Summary
-
1.
The cellular and synaptic pattern of the lateral geniculate body of the monkey has been studied electronmicroscopically by using microdissected portions from individual layers. For general orientation and comparison the Golgi technique has been utilised extensively.
-
2.
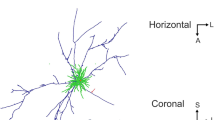
This technique revealed four different types of neuron whose distribution differs in the various layers. The first type has 3–4 stem dendrites, which possess tiny side branches or appendages. The second type is smaller and has 8–10 stem dendrites. The third type is a Golgi type II cell with very long dendrites with bushy terminal arborisations. The fourth type are very small neurons and it is difficult to separate them from glial cells with certainty.
-
3.
The synaptic organisation has been examined in great detail, in particular the different composition of the glomeruli in different layers. Seven components of a glomerulus have been found whose individual contributions vary in different layers. These components are: main axon, main dendrite, peripheral axons, peripheral dendrites, dendritic and axonal thorns and glia lamellae.
-
4.
In addition to this synaptic pattern a further interesting synapse has been found, an axo-axonal type in contact with the initial segment of a large axon of a geniculate cell.
Zusammenfassung
-
1.
Der zelluläre Aufbau und die synaptische Organisation einzelner Schichten des Corpus geniculatum laterale des Affen wurde mit der Golgi-Technik und elektronenmikroskopisch untersucht. Die kleinen Gewebsstücke aus verschiedenen Regionen einer bestimmten Schicht wurden für die Elektronenmikroskopie durch Mikrosektion nach vorheriger Anfärbung des ganzen Geniculatum präpariert.
-
2.
In Golgipräparaten lassen sich vier Neuronenarten unterscheiden, deren quantitative Verteilung in den Schichten verschieden ist. Die erste Art besitzt 3–4 Stammdendriten, die noch winzigste Seitenäste tragen. Die zweite Art ist kleiner und hat 8–10 Stammdendriten. Die dritte Art entspricht der Golgi-Zelle II. Ihre Stammdendriten sind sehr lang und mit dichten Endverzweigungen ausgestattet. Die vierte Zellart wird von kleinen, glia-ähnlichen Zellen gebildet. Diese lichtmikroskopischen Befunde sind für die elektronenmikroskopische Auswertung wertvoll.
-
3.
Die synaptische Organisation ist elektronenmikroskopisch analysiert worden, insbesondere die Zusammensetzung der Glomeruli. Sieben verschiedene neuronale und gliöse Fortsätze tragen dazu bei, aber ihre mengenmäßige Beteiligung ist für die einzelnen Schichten unterschiedlich. Diese Fortsätze setzen sich wie folgt zusammen: Ein Hauptaxon, ein Hauptdendrit, peripher gelegene kleinere Axone, peripher gelegene Dendriten, dornenartige Fortsätze der Dendriten und der Axone, Glialamellen.
-
4.
Eine weitere Synapsenart von besonderem Interesse zeigte sich in einer axo-axonalen Art, deren postsynaptische Teile von dem Initialsegment des efferenten Axons einer Geniculatumzelle gebildet werden.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andres, K. H.: Mikropinozytose im Zentralnervensystem. Z. Zellforsch. 64, 63–73 (1964).
Beresford, W. A.: Fibre degeneration following lesions of the visual cortex of the cat. In: The visual system: Neurophysiology and psychophysics (ed. by Jung and H. Kornhuber). Berlin-Göttingen-Heidelberg: Springer 1961.
Campos-Ortega, J. A., M. Blank u. P. Glees: Die absteigenden Verbindungen der Sehrinde des Halbaffen Galago crassicaudatus. Experientia (Basel) (In press).
—, and P. Glees: The termination of ipsilateral and contralateral optic fibers in the lateral geniculate body of Galago crassicaudatus. J. comp. Neurol. 129, 279–284 (1967a).
—: The visual subcortical connexions in the squirrel monkey Saimiri sciureus. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 191, 93–95 (1967b).
Colonnier, M., and R. W. Guillery: Synaptic organization in the lateral geniculate nucleus of the monkey. Z. Zellforsch. 62, 333–335 (1964).
Dalton, J. A.: A chrome-osmium fixative for electron-microscopy. Anat. Rec. 121, 281 (1955).
Glees, P.: Termination of optic fibres in the lateral geniculate body. Nature (Lond.) 146, 745 (1940).
