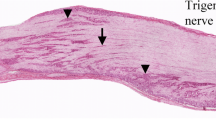
Summary
This study was designed to investigate the effects of multiple denervation procedures on calcitonin gene-related peptide- and substance P-immunoreactive neurons in sympathetic and sensory cranial ganglia and in selected targets. Sympathectomy by long-term guanethidine treatment induced a pronounced increase in calcitonin gene-related peptide-immunoreactive and substance P-immunoreactive nerve fibres in all the tissues investigated, in contrast to a significant reduction of immunoreactive cell bodies. Neonatal capasaicin treatment abolished substance P immunoreactivity in many targets and caused a dramatic reduction of substance P-immunoreactive sensory nerve cell bodies; calcitonin gene-related peptide-immunoreactive nerve density was decreased, but the number of immunoreactive nerve cell bodies was unchanged. Guanethidine treatment of capsaicin-injected rats reversed the loss of calcitonin gene-related peptide-immunoreactive nerves, but not that of substance P-immunoreactive neurons. In the iris, capsaicin treatment had little effect on calcitonin gene-related peptide- and substance P-immunoreactive nerves, suggesting that in rats the majority of these fibres originate from capsaicin-insensitive neurons. The results suggest that the denervation procedures used in this study alter the synthesis and transport of neuropeptides in sensory neurons in conjunction with changes in the number of nerve fibres.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aberdeen J, Corr L, Milner P, Lincoln J, Burnstock G (1990) Marked increase in calcitonin gene-related peptide containing nerves in the developing rat following long-term sympathectomy with guanethidine. Neuroscience 35:175–184
Andres KH, Düring M von, Muszynski K, Schmidt RF (1987) Nerve fibres and their terminals of the dura mater encephali of the rat. Anat Embryol 175:289–301
Black I (1986) Trophic molecules and evolution of the nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:8249–8252
Carvalho TLL, Hodson NP, Blank MA, Wilson PF, Mulderry PK, Bishop AE, Gu J, Bloom SR, Polak JM (1986) Occurrence, distribution and origin of peptide-containing nerves of guinea-pig and rat male genitalia and the effects of denervation on sperm characteristics. J Anat 149:121–141
Cole DF, Bloom SR, Burnstock G, Butler JM, McGregor GP, Saffrey MJ, Unger WJ, Zhang SQ (1983) Increase in SP-like immunoreactivity in nerve fibres of rabbit iris and ciliary body one to four months following sympathetic denervation. Exp Eye Res 37:191–197
De la Torre JC, Surgeon JW (1976) A morphological approach to rapid and sensitive monoamine histofluorescence using a modified glyoxylic acid technique: the SPG method. Histochemistry 49:81–93
Edvinsson L, Uddman R (1982) Immunohistochemical localization and dilatory effect of substance P on human cerebral vessels. Brain Res 232:466–471
Edvinsson L, Ekman R, Jansen I, McCulloch J, Uddman R (1987) Calcitonin gene-related peptide and cerebral vessels: distribution and vasomotor effects. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 7:720–728
Ekström J, Ekman R, Håkanson R, Sjögren S, Sundler F (1988) Calcitonin gene-related peptides in rat salivary glands: neuronal localization, depletion upon nerve stimulation and effects on salivation in relation to substance P. Neuroscience 26:933–949
Fitzgerald M (1983) Capsaicin and sensory neurones — a review. Pain 15:109–130
Franco-Cereceda A, Henke H, Lundberg JM, Petermann J, Hökfelt T, Fischer JA (1987) Calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) in capsaicin-sensitive substance P-immunoreactive sensory neurons in animals and man: distribution and release by capsaicin. Peptides 8:399–410
Gibbins IL, Furness JB, Costa M, MacIntyre I, Hillyard CJ, Girgis S (1985) Co-localization of calcitonin gene-related peptide-like immunoreactivity with substance P in cutaneous, vascular and visceral sensory neurons of guinea pigs. Neurosci Lett 57:125–130
Gibson SJ, Polak JM, Bloom SR, Sabate IM, Mulderry PM, Ghatei MA, McGregor GP, Morrison JEB, Kelly JS, Evans RM, Rosenfeld MG (1984) Calcitonin gene-related peptide immunoreactivity in the spinal cord of man and eight other species. J Neurosci 4:3101–3111
Hsu SM, Soban E (1982) Colour modification of diaminobenzidine (DAB) precipitation by metallic ions and its application for double immunohistochemistry. J Histochem Cytochem 30:1079–1082
Isaacson L, Saffran BN, Crutcher KA (1990) Intracerebral NGF infusion induces hyperinnervation of cerebral blood vessels. Neurobiol Aging 11:51–55
Jancso G, Kirali E, Jancso-Gabor A (1977) Pharmacologically induced selective degeneration of chemosensitive primary sensory neurons. Nature 270:741–743
