Summary
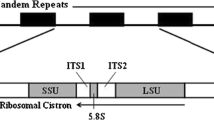
The organization of the ribosomal DNA (rDNA) repcat unit in the standard wild-type strain of Neurospora crassa, 74-OR23-1A, and in 30 other wild-type strains and wild-collected strains of N. crassa, N. tetrasperma, N. sitophila, N. intermedia, and N. discreta isolated from nature, was investigated by restriction enzyme digestion of genomic DNA, and probing of the Southern-blotted DNA fragments with specific cloned pieces of the rDNA unit from 74-OR23-1A. The size of the rDNA unit in 74-OR23-1A was shown to be 9.20 kilobase pairs (kb) from blotting data, and the average for all strains was 9.11+0.21 kb; standard error=0.038; coefficient of variation (C.V.)=2.34%. These data indicate that the rDNA repeat unit size has been highly conserved among the Neurospora strains investigated. However, while all strains have a conserved HindIII site near the 5′ end of the 25 S rDNA coding sequence, a polymorphism in the number and/or position of HindIII sites in the nontranscribed spacer region was found between strains. The 74-OR23-1A strain has two HindIII sites in the spacer, while others have from 0 to at least 3. This restriction site polymorphism is strain-specific and not species-specific. It was confirmed for some strains by restriction analysis of clones containing most of the rDNA repeat unit. The current restriction map of the 74-OR23-1A rDNA repeat unit is presented.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnheim N, Southern EM (1977) Heterogeneity of the ribosomal genes in mice and men. Cell 11:363–370
Barratt RW (1962) Origin of important wild type stocks of N. crassa. Neurospora Newslett 2:24–25
Botchan P, Reeder RH, Dawid IB (1977) Restriction analysis of the nontranscribed spacers of Xenopus laevis ribosomal DNA. Cell 11:599–607
Cox RA, Peden K (1979) A study of the organisation of the ribosomal ribonucleic acid gene cluster of Neurospora crassa by means of restriction endonuclease analysis and cloning in bacteriophage lambda. Mol Gen Genet 174:17–24
Free SJ, Rice PW, Metzenberg RL (1979) Arrangement of the genes coding for ribosomal ribonucleic acids in Neurospora crassa. J Bacteriol 137:1219–1226
Krumlauf R, Marzluf GA (1979) Characterization of the sequence complexity and organization of the Neurospora crassa genome. Biochemistry 18:3705–3713
Krumlauf R, Marzluf GA (1980) Genome organization and characterization of the repetitive and inverted repeat DNA sequences in Neurospora crassa. J Biol Chem 255:1138–1145
Maniatis T, Fritsch EF, Sambrook J (1982) In: Molecular cloning. A laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, New York
Metzenberg RL, Stevens JN, Baisch TJ (1983) 5S RNA genes of Neurospora crassa: Conservation and divergence in a dispersed gene family. Microbiology-1983. American Society for Microbiology Publications, Washington DC, pp 190–194
Petes TD (1979) Meiotic mapping of yeast ribosomal DNA on chromosome XII. J Bacteriol 138:185–192
Petes TD, Botstein DB (1977) Simple Mendelian inheritance of the reiterated ribosomal DNA of yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 74:5091–5095
Rae PMM, Barnett T, Murtif VL (1981) Nontranscribed spacers in Drosophila ribosomal DNA. Chromosoma 82:637–655
Rodland KD, Russell PJ (1982) Regulation of ribosomal RNA cistron number in a strain of Neurospora crassa with a duplication of the nucleolus organizer region. Biochim Biophys Acta 697:162–169
Russell PJ, Hammett JR, Selker EU (1976) Neurospora crassa cytoplasmic ribosomes: Ribosomal ribonucleic acid synthesis in the wild type. J Bacteriol 127:785–793
Schlitt SC, Russell PJ (1974) Neurospora crassa cytoplasmic ribosomes: Isolation and characterization of a cold-sensitive mutant defective in ribosome biosynthesis. J Bacteriol 120:666–671
Selker EU, Yanofsky C, Driftmier K, Metzenberg RL, Alzner-DeWeerd B, RajBhandary UL (1981) Dispersed 5S RNA genes in N. crassa: Structure, expression and evolution. Cell 24:819–828
Southern EM (1975) Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol 98:5–517
Thayer RE (1979) An improved method for detecting foreign DNA in plasmids of Escherichia coli. Anal Biochem 98:60–63
Wellauer PK, Dawid IB (1977) The structural organization of ribosomal DNA in Drosophila melanogaster. Cell 10:193–212
Wellauer PK, Dawid IB (1978) Ribosomal DNA in Drosophila melanogaster II. Heteroduplex mapping of cloned and uncloned rDNA. J Mol Biol 126:769–782
Zamb TJ, Petes TD (1982) Analysis of the junction between ribosomal RNA genes and single-copy chromosomal sequences in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Cell 28:355–364
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by F. Kaudewitz
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Russell, P.J., Wagner, S., Rodland, K.D. et al. Organization of the ribosomal ribonucleic acid genes in various wild-type strains and wild-collected strains of Neurospora . Mol Gen Genet 196, 275–282 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00328060
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00328060