Abstract
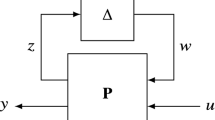
This paper introduces a methodology for simultaneously designing a minimum weight structure and robust active controls to reduce vibrations in an aircraft structure due to external disturbances. The design problem is posed as a mathematical optimization problem with the principal objective function being the weight of the structure. The robust control design is achieved by specifying appropriate constraints on singular values of the closed-loop transfer matrices. The control approach selected for this purpose is based on designing a dynamic compensator that simultaneously minimizes the upper bound of a quadratic performance index H 2 and the H ∞ norm of a disturbance transfer function of a multi-input/multi-output system. The controller can tolerate both real parameter uncertainty in the structural frequencies and damping, and unmodelled dynamics. The design variables are the crosspsectional areas of the structure and the parameters used in the design of a control system. The method was applied to three structures idealized with membrane elements, shear panels and bar elements with embedded actuators and sensors simulating an active flexible aircraft wing.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
BandaS. S.; YehH. H.; HeiseS. A. 1991: Robust Control of Uncertain Systems with Combined H ∞ and LQG Optimization. Int. J. Systems Sc. 22: 85–96
Belegundu, A. D.; Berke, L.; Patniak, S. N. 1993: An Optimization Program Based on Method of Feasible Directions-Theory and User's Guide. NASA Report, June 1993
ChiangR. Y.; SafonovM. G. 1992: H ∞ Synthesis Using a Bilinear Pole Shifting Transform,” J. of Guidance Control and Dynamics. 15: 1111–1117
Dailey, R. L.; Doyle, J. C.; Stein, G. 1990: Lecture Notes for the Workshop on H ∞ and μ Methods for Robust Control. American Control Conference, San Diego CA
GrandhiR. V.; HaqI.; KhotN. S. 1991: Enhanced Robustness in Integrated Structural/Control Systems Design. AIAA Journal. 29: 1168–1173
HaftkaR. T.; MartinovicA.; HallauerJr.W. L. 1985: Enhanced Vibration Controllability by Minor Structural Modifications. AIAA Journal. 23: 1260–1266
JayasuriyaS.; YanivO.; NwokahO. D.; ChaitY. 1992: Benchmark Problem Solution by Quantitative Feedback Theory. J. of Guidance, Control and Dynamics. 15: 1087–1093
KhotN. S. 1988: Structures/Control Optimization to Improve the Dynamic Response of Space Structures. Computational Mechanics. 3: 179–186
Khot, N. S. 1992: Consideration of Robustness in Optimum Structural and Control Design. Presented at the Fourth AIAA/USAF/NASA/OAI Symposium on Multidisciplinary Analysis and Optimization, Cleveland OH
KhotN. S.; VeleyD. E. 1992: Robustness Characteristics of Optimum Structural/Control Design. Journal of Guidance, Control and Dynamics. 15: 81–87
Khot, N. S.; Öz, H. 1993: Structural-Control Optimization with H 2 and H ∞ Constraints. Presented at the 34th AIAA/ASME/ASCE/AHS/ASC Structures, Structural Dynamics, and Materials Conference, La Jolla CA: 1429–1436
KhotN. S.; HeiseS. A. 1994: Consideration of Plant Uncertainties in the Optimum Structural-Control Design. AIAA J., 32: 610–615
LimK. B.; JunkinsJ. L. 1989: Robust Optimization of Structural and Controller Parameters. J. Guidance. 12: 89–96
LustR. V.; SchmitL. A. 1988: Control Augmented Structural Synthesis. AIAA 26: 86–95
Maghami, P. G.; Joshi, S. M.; Armstrong, E. S. 1993: An Optimization-Based Integrated Controls-Structures Design Methodology for Flexible Space Structures. NASA Technical Paper 3283
RaoS. S. 1988: Combined Structural and Control Optimization of Flexible Structures. Engineering Optimization. 13: 1–16
SalamaM.; GarbaJ.; DemesetzL. 1988: Simultaneous Optimization of Controlled Structures. Computational Mechanics. 3: 275–282
Öz, H.; Khot, N. S. 1994: Optimization for Efficient Structure-Control Systems. Journal of Guidance, Control and Dynamics. 17:
WieB.; LiuQ.; ByunK. W. 1992: Robust H ∞ Control Synthesis Method and its Application to Benchmark Problems. J. of Guidance, Control and Dynamics. 15: 1140–1148
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by S. N. Atluri, 12 January 1995
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khot, N.S. Optimum structural design and robust active control using singular value constraints. Computational Mechanics 16, 208–215 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00369782
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00369782