Abstract
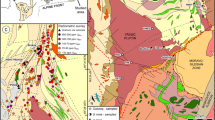
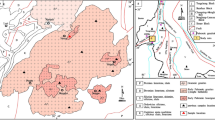
The initial 87Sr/86Sr ratios of twelve basalt flows of Jurassic age on Storm Peak in the Queen Alexandra Range are anomalously high and range from 0.7094–0.7133. The average value is 0.7112±0.0013 (1σ). The concentrations of rubidium and strontium have arithmetic means of 60.6±19.4 ppm and 128.8±11.9 ppm, respectively. The corresponding average Rb/Sr ratio is 0.47 which is also anomalously high for rocks of basaltic composition. In addition, these rocks have high concentrations of SiO2 (56.50%) and K2O (1.29%) and are depleted in Al2O3 (12.92%), MgO (3.44%) and CaO (7.91%) compared to average continental tholeiites. They are nevertheless classified as basalts on the basis of the composition of microphenocrysts.
The initial 87Sr/86Sr ratios and all of the chemical parameters of the flows exhibit systematic stratigraphic variations. These are interpreted as indicating the occurrence of four eruptive cycles. In a typical cycle the initial 87Sr/86Sr ratios of successive flows and their concentrations of SiO2, FeO (total iron), Na2O, K2O, P2O5, Rb and Sr decrease in ascending stratigraphic sequence while the concentrations of TiO2, Al2O3, MgO, CaO and MnO increase upward. The initial 87Sr/86Sr ratios of the flows show a strong positive correlation with the strontium concentration. Similar correlations are observed between the initial 87Sr/86Sr ratios and all of the major oxide components. These relationships are incompatible with the hypothesis that these flows are the products of crystal fractionation of a-34 magma at depth under closed-system conditions. It is suggested that the flows resulted from the hybridization of a normal tholeiite basalt magma by assimilation of varying amounts of granitic rocks in the Precambrian basement which underlies the entire Transantarctic Mountain chain.
Mixtures of two components having different 87Sr/86Sr ratios and differing strontium concentrations are related to each other by hyperbolic mixing equation. Such an equation was fitted by least squares regression of data points to a straight line in coordinates of initial 87Sr/86Sr and the reciprocals of the concentrations of strontium. This equation and plots of strontium versus other oxides were then used to estimate the chemical composition of the parent basalt magma and of the granitic contaminant by substituting reasonable estimates of their 87Sr/86Sr ratios. The chemical composition of the parent basalt (87Sr/86Sr=0.706) is generally compatible with that of average continental tholeiite, but is distinctive by having a low concentration of strontium (117 ppm). The chemical composition of the contaminant (87Sr/86Sr=0.720) is enriched in strontium (173 ppm), SiO2, FeO (total iron) and the alkalies but is depleted in Al2O3, MgO and CaO. The data for strontium indicate that the lava flows on Storm Peak contain between 20 and 40% of this granitic contaminant. The contamination of basalt magma is not a local event but is characteristic of the Jurassic basalt flows and diabase sills throughout the Transantarctic Mountains and in Tasmania.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barrett, P. J.: Stratigraphy and petrology of the mainly fluviatile Permian and Triassic part of the Beacon Supergroup, Beardmore Glacier area. In: Antarctic Geology and Geophysics, R. J. Adie, ed., p. 365–372. Oslo: Universitetsforlaget 1972
Barrett, P. J., Elliot, D. H.: The early Mesozoic volcaniclastic Prebble Formation, Beardmore Glacier area. In: Antarctic Geology and Geophysics, R. J. Adie, ed., p. 403–409. Oslo: Universitetsforlaget 1972
Bowman, J. R.: Use of the isotopic composition of strontium and SiO2 content in determining the origin of Mesozoic basalt from Antarctica. Unpublished MSc. thesis, Dept. Geol., The Ohio State University, Columbus, Ohio, 179 pp. (1971)
Bowman, J. R., Faure, G., Elliot, D. H.: Isotope geochemistry of strontium of the Kirkpatrick Basalt, Storm Peak, Transantarctic Mountains. Abstracts with Programs, Geol. Soc. Am. 5, No. 7, 557 (1973)
