Summary
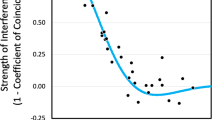
Fine structure map expansion is a marker effect which can be explained on the basis of the repair of mismatched bases in hybrid DNA. The chance of a mismatched base pair being corrected independently of a closely linked mismatched pair will sharply increase as the distance between the two sites becomes greater than the length of the DNA segment involved in the correction process. The consequences of this explanation are worked out and it is shown that, if it is true, the mapping curve should show three phases: an initial additive phase when the recombining sites are closely linked, a phase of increased slope—map expansion-and a final additive phase of reduced slope beyond the expansion region. Comparison of the initial and final slopes should yield information on the relation between gene conversion and crossing-over. Many sets of experimental data show a clear transition from the initial additive region to that of map expansion, but evidence for the predicted final phase is scanty, possibly because fine structure maps cover too small a region of the chromosome. Using data from genes with known products, estimates can be made of the minimum length of the DNA segments involved in correction. These are calculated as about 40 nucleotides in fission yeast and at least 130 nucleotides in Neurospora.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carsiotis, M., Appella, E., Provost, P., Germershausen, J., Suskind, S. R.: Chemical and physical studies of the structure of tryptophan synthetase fromNeurospora crassa. Biochem. biophys. Res. Commun.18, 877–888 (1965).
de Lucia, P., Cairns, J.: Isolation of anE. coli strain with a mutation affecting DNA polymerase. Nature (Lond.)224, 1164–1166 (1969).
Emerson, S.: Linkage and recombination at the chromosome level. In: Genetic organisation I. (ed. by E. W. Caspair and A. W. Ravin), p. 267. New York: Academic Press 1969.
Fogel, S., Mortimer, R. K.: Informational transfer in meiotic gene conversion. Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. (Wash.)62, 96–103 (1969).
Goodman, H. M., Abelson, J., Landy, A., Brenner, S., Smith, J. D.: Amber suppression: a nucleotide change in the anticodon of a tyrosine transfer RNA. Nature (Lond.)217, 1019–1024 (1968).
Hawthorne, D. C.: The selection of nonsense suppressors in yeast. Mutation Res.7, 187–197 (1969).
Holliday, R.: A mechanism for gene conversion in fungi. Genet. Res. Camb.5, 282–304 (1964).
—: Genetic recombination in fungi. In: Replication and recombination of genetic material (ed. by W. J. Peacock and R. D. Brock), p. 157. Canberra: Australian Academy of Science 1968.
—, Whitehouse, H. L. K.: The wrong way to think about gene conversion? Molec. Gen. Genetics107, 85–93 (1970).
Kelly, R. B., Atkinson, M. R., Huberman, J. A., Kornberg, A.: Excision of thymine dimers and other mismatched sequences by DNA polymerase ofEscherichia coli. Nature (Lond.)224, 495–501 (1969).
Kornberg, A.: Active centre of DNA polymerase. Science163, 1410–1418 (1969).
Leupold, U.: Intragene Rekombination und allele Komplementierung. Arch. Klaus-Stift. Vererb.-Forsch.36, 89–117 (1961).
—: Genetic studies on nonsense suppressors inSchizosaccharomyces pombe. (Abstr.) Heredity,25, 493 (1970).
Leupold, U. Hofer, F.: In preparation (1970).
Mousseau, J.: Analyse de la structure fine d'un gène chezAscobolus immersus. Contribution à l'étude de la recombination méiotique. Thesis. University of Paris (1967).
Norkin, L. C.: Marker-specific effects in genetic recombination. J. Molec. Biol.51, 633 (1970).
Rossignol, J.-L.: Phenomènes de recombinaison intragénique et unité fonctionelle d'un locus chez l'Ascobolus immersus. Thesis, University of Paris (1964).
— Existence of homogeneous categories of mutants exhibiting various conversion patterns in gene 75 ofAscobolus immersus. Genetics63, 795–805 (1969)
Siddiqi, O. H.: The genetic fine structure of thepaba-1 region ofAspergillus nidulans. Genet. Res. Camb.3, 69–80 (1962).
—, Putrament, A.: Polarized negative interference in thepaba-1 region ofAspergillus nidulans. Genet. Res. Camb.4, 12–20 (1963).
Smith, B. R.: Interallelic recombination at thehis-5 locus inNeurospora crassa. Heredity20, 257–276 (1965).
Spatz, H. Ch., Trautner, T. A.: One way to do experiments on gene conversion? Transfection with heteroduplexSPP1 DNA. Molec. Gen. Genetics109, 84–106 (1970).
Suyama, Y., Lacy, A. M., Bonner, D. M.: A genetic map of thetd locus ofNeurospora crassa. Genetics49, 135–144 (1964).
Whitehouse, H. L. K., Hastings, P. J.: The analysis of genetic recombination on the polaron hybrid DNA model. Genet. Res. Camb.6, 27–92 (1965).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by R. H. Pritchard
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fincham, J.R.S., Holliday, R. An explanation of fine structure map expansion in terms of excision repair. Molec. Gen. Genet. 109, 309–322 (1970). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00267701
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00267701