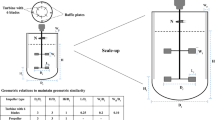
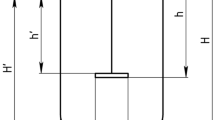
Abstract
The environment in which live microorganisms has a major impact on their productivity. One important factor is the mechanical mixing that is used to promote good heat and mass transfer in bioreactors. In this paper, the performance of reciprocating plate bioreactors is first evaluated for their ability to produce high oxygen transfer coefficients. Pure water and a glycerol water (50∶50 wt%) solution are used for this evaluation. Then, the performance of reciprocating plate bioreactors for the production of an exocellular polysaccharide (pullulan) by yeast Aureobasidium pullulans is analyzed in terms of quantity and quality of the polysaccharide. Results clearly show that a more efficient substrate utilisation is achieved with reciprocating plate bioreactors.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- A m:
-
amplitude
- C :
-
constant in Eq. (1)
- D m:
-
diameter
- H L m:
-
height of liquid in the column
- K L a 1/s:
-
overall oxygen mass transfer coefficient
- P g/l:
-
pullulan concentration
- P G W:
-
gassed power input
- U G m/s:
-
superficial gas velocity
- V L m3 :
-
liquid volume
- α,β:
-
constant in Eq. (1)
- g3:
-
gas holdup
- \(\dot \gamma\) s−1 :
-
shear rate
- η Pa s:
-
viscosity
- φ :
-
fractional free area
References
Doran, P. M.: Design of reactors for plant cells and organs. In: Advances in Biochemical Engineering Biotechnology (Ed.: A. Fiechter), Springer-Verlag 48 (1993) 113–168
Schügerl, K.: Oxygen transfer into highly viscous media. In: Advances in Biochemical Engineering Biotechnology (Ed.: A. Fiechter), Springer-Verlag 19 (1981) 71–174
Schügerl, K.: New bioreactors for aerobic processes. Int. Chem. Eng. 22, 4 (1982) 591–610
Nagata, S.: Mixing principles and applications. John Wiley & Sons, New York, 1975
Skelland, A. H. P.: Mixing and agitation of non-Newtonian fluids. In: Handbook of Fludis in Motion, Chap. 7 (Eds: N. P. Cheremisionoff and R. Gupta), Ann Arbor Science, New York (1993) 179–209
Ulbrecht, J. J.; Carreau, P.: Mixing of viscous non-Newtonian liquids. In: Mixing of Liquids by Mechanical Agitation (Eds.: J. J. Ulbrecht and G. R. Patterson), Gordon and Breach Science Pub., New York 1 (1985) 93–137
Tanguy, P. A.; Lacroix, R.; Bertrand, F.; Choplin, L.; Brito De la Fuente, E.: Finite element analysis of viscous mixing with helical ribbon-screw impeller. AlChE J. 38, 6 (1991) 939–944
Brauer, H.: Growth of fungi and bacteria in the reciprocating jet bioreactor. Bioprocess Engineering 6 (1991) 1–15
Prokop, A.; Rosenberg, M. Z.: Bioreactor for mammalian cell culture. In: Advances in Biochemical Engineering Biotechnology (Ed.: A. Fiechter), Springer-Verlag 39 (1989) 29–71
Bailey, J. E.; Ollis, D. F.: Biochemical Engineering Fundamentals, 2nd Ed., McGraw-Hill Book Company, New York 1986
Merchuk, J. C.: Shear Effects on suspended cells. In Advances in Biochemical Engineering Biotechnology (Ed.: A. Fiechter), Springer-Verlag 44 (1991) 65–95
Toma, M. K.; Ruklisha, M. P.; Vanags, J. J.; Zeltina, M. O.; Leite, M. P.; Galinina, N. I.; Viesturs, V. E.; Tengerdy, R. P.: Inhibition of microbial growth and metabolism by excess turbulence. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 38 (1991) 552–556
Nocentini, M.; Magelli, F.; Pasquali, G.; Fajner, D.: A fluid-dynamic study of a gas-liquid, non-standard vessel stirred by multiple impellers. The Chem. Eng. Journal 37 (1988) 53–56
Tecante, A. C.: Mass transfer in rheologically complex fluids in helical ribbon screw-agitated and aerated tank. Ph.D. Thesis, Univ. Laval, Quebec 1991
Moo-Young, M.; Blanch, H. W.: Design of biochemical reactors — Mass transfer criteria for simple and complex systems. In: Advances in Biochemical Engineering Biotechnology (Ed.: A. Fiechter), Springer-Verlag 19 (1981) 1–69
Veljkovic, V.; Skala, D.: Mass transfer characteristics in a gas-liquid reciprocating plate column. II. Interfacial area. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 66 (1988) 200–210
Aiba, S.; Humphrey, A. E.; Millis, M.: Biochemical Engineering. New York, Academic Press 1973
Jarai, M.: Factors affecting the scale-up of aerated ferementation processes. Int. Chem. Eng. 19, 4 (1979) 710–707
Lounes, M.; Thibault, J.: Mass transfer in a reciprocating plate bioreactor. Chem. Eng. Comm. 127 (1994) 169–189
Godfrey, J. C.; Houlton, D. A.; Marley, S. T.; Marrocchelli, A.; Slater, M. J.: Continuous phase axial mixing in pulsed sieve plate liquid-liquid extraction columns. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 66 (1988) 445–457
Lounes, M.; Thibault, J.: Hydrodynamics and power consumption of a reciprocating plate gas-liquid column. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 71 (1993) 497–506
Baird, M. H. I.; Rama Rao, N. V.: Characteristics of countercurrent reciprocating plate bubble column. II. Axial mixing and mass transfer. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 66 (1988) 222–231
Linek, V.; Vacek, V.; Benes, P.: A critical review and experimental verification of the correct use of the dynamic method for the determination of oxygen transfer in aerated agitated vessels to water, Chem. Eng. J. 34 (1987) 11–34
Nocentini, M.; Fajner, D.; Pasquali, G.; Magelli, F.; Gas-liquid mass transfer and holdup in vessels stirred with multiple Rushton turbines: Wter and water-glycerol solutions. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 32 (1993) 19–26
Perez, J. F.; Sandall, O. C.: Gas absorption by non-Newtonian fluids in agitated vessels. AlChE J. 20, 4 (1974) 770–775
LeDuy, A.; Marsan, A. A.; Coupal, B.: A study of the rheological properties of a non-Newtonian fermentation broth, Biotechnol. Bioeng. 16 (1974) 61–76
Rho, D.; Mulchandani, A.; Luong, J. H. T.; LeDuy, A.: Oxygen requirement in pullulan fermentation. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 28 (1988) 361–366
Lacroix, C.: Effet du pH sur la production en discontinu du pullulane par fermentation du sucrose. Master Thesis, Université Laval, Quebec, Canada 1985
McNeil, B.; Kristiansen, B.: Temperature effects on polysaccharide formation by Aureobasidium pullulans in stirred tanks. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 12 (1990) 521–526
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lounes, M., Audet, J., Thibault, J. et al. Description and evaluation of reciprocating plate bioreactors. Bioprocess Engineering 13, 1–11 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00368758
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00368758