Abstract
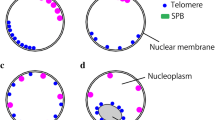
Chromosomes in G1, S, G2 and early prophase of Allium cepa root tip nuclei are oriented in the same position as telophase chromosomes. The centromeric heteroehromatin is aggregated in a chromocenter at one side of the nucleus, the telomeres scattered at the opposite side. Telomeres appear to associate with other telomeres in interphase in a roughly two by two fashion. Telomere-centromere DNA is late replicating. These results support the conclusion that chromosomes in higher organisms frequently maintain their telophase orientation from the end of telophase, during interphase and well into the next prophase.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashley, T., Wagenaar, E. B.: Telomeric associations of gametic and somatic chromosomes in diploid and autotetraploid Ornithogalum virens. Canad. J. Genet. Cytol. 19, 61–76 (1974)
Bajer, A.: Behavior and fine structure of spindle fibers during mitosis in endosperm. Chromosoma (Berl.) 25, 249–281 (1968)
Bajer, A., Molè-Bajer, J.: Cine-micrographic studies on mitosis in endosperm. II. Chromosome, cytoplasmic and brownian movements. Chromosoma (Berl.) 7, 558–607 (1956)
Bajer, A., Molè-Bajer, J.: Formation of spindle fibers, kinetochore orientation, and behavior of the nuclear envelope during mitosis in endosperm. Chromosoma (Berl.) 27, 448–484 (1969)
Bauer, H.: Structure and arrangement of salivary gland chromosomes in Drosophila species. Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. (Wash.) 22, 216–222 (1936)
Brown, S. W.: Heterochromatin. Science 151, 417–425 (1966)
Carlson, J. G.: On the mitotic movement of chromosomes. Science 124, 203–206 (1956)
Davidson, E. H., Britten, R. J.: Organization, transcription and regulation in the animal genome. Quart. Rev. Biol. 48, 565–613 (1973)
Dobzhansky, T.: Genetics and the origin of species, 3rd edit., p. 212–253. New York: Columbia University Press 1957
Eckhardt, R. A., Gall, J. G.: Satellite DNA associated with heterochromatin in Rhynchosciara. Chromosoma (Berl.) 32, 407–427 (1971)
Ellison, J. R., Barr, H. J.: Quinacrine fluorescence of specific chromosome regions. Chromosoma (Berl.) 36, 375–390 (1972)
Evans, H. J.: Chromatid aberrations induced by gamma irradiation. I. The structure and frequency of chromatid interchanges in diploid and tetraploid cells of Vicia faba. Genetics 46, 257–275 (1961)
Fussell, C. P.: The interphase position of chromosomes in onion root tip nuclei. J. Cell Biol. 55, 79A (1972)
Gill, B. S., Kimber, G.: The Giemsa C-banded karyotype of rye. Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. (Wash.) 71, 1247–1249 (1974)
Heitz, E.: Die Herkunft der Chromocentren. Dritter Beitrag zur Kenntnis der Beziehung zwischen Kernstruktur und qualitativer Verschiedenheit der Chromosomen in ihrer Längsrichtung. Planta (Berl.) 18, 571–636 (1932)
Hsu, T. C., Arrighi, F. E., Saunders, G. F.: Compositional hetergeneity of human heterochromatin. Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. (Wash.) 69, 1464–1466 (1972)
Kaufmann, B. P., Iddles, M. K.: Ectopic pairing in salivary gland chromosomes of Drosophila melanogaster. I. Distributional patterns in relation to puffing. Portug. Acta Biol. 7, 225–248 (1963)
Kitani, Y.: Orientation, arrangement and association of somatic chromosomes. Jap. J. Genetics 38, 244–256 (1963)
Kumar, S., Natarajan, A. T.: Kinetics of two-break chromosome exchanges and the spatial arrangement of chromosome strands in the interphase nucleus. Nature (Lond.) 209, 796–797 (1966)
