Abstract
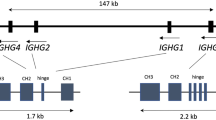
A human heavy chain variable region subgroup III pseudogene (HV3.3) was isolated, characterized, and sequenced. When HV3. was hybridized to Southern blots of human DNA, two potentially informative polymorphic bands, resulting from 2.7 kb Hind III (HH2.7) and 7.3 kb Eco RI(HE7.3) fragments, were detected with frequencies of 0.553 and 0.606, respectively. These polymorphic bands showed Mendelian segregation in families and appeared to be in tight linkage disequilibrium with each other (χ 21 =24.91, P<0.001). Evidence from sibling-pair data indicated linkage of the Hind III polymorphic band to constant region allotypic and restriction fragment length polymorphism markers. Bands representing alternative forms of the polymorphic restriction sites were not detected for either HH2.7 or HE7.3. This indicates either that the alternative fragments comigrate with homologous fragments resulting from conserved restriction sites, or that the polymorphism is due to a gene duplication or deletion. No band segregating with HH2.7 was found in separate digests using eight other enzymes. Although this indicates that a major deletion is unlikely, it does not exclude the possibility of a gene deletion or duplication affecting the intergenic region(s) of one or more homologous genes. Whatever the precise explanation, these findings support the hypothesis that there is polymorphic variation of V H gene repertoires in man.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams, J. M., Gough, N. M., Webb, E. A., Tyler, B. M., Jackson, J., and Cory, S.: Molecular cloning of mouse immunoglobulin heavy chain messenger ribonucleic acids coding for mu, alpha, gamma 1,gamma 2a, and gamma 3 chains. Biochemistry 19: 2711–2719, 1980
Bech-Hansen, N. T., Linsley, P. S., and Cox, D. W.: Restriction fragment length polymorphisms associated with immunoglobulin C gamma genes reveal linkage disequilibrium and genomic organization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 80: 6952–6956, 1983
Benton, W. D. and Davis, R. W.: Screening lambda gt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science 196: 180–182, 1977
Chaabani, H., Bech-Hansen, N. T., and Cox, D. W.: A multigene deletion within the immunoglobulin heavy-chain region. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 37: 1164–1171, 1985
Cox, D. W., Markovic, V. D., and Teshima, I. E.: Genes for immunoglobulin heavy chains and for alphal-antitrypsin are localized to specific regions of chromosome 14q. Nature 297: 428–430, 1982
Davis, R. W., Botstein, D., and Roth, J. R.: A Manual far Genetic Engineering: Advanced Bacterial Genetics, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, New York, 1980
Geever, R. F., Wilson, L. B., Nallaseth, F. S., Milner, P. F., Bittner, M., and Wilson, J. T.: Direct identification of sickle cell anemia by blot hybridization. Proc. Nod. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 78: 5081–5085, 1981
Gusella, J. F., Wexler, N. S., Comically, P. M., Naylor, S. L., Anderson, M. A., Tanzi, R. E., Watkins, P. C., Ottina, K., Wallace, M. R., Sakaguchi, A. Y., Young, A. B., Shoulson, I., Bonilla, E., and Martin, J. B.: A polymorphic DNA marker genetically linked to Huntington's disease. Nature 306: 234–238, 1983
Honjo, T.: Immunoglobulin genes. Anna. Rev. Immunol. 1: 499–528, 1983
Honjo, T. and Habu, S.: Origin of immune diversity: Genetic variation and selection. Anna. Rev. Biochem. 54: 803–830, 1985
Hood, L., Campbell, J. H., and Elgin, S. C. R.: The organization, expression, and evolution of antibody genes and other multigene families. Annu. Rev. Genet. 9: 305–353, 1975
Hoopes, B. C. and McClure, W. R.: Studies on the selectivity of DNA precipitation by spermine. Nucleic Acids Res. 9: 5493–5504, 1981
Johnson, M. J., Natali, A. M., Cann, H. M., Honjo, T., and Cavalli-Sforza, L. L.: Polymorphisms of a human variable heavy chain gene linkage with constant heavy chain genes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 81: 7840–7844, 1984
Kabat, E. A., Wu, T. T., Bilofsky, H., Reid-Miller, M., and Perry, H. (eds.): Sequences of Proteins of Immunological Interest, Department of Health and Human Services, Public Health Service, NIH, Bethesda, Maryland, 1983
Kan, Y. W. and Dozy, A. M.: Antenatal diagnosis of sickle-cell anaemia by DNA analysis of amniotic-fluid cells. Lancet 2: 910–911, 1978
Kemp, D. J., Tyler, B., Bernard, O., Gough, N., Gerondakis, S., Adams, J. M., and Cory, S.: Organization of genes and spacers within the mouse immunoglobulin VH locus. J. Mol. Appl. Genet. 1: 245–261, 1981
Kirsch, I. R., Morton, C. C., Nakahara, L., and Leder, P.: Human immunoglobulin heavy chain genes map to a region of translocations in malignant B lymphocytes. Science 216: 301–303, 1982
LeFranc, M.-P. and Rabbitts, T.H.: Human immunoglobulin heavy chain A2 gene allotype determination by restriction fragment length polymorphism. Nucleic Acids Res. 12: 1303–1311, 1984
Li, C. C.: Population Genetics, The University of Chicago Press, Chicago, 1955
Little, P. F. R., Annison, G., Darling, S., Williamson, R., Camba, L., and Modell, B.: Model for antenatal diagnosis of beta-thalassaemia and other monogenic disorders by molecular analysis of linked DNA polymorphisms. Nature 285: 144–147, 1980
