubled haploid lines that were produced, 3 were yellow-seeded canola lines. This result was not significantly different than the predicted frequency of 1 in 64 for the homozygous recessive phenotype in a doubled haploid population segregating for six recessive genes. Thus, the study supports previous models of inheritance determined for yellow seededness and glucosinolate content in Brassica napus. Also, since the chances of obtaining a plant with the same characteristics in a F2 population are 1 in 4,096, the underscore results the advantages of using haploidy to introgress recessive traits into Brassica napus canola.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Choo TM, Reinbergs E, Kasha KJ (1985) Use of haploids in breeding barley. Plant Breed Rev 3:219–252
Chuong PV, Beversdorf WD (1985) High frequency embryogenesis through isolated microspore culture in Brassica napus L. and Brassica carinata Braun. Plant Sci 39:219–226
Chuong PV, Beversdorf WD, Powell AD, Pauls KP (1988) Somatic transfer of cytoplasmic traits in Brassica napus L. by haploid protoplast fusion. Mol Genet 211:197–201
Coventry J, Kott L, Beversdorf WD (1988) Manual for microspore culture technique for Brassica napus. Dept Crop Sci Tech Bull Univ Guelph, OAC Publ 0489
Daun JK, DeClerq, DR (1988) Quality of yellow and dark seeds in Brassica campestris canola varieties candle and tobin. JAOCS 65:122–126
Foroughi-Wehr B, Wenzel G (1989) Androgenetic haploid production. IAPTC Newsl 58:11–18
Gamborg OL, Miller RA, Ojima K (1968) Nutrient requirements of suspension cultures of soybean root cell. Exp Cell Res 50:151–158
Harvey BL, Downey RK (1964) The inheritance of erucic acid content in rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) Can J Plant Sci 44:104–111
Love HK (1988) Inheritance of seed aliphatic glucosinolates in oilseed Brassica species. Ph. D. thesis, University of Saskatchewan, Saskatoon, Canada
Neuhaus W, Spangenberg G, Mittelsten-Scheid O, S-Schweiger H (1987) Transgenic rapeseed plants obtained by microinjection of DNA into microspore-derived embryoids. Theor Appl Genet 75:30–36
Shirzadegan M (1986) Inheritance of seed color in Brassica napus L. Z Pflanzenzücht 96:140–146
Shirzadegan M, Röbbelen G (1985) Influence of seed color and hull proportion on quality properties of seeds in Brassica napus L. Fette Seifen Anstrichm 87:235–237
Siebel J, Pauls KP (1989a) Inheritance patterns of erucic acid content in populations of Brassica napus microspore-derived spontaneous diploids. Theor Appl Genet 77:489–494
Siebel J, Pauls KP (1989b) Alkenyl glucosinolate levels in androgenic populations of Brassica napus. Plant Breed 103:124–132
Swanson EB, Coumans MP, Brown GL, Patel JD, Beversdorf WD (1988) The characterization of herbicide tolerant plants in Brassica napus L. after in vitro selection of microspores and protoplasts. Plant Cell Rep 7:83–87
Swanson EB, Herrgesell MJ, Arnoldo M, Sippell DW, Wong RSC (1989) Microspore mutagenesis and selection: Canola plants with field tolerance to the imidazolinones. Theor Appl Genet 78:525–530
Thies W (1976) Quantitative gas-liquid chromatography of glucosinolates on a microliter scale. Fette Seifen Anstrichm 78:231–234
Zhou YM, Liu HL (1987) Inheritance of total glucosinolate content in Brassica napus. Plant Breed Abstr 58:6006
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by G. Wenzel
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Henderson, C.A.P., Pauls, K.P. The use of haploidy to develop plants that express several recessive traits using light-seeded canola (Brassica napus) as an example. Theoret. Appl. Genetics 83, 476–479 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00226536
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00226536