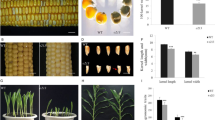
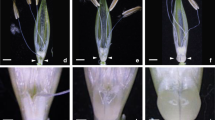
Summary
A conditional seedling lethal, monogenic recessive, endosperm mutant is described. Phenotypic can be accomplished when embryos are cultured in vitro on media supplemented with proline. The efficiency of the repair is proportional to the concentration of proline in the medium. Normal growth is resumed at a dose of 160 mg/l. All the data collected are most easily interpreted by assuming that the mutant, symbolized pro has a genetic block in the biosynthetic route leading to proline.
This is probably the first case of a strict genetic requirement for an amino acid to be reported in Zea mays. The possible reasons for the difficulties encountered in isolating obligate auxotrophs in higher plants are briefly reviewed.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature
Arnon, D.I.: Copper enzymes in isolated chloroplasts — Polyphenoloxidase in Beta vulgaris. Plant Physiol. 24, 1–15 (1949)
Carlson, P.: Induction and isolation of auxotrophic mutants in somatic cell cultures of Nicotiana tabacum. Science 168, 487–489 (1970)
Guha, S.; Maheshawari, S.C.: In vitro production of embryos from anthers of Datura. Nature, Lond. 204, 497 (1964)
Heller, R.: De l'influence de la concentration en ions potassium du milieu sur la croissance des cultures de tissues vegetaux. C.R. Soc. Biol. 142, 949–952 (1948)
Kao, F.; Puck, I.I.: Genetics of somatic mammalian cells. IV. Properties of Chinese hamster cell mutants with respect to the requirement for proline. Genetics 55, 513–524 (1967)
Lamport, D.I.A.: The isolation and partial characterization of hydroxyproline rich glycopeptides obtained by enzymic degradation of primary cell walls. Biochemistry 8, 1155–1163 (1969)
Land, J.B.; Norton, G.: The nature of the leucine requirement of the barley mutant xan-b61. Genet. Res. 15, 135–137 (1970)
Langridge, J.: Biochemical mutations in the crucifer Arabidopsis thaliana. Nature 176, 260 (1955)
Langridge, J.: A hypothesis of developmental selection exemplified by lethal and semilethal mutants of Arabidopsis. Aust. J. Biol. Sci. 11, 58–68 (1958)
Langridge, J.; Brock, R.O.: A thiamine-requiring mutant of the tomato. Aust. J. Biol. Sci. 14, 66–69 (1961)
Li, S.L.; Rédei, G.P.; Gowans, C.S.: A phylogenetic comparison of mutation spectra. Molec. Gen. Genetics 100, 77–83 (1967)
Loppes, R.: A new class of arginine-requiring mutants in Chlamydomonas reinhardi. Molec. Gen. Genetics 104, 172–177 (1969)
Melchers, G.: Haploids for breeding by mutation and recombination. In: Polyploidy and induced mutations in plant breeding, 221–231. Vienna: IAEA 1974
Nelson, D.E.; Burr, B.: Biochemical Genetics of higher plants. Ann. Rev. Plant Physiol. 24, 493–518 (1973)
Neuffer, M.G.: Absence of auxotrophic mutants in corn and other eukaryotes. Maize Genet. Coop. News Letter 48, 118–120 (1974)
Oaks, A.; Beever, H.: The requirements for organic nitrogen in Zea mays embryos. Plant Physiol. 39, 37–43 (1964)
Oaks, A.; Bidwell, R.G.: Compartmentation of intermediary metabolities. Ann. Rev. Plant Physiol. 21, 43–66 (1970)
Rédei, G.P.: Genetic control of 2,5-dimethyl-4-amino pyrimidine requirement in Arabidopsis thaliana. Genetics 45, 1007 (1960)
Rédei, G.P.: Genetic blocks in the thiamine synthesis of the angiosperm Arabidopsis. Amer. J. Bot. 52, 834–841 (1965)
Rédei, G.P.: Induction of auxotrophic mutations in plants. In: Genetic manipulations with plants, Ed. Ledoux L. New York: Plenum Press 1974
Vogel, H.J.; Bonner, D.M.: On the glutamate prolineornithine interrelation in Neurospora crassa. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S. 40, 688–694 (1954)
Walles, B.: Macromolecular physiology of plastids. IV. An amino acid requirement of lethal chloroplast mutants in barley. Hereditas 50, 317–344 (1963)
von Wettstein, D.: Chlorophyll-Letale und der submikroskopische Formwechsel der Plastiden. Exptl. Cell Res. 12, 427–506 (1957)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by H. Stubbe
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gavazzi, G., Nava-Racchi, M. & Tonelli, C. A mutation causing proline requirement in Zea mays . Theoret. Appl. Genetics 46, 339–345 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00281675
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00281675