Kessler JA (1986) Parasympathetic, sympathetic and sensory interactions in the iris: nerve growth factor regulates cholinergic ciliary ganglion innervation in vivo. J Neurosci 5:2719–2725
Kessler JA, Black IB (1980) Nerve growth factor stimulates the development of substance P in sensory ganglia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 77:649–652
Kessler JA, Bell WO, Black IB (1983) Interaction between the sympathetic and sensory innervation of the iris. J Neurosci 3:1301–1307
Landis SC, Fredieu JR (1986) Coexistence of calcitonin gene-related peptide and vasoactive intestinal peptide in cholinergic sympathetic innervation of rat sweat glands. Brain Res 377:177–181
Lee Y, Kaway Y, Shiosaka S, Takami K, Kiyama H, Hillyard CJ, MacIntyre I, Emson PC, Toyama M (1985) Coexistence of calcitonin gene-related peptide and substance P-like peptide in single cells of the trigeminal ganglion of the rat: immunohistochemical analysis. Brain Res 330:194–196
Lindsay RM, Harmar AJ (1989) Nerve growth factor regulates expression of neuropeptide genes in adult sensory neurons. Nature 337:362–364
Lindvall O, Björklund A (1974) The glyoxylic acid fluorescence histochemical method: a detailed account of the methodology for the visualization of central catecholamine neurons. Histochemistry 39:97–127
Matsuyama T, Wamaka A, Yoneda S, Kimura K, Kamada T, Girgis S, MacIntyre I, Emson PC, Tohyama M (1986) Two distinct calcitonin gene-related peptide-containing peripheral nervous system: distribution and quantitative differences between the iris and cerebral artery with special reference to substance P. Brain Res 373:205–212
Miller MS, Buck SH, Yamamura HI, Busks TF (1982) Regulation of substance P by nerve growth factor: disruption by capsaicin. Brain Res 250:193–196
Rosenfeld MG, Mermod JJ, Amara SG, Swanson LW, Sawchenko PE, Rivier J, Vale WW, Evans RM (1983) Production of a novel neuropeptide encoded by the calcitonin gene via tissue-specific RNA processing. Nature 304:129–135
Rossi F, Scevola D (1935) Contributo alla conoscenza della distribuzione delle fibre nervose nella dura madre encefalica. Monitore Zool Ital 45:289
Saito A, Goto K (1986) Depletion of calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) by capsaicin in cerebral arteries. J Pharmacobio Dyn 9:613–619
Scadding JW (1980) The permanent anatomical effects of neonatal capsaicin on somatosensory nerves. J Anat 131:473–484
Schon F, Ghatei M, Allen JM, Mulderry PK, Kelly JS, Bloom SR (1985) The effect of sympathectomy on calcitonin gene-related peptide levels in the rat trigeminovascular system. Brain Res 348:197–200
Silverman JD, Kruger L (1989) Calcitonin gene-related peptide-immunoreactive innervation of the rat head with emphasis on specialized sensory structures. J Comp Neurol 280:303–330
Skofitsch G, Jacobowitz DM (1985) Calcitonin gene-related peptide coexists with substance P in capsaicin sensitive neurons and sensory ganglia of the rat. Peptides 6:747–754
Suzuki N, Hardebo JE, Owman C (1989) Origins and pathways of cerebrovascular nerves storing substance P and calcitonin gene-related peptide in rat. Neuroscience 31:427–438
tenTuscher MPM, Klooster J, Want JJL van der, Lamers WPMA, Vrenson GFJM (1989) The allocation of nerve fibres to the anterior eye segment and peripheral ganglia of rats. I. The sensory innervation. Brain Res 494:95–104
tenTuscher MPM, Klooster J, Baljet B, Van der Werf F, Vrensen GFJM (1990) Pre- and post-ganglionic nerve fibres of the pterygopalatine ganglion and their allocation to the eyeball of rats. Brain Res 517:315–323
Terenghi G, Polak JM, Probert L, McGregor GP, Ferri GL, Blank MA, Butler JM, Unger WG, Zhang SQ, Cole DF, Bloom SR (1982) Mapping, quantitative distribution and origin of substance P and VIP-containing nerves in the urea of guinea pig eye. Histochemistry 75:399–417
Terenghi G, Polak JM, Ghatei MA, Mulderry PK, Butler JM, Unger WG, Bloom SR (1985) Distribution and origin of CGRP-immunoreactivity in the sensory innervation of the mammalian eye. J Comp Neurol 233:505–516
Terenghi G, Zhang S-Q, Unger WG, Polak JM (1986) Morphological changes of sensory CGRP-immunoreactive and sympathetic nerves in peripheral tissue following chronic denervation. Histochemistry 86:89–95
Yamamoto K, Senba E, Matsunaga T, Tohyama M (1989) Calcitonin gene-related peptide containing sympathetic preganglionic and sensory neurons projecting to the superior cervical ganglion of the rat. Brain Res 487:158–164
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mione, M.C., Cavanagh, J.F.R., Kirkpatrick, K.A. et al. Plasticity in expression of calcitonin gene-related peptide and substance P immunoreactivity in ganglia and fibres following guanethidine and/or capsaicin denervation. Cell Tissue Res 268, 491–504 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00319156
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00319156