Summary
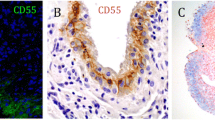
We have studied synthesis of the complement components and regulatory proteins of the alternative pathway and the membrane attack complex in synovial membrane. RNA was extracted from synovial tissue of patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) or osteoarthritis (OA) as well as from normal synovial membrane. Dot blot analysis showed the presence of mRNAs for all the complement components and regulatory proteins (C3, factor B, factor D, C5, C6, C7, C9, factor H, factor I, S-protein, SP-40, 40, DAF, MCP, CR1, CD59), except for properdin, C8α, C8β and C8γ in all three types of synovial membrane studied. In an attempt to determine which components were synthesised by each cell type, monocytes (mononuclear phagocytes), human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC), synovial membrane fibroblasts (from normal, OA and RA synovial membrane) and peripheral blood lymphocytes were cultured in vitro and secretion rates of individual components were measured and total cellular RNA analysed by northern blotting. Monocytes secreted properdin, C3, and factor H but not factor B, factor I, C5, C6, C7, C8 or C9. Fibroblasts and endothelial cells secreted factor B, factor H and factor I, but not properdin, C5, C6, C7, C8 or C9. Lymphocytes did not secrete any of these components. mRNAs encoding C3, factor B, factor H, S-protein, SP-40, 40, MCP and DAF were detected in all three other cell types (monocytes, fibroblasts and HUVEC), but factor I and CD59 mRNAs were not detected in monocytes. C5, C6, C7, C8α, C8β, CD8γ and C9 mRNAs were not detected in any of the cell types studied. Cell-specific differences were observed in the expression of the different mRNA species for DAF, MCP and CD59. The results of the present study demonstrate that synthesis of many complement components occurs in normal, RA and OA synovial membrane, and that this may be explained in part by synthesis in mononuclear phagocytes, endothelial cells and fibroblasts. The cellular sources of C5, C6, C7 and C9 mRNAs in synovial membrane have not been determined. The data also show that there are important cell-specific differences in the expression of the genes encoding both the alternative complement pathway components and the membrane regulatory components. These differences require further investigation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Weiler JM (1993) Introduction to complement. In: Whaley K, Loos M, Weiler J (eds) Complement in health and disease, 2nd edn. Kluwer Academic, Lancaster pp 1–37
Kohl J, Bitter-Suermann D (1993) Anaphylatoxins. In: Whaley K, Loos M, Weiler J (eds) Complement in health and disease, 2nd edn. Kluwer Academic, Lancaster, pp 299–324
Law SKA (1993) Complement receptors. In: Horton MA (ed) Blood cell biochemistry, 5. Macrophages and related cells. Plenum Press, New York, pp 223–259
Morgan BP (1993) Cellular responses to the membrane attack complex. In: Whaley K, Loos M, Weiler J (eds) Complement in health and disease, 2nd edn. Kluwer Academic, Lancaster, pp 325–352
Sledge CB (1989) Biology of the joint. In: Kelley WN, Harris ED, Ruddy S, Sledge CB (eds) Textbook of rheumatology, 3rd edn. Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 1–21
Ruddy S, Austen KF (1973) Activation of the complement system in rheumatoid synovium. Fed Proc 32:134–137
Morgan BP, Daniels RH, Williams BD (1988) Measurement of terminal complement complexes in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Immunol 73:473–478
Colten HR, Struck RC (1993) Synthesis of complement components and at extrahepatic sites. In: Whaley K, Loos M, Weiler J (eds) Complement in health and disease, 2nd edn. Kluwer Academic, Lancaster, pp 127–158
Gardner DL (1992) Rheumatoid arthritis, cell and tissue pathology. In: Gardner DL (ed) Pathological basis of connective tissue disease. Arnold, London, pp 444–526
Ruddy S, Colten HR (1974) Biosynthesis of complement proteins by synovial tissue. N Engl J Med 290:1284–1288
Reference deleted
De Bruijn MHL, Fey GH (1985) Human complement component C3: cDNA coding sequence and derived amino acid structure. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82:708–712
Morley BJ, Campbell RD (1984) Internal homologies of the Ba fragment from human complement component Factor B, a class III MHC antigen. EMBO J 3:153–157
Goundis D, Reid KBM (1988) Properdin, the terminal complement components, thrombospondin and C5 protein of malaria parasites contain similar sequence motifs. Nature 335:82–85
Min HY, Spiegelman BM (1986) Adipsin, the adipocyte serine protease: gene structure and control of expression by tumour necrosis factor. Nucleic Acids Res 8879–8892
Wetsel RA, Lemons RS, Le Beau MM, Barnum SR, Noack D, Tack BF (1988) Molecular analysis of human complement component C5: localisation of the structural gene to chromosome 9. Biochemistry 27:1474–1482
DiScipio RG, Hugli TE (1989) The molecular architecture of human complement component C6. J Biol Chem 264:16197–16206
SiScipio RG, Chakravarti DN, Muller-Eberhard MJ, Fey GH (1988) The structure of human complement component C7 and the C5b-7 complex. J Biol Chem 263:549–560