Compston, W., McDougall, I., Heier, K. S.: Geochemical comparison of the Mesozoic basaltic rocks of Antarctica, South Africa, South America and Tasmania. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 32, 129–149 (1968)
Elliot, D. H.: Jurassic tholeiitic basalts of the central Transantarctic Mountains, Antarctica. Proceed. Second Columbia River Basalt Symp., E. H. Gilmour, D. Stradling, eds., p. 301–325. Cheney: Eastern Wash. State College Press 1970
Elliot, D. H.: Major oxide chemistry of the Kirkpatrick Basalt, central Transantarctic Mountains. In: Antarctic Geology and Geophysics, R. J. Adie, ed., p. 413–418. Oslo: Universitetsforlaget 1972
Elliot, D. H., Tasch, P.: Lioesteriid conchostracans: A new Jurassic locality and regional and Gondwana correlations. J. Paleont. 41, 1561–1563 (1967)
Faure, G., Hill, R. L.: The age of the Falla Formation (Triassic), Queen Alexandra Range. Ant. J. US. 7, 264–266 (1973)
Faure, G., Hill, R. L., Jones, L. M., Elliot, D. H.: Isotope composition of strontium and silica content of Mesozoic basalt and dolerite from Antarctica. In: Antarctic Geology and Geophysics, R. H. Adie, ed., p. 617–624. Oslo: Univeritetsforlaget 1972
Faure, G., Powell, J. L.: Strontium isotope geology, 188 pp. Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer 1972
Ford, A. B., Boyd, W. W., Jr.: The Dufek Intrusion, a major stratiform gabbroic body in the Pensacola Mountains, Antarctica. XXIII Int. Geol. Congr. 2, 213–228 (1968)
Gunn, B. M.: Differentiation in Ferrar dolerites, Antarctica. New Zealand J. Geol. Geophys. 5, 820–863 (1962)
Gunn, B. M.: K/Rb and K/Ba ratios in Antarctic and New Zealand tholeiites and alkali basalts. J. Geophys. Res. 70, 6241–6247 (1965)
Gunn, B. M.: Modal and element variation in Antarctic tholeiites. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, 30 881–920 (1966)
Gunner, J.: Age and origin of the Nimrod Group and of the Granite Harbour Instrusives, Beardmore Glacier region, Antarctica. Unpubl. Ph. D. Dissert., Dept. Geology, The Ohio State University, 231 pp. (1971)
Gunner, J., Faure, G.: Rb-Sr geochronology of the Nimrod Group, central Transantarctic Mountains. In: Antarctic Geology and Geophysics, R. J. Adie, ed., p. 305–311. Oslo: Universitetsforlaget 1972
Hamilton, W.: Diabase sheets of the Taylor Glacier region, Victoria Land, Antarctica. U.S. Geol. Surv. Profess. Papers 456-B, 1–71 (1965)
Heier, K. S., Compston, W., McDougall, I.: Thorium and uranium concentrations, and the isotopic composition of strontium in the differentiated Tasmanian dolerites. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 29, 643–659 (1965)
Hill, R. L.: Strontium isotope composition of basaltic rocks of the Transantarctic Mountains, Antarctica. Unpublished M.Sc. thesis, The Ohio State University, Columbus, 87 pp. (1969)
Manson, V.: Geochemistry of basaltic rocks; Major elements. In: Basalts, H. H. Hess, ed., vol. 1, p. 213–269. New York: Interscience 1967
McDougall, I.: Differentiation of the Tasmanian dolerites: Red Hill dolerite-granophyre association. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 73, 279–315 (1962)
Prinz, M.: Geochemistry of basaltic rocks: Trace elements. In: Basalts, H. H. Hess, ed., vol. 1, p. 272–323. New York: Interscienee 1967
Pushkar, P., McBirney, A. R., Kudo, A. M.: The isotopic composition of strontium in Central American ignimbrites. Bull. Volcanol. 35, 265–294 (1972)
Schaeffer, B.: A Jurassic fish from Antarctica. Am. Mus. Novitates, No. 2395, 1–17 (1972)
Tatsumoto, M., Hedge, C. E., Engel, A. E. J.: Potassium, rubidium, strontium, thorium, uranium and the ratio strontium—87 to strontium—86 in oceanic tholeiite basalt. Science 150, 886–888 (1965)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Laboratory for Isotope Geology and Geochemistry, Contribution No. 33.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Faure, G., Bowman, J.R., Elliot, D.H. et al. Strontium isotope composition and petrogenesis of the Kirkpatrick basalt, Queen Alexandra Range, Antarctica. Contr. Mineral. and Petrol. 48, 153–169 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00383353
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00383353