Maniatis, T., Hardison, R. C., Lacy, E., Lancer, J., O'Connell, C., and Quon, D.: The isolation of structural genes from libraries of eucaryotic DNA. Cell 15: 687–701, 1978
Maniatis, T., Fritsch, E. F., and Sambrook, J.: Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, New York, 1982
Mathews, J. D.: Genetic markers in SLE: Overview-possible V-gene interactions. In R. L. Dawkins, P. J. Zilko, and F. E. Christiansen (eds.): Immunogenetics in Rheumatology, pp. 239–241, Excerpta Medica, Amsterdam, 1982
Matthyssens, G. and Rabbitts, T. H.: Structure and multiplicity of genes for the human inununoglobulin heavy chain variable region. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 77: 6561–6565, 1980
Migone, N., Feder, J., Cann, H., van West, B., Hwang, J., Takahashi, N., Honjo, T., Piazza, A., and Cavalli-Sforza, L. L.: Multiple DNA fragment polymorphisms associated with immunoglobulin mu chain switch-like regions in man. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 80: 467–471, 1983
Migone, N., Olivero, S., de Lange, G., Delacroix, D. L., Boschis, D., Altruda, F., Silengo, L., DeMarchi, M., and Carbonara, A. O.: Multiple gene deletions within the human immunoglobulin heavy chain cluster. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 81: 5811–5815, 1984
Migone, N., de Lange, G., Piazza, A., and Cavalli-Sforza, L. L.: Genetic analysis of eight linked polymorphisms within the human immunoglobulin heavy-chain region. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 37: 1146–1163, 1985
Monaco, A. P., Bertelson, C. J., Middlesworth, W., Colletti, C.-A., Aldridge, J., Fischbeck, K. H., Bartlett, R., Pericak-Vance, M. A., Roses, A. D., and Kunkel, L. M.: Detection of deletions spanning the muscular dystrophy locus using a tightly linked DNA segment. Nature 316: 842–845, 1985
Pech, M., Jaenichen, H.-R., Pohlenz, H.-D., Neumaier, P. S., Klobeck, H.-G., and Zachau, H. G.: Organization and evolution of a gene cluster for human immunoglobulin variable regions of the kappa type. J. Mol. Biol. 176: 189–204, 1984
Penrose, L. S.: The detection of autosomal linkage in data which consists of pairs of brothers and sisters of unspecified parentage. Ann. Eugen. 6: 133–138, 1935
Penrose, L. S.: The general purpose sib-pair linkage test. Ann. Eugen. 18: 120–124, 1953
Propert, D. N.: Detection of immunoglobulin polymorphisms. In M. J. Simons and B. D. Tait (eds.): Detection of Immune-Associated Genetic Markers, pp. 68–81, Churchill Livingstone, Edinburgh, 1984
Rabbitts, T. H., Bentley, D. L., Dunnick, W., Forster, A., Matthyssens, G. E. A. R., and Miltstein, C.: Immunoglobulin genes undergo multiple sequence rearrangements during differentiation. Cold Spring Harbor Symp. Quant. Biol. 45: 867–878, 1981
Rechavi, G., Bienz, B., Ram, D., Ben-Neriah, Y., Cohen, J. B., Zakut, R., and Givol, D.: Organization and evolution of immunoglobulin VH gene subgroups. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 79: 4405–4409, 1982
Rechavi, G., Ram, D., Glazer, L., Zakut, R., and Givol, D.: Evolutionary aspects of immunoglobulin VH gene subgroups. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 80: 855–859, 1983
Rigby, P. W. J., Dieckmann, M., Rhodes, C., and Berg, P.: Labelling deoxyribonucleic acid to a high pecific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J. Mol. Biol. 113: 237–251, 1977
Sanger, F., Nicklen, S., and Coulson, A. R.: DNA sequencing with chain terminating inhibitors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 74: 5463–5467, 1977
Siebenlist, U., Ravetch, J. V., Korsmeyer, S., Waldmann, T., and Leder, P.: Human immunoglobulin D segments encoded in tandem multigenic families. Nature 294: 632–635, 1984
Southern, E. M.: Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J. Mol. Biol. 98: 503–517, 1975
Takahashi, N., Nakai, S., and Honjo, T.: Cloning of human immunoglobulin p gene and comparison with mouse μ gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 8: 5983–5991, 1980
Tonegawa, S.: Somatic generation of antibody diversity. Nature 302: 575–581, 1983
Tsui, L. C., Buchwald, M., Barker, D., Braman, J. C., Knowlton, R., Schumm, J. W., Eiberg, H., Mohr, J., Kennedy, D., Plavsic, N., Zsiga, M., Markiewicz, D., Akots, G., Brown, V., Helms, C., Gravius, T., Parker, C., Rediker, K., and Donis-Keller, H.: Cystic fibrosis locus defined by a genetically linked polymorphic DNA marker. Science 230L: 1054–1057, 1985
Turnbull, I. F., Sriprakash, K. S., and Mathews, J. D.: Human immunoglobulin variable region genes: V κ polymorphisms suggest variation in V-gene repertoires. Immunogenetics 25: 193–199, 1987
Whittingham, S. and Propert, D. N.: Gm and Km allotypes, immune response and disease susceptibility. Monogr. Allergy 19, in press, 1986
Wyman, A. R. and White, R.: A highly polymorphic locus in human DNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 77: 6754–6758, 1980
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Previous address
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Turnbull, I.F., Bernard, O., Sriprakash, K.S. et al. Human immunoglobulin variable region genes: A new VH sequence used to detect polymorphism. Immunogenetics 25, 184–192 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00344033
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00344033