DiScipio RG, Gehring MR, Podack ER, Kan CC, Hugli TE, Fey GH (1984) Nucleotide sequence of cDNA and derived amino acid sequence of human complement component C9. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81:7298–7302
Rao AG, Howard OZM, Ng SC, Whitehead AS, Colten HR, Sodetz JM (1987) Complementary DNA and derived aminoacid sequence of the α-subunit of human complement protein C8: evidence for the existence of a separate α-subunit mRNA. Biochemistry 1987; 26:3556–3564
Howard OZM, Rao AG, Sodetz JM (1987) Complementary DNA and derived aminoacid sequence of the β-subunit of C8: identification of a close structural and ancestral relationship to the α-subunit of C9. Biochemistry 26:3565–3570
Ng SC, Rao AG, Howard OMZ, Sodetz JM (1987) The eighth component of human complement: evidence that it is an oligomeric serum protein assembled from products of three different genes. Biochemistry 26:5339–5233
Ripoche J, Day AJ, Harris TJ, Sim RB (1988) The complete aminoacid sequence of complement factor H. Biochem J 249:593–602
Catteral CF, Lyons A, Sim RB, Day AJ, Harris TJ (1987) Characterisation of primary amino acid sequence of human complement control protein factor I from an analysis of cDNA clones. Biochem J 242:849–856
Kirszbaum L, Sharpe JA, Murphy B, d'Aprice AJ, Classon B, Hudson P, Walker LD (1989) Molecular cloning and characterisation of the novel, human complement-associated protein, SP-40, 40: a link between the complement and reproductive systems. EMBO J 8:711–718
Lublin DM, Liszewski MK, Post TW, Arce MA, Le Beau MM, Rebentisch MB, Lemons LS, Seya T, Atkinson JP (1988) Molecular cloning and chromosomal localisation of human membrane cofactor protein (MCP). Evidence for inclusion in the mutigene family of complement regulatory proteins. J Exp Med 168:181–194
Medof ME, Lublin DM, Holers VM, Ayers DJ, Getty RR, Leykam JF, Atkinson JP, Tykocinski ML (1987) Cloning and characterisation of cDNAs encoding the complete sequence of decay-accelerating factor of human complement. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:2007–2011
Wong WW, Cahill JM, Rosen MD, Kennedy CA, Bonnacio ET, Morris MJ, Wilson JG, Klickstein LB, Fearon DT (1989) Structure of the human CR1 gene. Molecular basis of the structural and quantitative polymorphisms and identification of a new CR1-like molecule. J Exp Med 169:847–863
Davies A, Simmons DL, Hale G, Harrison RA, Tighe H, Lachmann PJ, Waldmann H (1989) CD59, an LY-6-like protein expressed in human lymphoid cells, regulates the action of the complement membrane attack complex on homologous cells. J Exp Med 170:637–654
Barbu V, Dawtry F (1989) Northern blot normalisation with a 28S rRNA oligonucleotide probe. Nucleic Acids Res 17:7115
Lappin DF, Birnie GD, Whaley K (1990) Modulation by interferons of the expression of monocyte complement genes. Biochem J 268:387–392
Warnick PR, Densen P (1990) Reduced C8 beta messenger RNA expression in families with hereditary C8 beta deficiency. J Immunol 146:1052–1056
Moffat GM, Lappin D, Birnie G, Whaley K (1989) Complement biosynthesis by synovial tissue. Clin Exp Immunol 78:54–60
Athanosou NA, Quinn J, Aeryet A, Pudle B, Woods CG, McGee JO'D (1988) The immunohistochemistry of synovial lining cells in normal and inflamed synovium. J Pathol 155:133–142
Lappin DF, Birnie GD, Whaley K (1990) Interferon-mediated transcriptional and post-transcriptional modulation of complement gene expression in human monocytes. Eur J Biochem 194:177–184
Whaley K (1980) Biosynthesis of the complement components and the regulatory proteins of the alternative complement pathway by human peripheral blood lymphocytes. J Exp Med 151:501–506
Schwaeble W, Dippold WG, Lvettig B, Jonas D, Schafer K-H M, Huemer HP, Dierich MP, Reid DBM (1993) Properdin, a positive regulator of complement activation is expressed in human T-cell lines and peripheral blood T-cells. Immunobiology (in press)
Hetland G, Johnson E, Falk RJ, Eskeland T (1986) Synthesis of complement components C5, C6, C7, C8 and C9 in vitro by human monocytes and assembly of the terminal complement complex. Scand J Immunol 24:421–428
Reed W, Roubey RAS, Dalzell JG, Matteucci BM, Myones BL, Hunt SW, Kolb WP, Ross GD (1990) Synthesis of complement component C5 by human B and T lymphoblastoid cell lines. Immunogenetics 31:145–151
Arend WP, Dyer JM (1990) Cytokines and cytokine inhibitors or antagonists in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 33:305–315
Russell SM, Sparrow RL, McKenzie IFC, Purcell DFJ (1992) Tissue-specific and allelic expression of the complement regulator CD46 is controlled by alternative splicing. Eur J Immunol 22:1513–1518
Moffat GM (1989) Complement synthesis in human synovial membrane. PhD Thesis, University of Glasgow
Lappin DF, Guc D, Hill A, McShane T, Whaley K (1992) Effect of interferon-8 on complement gene expression in different cell types. Biochem J 281:437–442
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guc, D., Gulati, P., Lemercier, C. et al. Expression of the components and regulatory proteins of the alternative complement pathway and the membrane attack complex in normal and diseased synovium. Rheumatol Int 13, 139–146 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00301260
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00301260