Summary
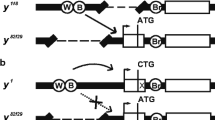
The spontaneous mutation white-apricot (wa) in Drosophila melanogaster has a considerably highter eye colour than the wild-type, and is caused by the insertion of a copia transposable element into a small intron of the white gene. We have analyzed an X-ray induced w a revertant (w aR59K1), whose eye pigmentation is incompletely restored, by in situ hybridization, Southern blotting and sequencing analysis. At the site where copia had originally inserted, we found one long terminal repeat of copia, flanked by a 5 bp duplication with the same polarity as the direction of transcription of the white locus. These results suggest that the w a reversion is due to homologous recombination between the two long terminal repeats of copia.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bender W, Akam M, Karch F, Beachy P, Peifer M, Spierer P, Lewis E, Hogness D (1983) Molecular genetics of the bithorax complex in Drosophila melanogaster. Science 221:23–29
Benton W, Davis RE (1977) Screening γ-gt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques. Science 196:180–182
Bingham P, Judd B (1981) A copy of the copia transposable element is very tightly linked to the w a allele at the white locus of Drosophila melanogaster. Cell 25:705–711
Bingham P, Levis R, Rubin G (1981) Cloning of DNA sequences from the white locus of Drosophila melanogaster by a novel and general method. Cell 25:693–704
Calos M, Miller H (1980) Transposable elements. Cell 20:579–595
Cammeron J, Loh E, Davis R (1979) Evidence for transposition of dispersed repetitive DNA families in yeast. Cell 16:739–751
Casey U, Roach A, Mullins J, Barck K, Nicolson M, Gardner M, Davidson M (1981) The U3 portion of feline leukemia virus DNA identifies horizontally acquired proviruses in leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 78:7778–7782
Collins M, Rubin G (1982) Structure of the Drosophila mutable allele, white-crimson, and its white-ivory and wild-type derivatives. Cell 30:71–79
Donner L, Tureck L, Ruscetti S, Fedele L, Sherr C (1980) Transformation-defective mutants of feline sarcoma virus which express a product of the viral ssc gene. J Virol 35:129–140
Dunsmuir P, Brorein W, Siomon M, Rubin G (1980) Insertion of the Drosophila transposable element copia generates a 5 base pair duplication. Cell 21:575–579
Eibel H, Gafner J, Stotz A, Philippsen P (1980) Characterization of the yeast mobile element Tyl. Cold Spring Harbor Symp Quant Biol 45:609–617
Enquist L, Sternberg M (1980) In vitro packaging of λ Dam vectors and their use in cloning DNA fragments. Methods in enzymology, vol 68. Academic Press, New York, pp 281–298
Farabough P, Fink G (1980) Insertion of the eukaryotic transposable element Ty 1 creates a 5-base pair duplication. Nature 286:352–356
Finnegan J, Rubin G, Young M, Hogness D (1977) Repeated gene families in Drosophila melanogaster. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol 42:1053–1063
Flavell A, Ish-Horowicz D (1981) Extrachromosomal circular copies of the eukaryotic transposable element copia in cultured Drosophila cells. Nature 292:591–595
Gehring WJ, Paro R (1980) Isolation of a hybrid plasmid with homologous sequences to a transposing element of Drosophila melanogaster. Cell 19:897–904
Goldberg M, Paro R, Gehring WJ (1982) Molecular cloning of the white locus region of Drosophila melanogaster using a large transposable element. The EMBO J 1:93–98
Hanahan D, Meselson M (1980) Plasmid screening at high colony density. Gene 10:63–67
Jeffreys A, Flavell R (1977) A physical map of the DNA regions flanking the rabbit β-globin gene. Cell 12:429–439
Jenkins A, Copeland N, Taylor B, Lee B (1981) Dilute coat colour mutation DBA/2j mice is associated with the site of integration of an ecotropic MuLV genome. Nature 293:370–374
Karn J, Brenner S, Barnett L, Cesareni G (1980) Novel bacteriophage =gl cloning vector. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 77:5172–5176
Kugimiya W, Ikenaga H, Saigo K (1983) Close relationship between the the long terminal repeats of avian leukosis sarcoma virus and copia like movable genetic element of Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 80:3193–3197
Kulkusgin V, Ilyin Y, Georgiev G (1981) Mobile dispersed genetic element MDG1 of Drosophila melanogaster: nucleotide sequence of long terminal repeats. Nucl Ac Res 9:3451–3464
Langer P, Levine M, Ward D (1982) Immunological method for mapping genes on Drosophila polytene chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 79:4381–4385
Levis R, Dunsmuir P, Rubin G (1980) Terminal repeat of the Drosophila transposable element copia: nucleotide sequence and genomic organization. Cell 21:581–588
Levis R, Bingham P, Rubin G (1982) Physical map of the white locus of Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Sci USA 79:564–568
Levis R, O'Hare K, Rubin G (1984) Effects of transposable element insertions on RNA encoded by the white gene of Drosophila. Cell 38:471–481
Maxam A, Gilbert W (1977) A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 74:560–564
McGinnis W, Sherman A, Beckendorf S (1983) A transposable element inserted just 5′ to a Drosophila glue protein gene alters gene expression and chromatin structures. Cell 34:75–84
Mount S (1982) A catalogue of splice junction sequences. Nucl Ac Res 10:459–472
O'Hare K, Rubin G (1983) Structure of P transposable elements and their sites of insertion and excision in the Drosophila melanogaster genome. Cell 34:25–35
Pardue M, Gall J (1975) Nucleic acid hybridization to the DNA of cytological preparations. In: Prescott D (ed) Methods in cell biology, vol 10. Academic Press, New York, pp 1–16
Pirrotta V, Bröckl C (1984) Transcription of the Drosophila white locus and some of its mutants. The EMBO J 3:563–568
Rasmuson B, Green M, Evertson G (1960) Qualitative and quantitative analyses of eye pigments and pteridines in back mutations of the mutant w wa in Drosophila melanogaster. Hereditas 46:635–650
Roeder G, Fink G (1980) DNA rearrangements associated with a transposable element in yeast. Cell 21:239–250
Rubin G, Kidwell M, Bingham P (1982) The molecular basis of P-M hybrid dysgenesis: The nature of induced mutations. Cell 29:987–994
Rubin G (1983) Dispersed repetitive DNAs in Drosophila. In: Mobile genetic elements: Dispersed repetitive DNAs in Drosophila, Academic Press, New York, pp 329–361
Sanger F, Nicklen S, Coulson A (1977) DNA sequencing with chain terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 74:5463–5467
Smith G, Summers M (1980) The bidirectional transfer of DNA and RNA to nitrocellulose or diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper. Annal Biochem 109:123–129
Truett M, Jones R, Potter S (1981) Unusual structures of the FB family of transposable elements in Drosophila. Cell 24:753–763
Varmus H (1983) Retroviruses. In: Mobile genetic elements, Academic Press, New York, pp 411–503
Wensink P, Finnegan D, Donelson J, Hogness DS (1974) A system for mapping DNA sequences in the chromosomes of Drosophila melanogaster. Cell 3:315–325
Will B, Bayer A, Finnegan D (1981) Nucleotide sequence of terminal repeats of 412 transposable elements of Drosophila melanogaster. J Mol Biol 153:897–915
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by M.M. Green
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Carbonare, B.D., Gehring, W.J. Excision of copia element in a revertant of the white-apricot mutation of Drosophila melanogaster leaves behind one long-terminal repeat. Molec Gen Genet 199, 1–6 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00327501
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00327501