Lafontaine, J. G., Lord, A.: Organization of nuclear structures in mitotic cells. In: Handbook of molecular cytology (A. Lima-de-Faria, ed.), p. 381–411. Amsterdam: North-Holland Publishing Co. 1969
Levan, A.: Heterochromaty in chromosomes during their contraction phase. Hereditas (Lund) 32, 449–468 (1946)
Lima-de-Faria, A., Jaworska, H.: Late DNA synthesis in heterochromatin. Nature (Lond.) 217, 138–142 (1968)
Macgregor, H. C., Kezer, J.: The chromosomal localization of heavy satellite DNA in the testis of Plethodon c. cinereus. Chromosoma (Berl.) 33, 167–182 (1971)
Matagne, R.: Duration of mitotic cycle and patterns of DNA replication in chromosomes of Allium cepa. Caryologia (Firenze) 21, 209–224 (1968)
Metz, C. W.: Chromosome studies on the Diptera II. J. exp. Zool. 21, 213–279 (1916)
Mirsky, A. E., Osawa, S.: The interphase nucleus. In: The cell II. (J. Brachet and A. E. Mirsky, eds.), p. 677–770. New York: Academic Press 1961
Pardue, M. L.: Localization of repeated DNA sequences in Xenopus chromosomes. Cold Spr. Harb. Symp. quant. Biol. 38, 475–482 (1974)
Rudkin, G. T.: The structure and function of heterochromatin. Genetics Today. Proc. XI Internat. Congr. of Genetics, p. 359–374. The Hague 1963
Sax, K.: An analysis of X-ray induced chromosomal aberrations in Tradescantia. Genetics 25, 41–68 (1940)
Stebbins, G. L., Jr.: Variation and Evolution in Plants, p. 442–475. New York: Columbia university Press 1950
Stebbins, G. L.: Chromosomal variation and evolution. Science 152, 1463–1469 (1966)
Sutton, W. S.: On the morphology of the chromosome group in Brachystola magna. Biol. Bull. 4, 24–39 (1902)
Sved, J. A.: Telomere attachment of chromosomes. Some genetical and cytological consequences. Genetics 53, 747–756 (1966)
Swanson, C. P.: Cytology and cytogeneties. Englewood Cliffs, N. J.: Prentice-Hall, Inc. 1957
Swift, H.: The organization of genetic material in eukaryotes: Progress and prospects. Cold Spr. Harb. Symp. quant. Biol. 38, 963–979 (1974)
Vanderlyn, L.: Somatic mitosis in the root tip of Allium cepa—A review and reorientation. Bot. Rev. 14, 270–318 (1948)
Van't Hof, J.: Relationships between mitotic cycle duration, S period duration and the average rate of DNA synthesis in the root meristem cells of several plants. Exp. Cell Res. 39, 48–58 (1965)
Wagenaar, E. B.: End-to-end chromosome attachments in mitotic interphase and their possible significance to meiotic chromosome pairing. Chromosoma (Berl.) 26, 410–426 (1969)
Wilson, E. B.: The cell in development and heredity, 3rd ed. New York: The Macmillan Company 1925
Wimber, D. E.: Chromosome breakage produced by tritium-labeled thymidine in Tradescantia palusosa. Proc; nat. Acad. Sci. (Wash.) 45, 839–846 (1959)
Wolff, S.: Handling of root tips. In: Methods in cell physiology I. (D. M. Prescott, ed.) p. 215–227. New York: Academic Press 1964
Yamada, M., Puck, T. T.: Action of radiation on mammalian cells. IV. Reversible mitotic lag in the S3 HeLa cell produced by low doses of x-rays. Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. (Wash.) 47, 1181–1191 (1961)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fussell, C.P. The position of interphase chromosomes and late replicating DNA in centromere and telomere regions of Allium cepa L.. Chromosoma 50, 201–210 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00283240
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00283240