Summary
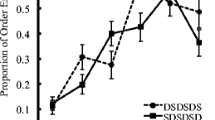
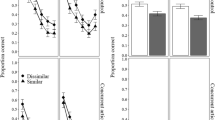
An experiment was presented to test a functionalistic interpretation of the modality effect. This shows a superior recall performance for auditorily as opposed to visually presented verbal information. A total of 60 subjects were presented with mixed-mode (auditory-visual words), mixed-language (Swedish-English words), or mixed-category (category-unrelated words) lists, and were asked to recall the words of each list in any preferred order. The degree of organization according to modality, language, or category and the recall performance were measured. Organization by modality was significantly higher than organization by language or category as predicted by the functionalistic view proposed. The recall performance obtained for auditory and visual words differed in a way predicted by the functionalistic view.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bower GH (1970) Organizational factors in memory. Cognit Psychol 1:18–46
Craik FIM (1969) Modality effects in short-term storage. J Verbal Learn Verbal Behav 8:658–664
Crowder RG, Morton J (1969) Precategorical acoustic storage (PAS). Percep Psychophys 5:365–373
Hintzman DL, Block RA, Inskeep RN (1972) Memory for mode of input. J Verbal Learn Verbal Behav 11:741–749
Kirman JH (1973) Tactile communication of speech: A review and an analysis. Psychol Bull 80:54–74
Laughery KR, Pinkus AL (1966) Short-term memory: Effects of acoustic similarity, presentation rate and presentation mode. Psychonom Sci 6:285–286
Mandler G (1967) Organization and memory. In: Spence KW, Spence IT (eds) The psychology of learning and motivation. Vol. I. Academic, New York, pp 327–372
Mandler G (1979) Elaboration and distinctiveness in episodic memory. In: Nilsson L-G (ed) Perspectives on memory research. Erlbaum, Hillsdale, NJ, pp 293–327
Murdock BB Jr, Walker KD (1969) Modality effects in free recall. J Verbal Learn Verbal Behav 8:665–676
Nilsson L-G (1973a) Organization by modality in short-term memory. J Exp Psychol 100:246–253
Nilsson L-G (1973b) Category norms for verbal material. (Rep. No. 135.) Uppsala, Sweden: University of Uppsala, Department of Psychology
Nilsson L-G (1974) Further evidence for organization by modality in short-term memory. J Exp Psychol 103:948–957
Nilsson L-G (1979) A functional interpretation of the modality effect. Scand J Psychol 20:259–265
Nilsson L-G, Ohlsson K, Rönnberg J (1977) Capacity differences in processing and storage of auditory and visual input. In: Dornic S (ed) Attention and Performance VI. Erlbaum, Hillsdale NJ, pp 629–645
Nilsson L-G, Ohlsson K, Rönnberg J (1980) Processing and storage explanations of the modality effect. Acta Psychol 44:41–50
Roenker DL, Thompson CP, Brown SC (1971) Comparisons of measures for the estimation of clustering in free recall. Psychol Bull 76:45–48
Rönnberg J (1980) Conceptions of remembering as task-skill interactions. Doctoral dissertation. University of Uppsala, Sweden
Rönnberg J, Ohlsson K (1980) Channel capacity and processing of modality specific information. Acta Psychol 44:253–267
Rönnberg J, Archer T, Ohlsson K (1980) Temporal factors in audition and vision. Scand J Psychol 4:241–247
Slamecka NJ (1968) An examination of trace storage in free recall J Exp Psychol 76:504–513
Sperling G (1967) Successive approximations to a model for short-term memory. Acta Psychol 27:285–292
Tulving E, Colotla VA (1970) Free recall of trilingual lists. Cognit Psychol 1:86–98
Tulving E, Donaldson E (eds) (1972) Organization of memory. Academic, New York
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rönnberg, J., Nilsson, LG. & Ohlsson, K. Organization by modality, language, and category compared. Psychol. Res 44, 369–379 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00309331
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00309331