—, M. Hasan, and K. Tischner: The cytological distribution of “osmiophilic bodies” in the normal and degenerating lateral geniculate nucleus of the monkey. Acta neuropath. (Berl.) 8, 285–291 (1967).
—, and W. E. Le Gros Clark: The termination of optic fibres in the lateral geniculate body of the monkey. J. Anat. (Lond.) 75, 295–310 (1941).
—, K. Meller, and J. Eschner: Terminal degeneration in the lateral geniculate body of the monkey; an electronmicroscope study. Z. Zellforsch. 71, 29–40 (1966).
—, and V. Neuhoff: Preparing the lateral geniculate body for various methods assessing trans synaptic neuronal atrophy. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 191, 96–98 (1967).
Guillery, R. W.: A study of Golgi preparations from the dorsal lateral geniculate nucleus of the adult cat. J. comp. Neurol. 128, 21–50 (1966).
—: Patterns of fibre degeneration in the dorsal lateral geniculate nucleus of the cat following lesions in the visual cortex. J. comp. Neurol. 130, 197–222 (1967).
Karlsson, U.: Three-dimensional studies of neurons in the lateral geniculate nucleus of the rat. III. Specialized neuronal contacts in the neuropil. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 17, 137–157 (1967).
Karnovsky, M. S.: Simple methods for staining with lead of high pH in electron microscopy. J. biophys. biochem. Cytol. 11, 729–732 (1961).
Larramendi, L. M. H., and T. Victor: Synapses on the Purkinje cell spines in the mouse. An electronmicroscopic study. Brain Research 5, 15–30 (1967).
McMahan, U. J.: Fine structure of synapses in the dorsal nucleus of the lateral geniculate body of normal and blinded rats. Z. Zellforsch. 76, 116–146 (1967).
O'Leary, J. L.: A structural analysis of the lateral geniculate nucleus of the cat. J. comp. Neurol. 73, 405–430 (1940).
Peters, A., and S. L. Palay: The morphology of laminae A and Al of the dorsal nucleus of the lateral geniculate body of the cat. J. Anat. (Lond.) 100, 451–486 (1966).
Ramon y Cajal, S., y F. de Castro: Elementos de tècnica microgràfica del sistema nervioso. Tipografìa Artìstica. Madrid 1933.
Sabatini, D. D., K. Bensch, and R. J. Barrnett: Cytochemistry and electronmicroscopy. J. biophys. biochem. Cytol. 17, 19–38 (1963).
Smith, J. M., J. L. O'Leary, A. B. Harris, and A. J. Gay: Ultrastructural features of the lateral geniculate nucleus of the cat. J. comp. Neurol. 123, 357–378 (1964).
Szentágothai, J.: The structure of the synapse in the lateral geniculate body. Acta anat. (Basel) 55, 166–185 (1963).
—: The use of degeneration methods in the investigation of short neuronal connexions. Progr. Brain Res., vol. 14, p. 1–32. Degenerative patterns in the nervous system, ed. by M. Singer and J. P. Schadé. Amsterdam: Elsevier 1965.
—: J. Hamori, and Th. Tömböl: Degeneration and electronmicroscope analysis of the synaptic glomeruli in the lateral geniculate body. Exp. Brain Res. 2, 283–301 (1966).
Tello, J. F.: Disposiciòn macroscòpica y estructura del cuerpo geniculado externo. Trab. Lab. Invest. Biol. Univ. Madrid 3, 39–62 (1904).
Uchizono, K.: Characteristics of excitatory and inhibitory synapses in the central nervous system of the cat. Nature (Lond.) 207, 642–643 (1965).
Valverde, F.: Intrinsic organization of the amygdaloid complex. A Golgi study in the mouse. Trab. Inst. Cajal Invest. biol. 54, 291–314 (1962).
Walberg, F.: The fine structure of the cuneate nucleus in normal cats and following interruption of afferent fibres. An electron microscopical study with particular reference to findings made in Glees and Nauta sections. Exp. Brain Res. 2, 107–128 (1966).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
We wish to thank Frau I. Bernhard, Frau M. Bothe and Mr. Ph. Tiplady for technical assistance and the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (Gl. 28/12, Ne. 46/4) for their financial support.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Campos-Ortega, J.A., Glees, P. & Neuhoff, V. Ultrastructural analysis of individual layers in the lateral geniculate body of the monkey. Z. Zellforsch. 87, 82–100 (1968). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00326562
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00326562