Abstract
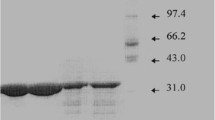
Penicillin amidase is a periplasmic enzyme in Escherichia coli. Conventionally, the periplasmic enzymes are released into the medium by osmotic shock which is tedious involving a number of centrifugation steps. The present communication deals with a simple technique for the release of penicillin amidase by chloroform shock. Experimental findings show that the periplasmic penicillin amidase does not show any variation by the chloroform treatment. This analysis was also extended to the E. coli cells grown at various concentrations of phenylacetic acid, optimal concentration of phenylacetic acid plus glucose and lactic acid.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Poulsen, P.B.: Current applications of immobilized enzymes for manufacturing purposes. Biotechnol. Gen. Eng. Rev. 1 (1984) 121–140
Babu, P.S.R.: Studies on biosynthesis of penicillin amidase in Escherichia coli, stabilization and immobilization of the enzyme associated with whole cells. Ph.D. Thesis, Indian Institute of Technology, Madras 1991, 331–333
Heppel, L.A.: The concept of periplasmic enzymes. In: Rothfield, L.I. (Ed.): Structure and function of biological membranes, 223–247, New York: Academic press 1971
Rodriguez, M.; Guereca, L.; Valle, F.; Quinter, R.; Lopez-Mungula, A.: Penicillin acylase extraction by osmotic shock. Proc. Biochem. 27 (1992) 217–223
Ames, G.F.; Prody, C.; Kutsu, S.: Simple rapid and quantitative release of periplasmic proteins by chloroform J. Bacteriol. 160 (1984) 1181–1183
Babu, P.S.R.; Panda, T.: Studies on improved techniques for immobilizing and stabilizing penicillin amidase associated with E. coli cells. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 13 (1991) 676–682
Mallette, M.F.: Evaluation of growth by physical and chemical means In: Norris, J.R.; Ribbons, D.W. (Eds.): Methods in Microbiology, Vol. I, 521–526. London: Academic press 1969
Babu, P.S.R.; Panda, T.: The role of phenylacetic acids in biosynthesis of penicillin amidase in E. coli. Bioproc. Eng. 6 (1991) 71–74
Laemmll, U.K.: Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227 (1970) 680–685
Morrisey, J.M.: Silver stain for proteins in polyacrylamide gels: A modified procedure for enhanced uniform sensitivity. Anal. Biochem. Biotechnol. 117 (1981) 307–310
Mecke, D.: L-Glutamine determination with glutamine synthatase. In: Bergmeyer, H.U. (Ed.): Methods of Enzymatic analysis, Vol. 4, 1716–1719. New York: Academic press 1974
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jagannadha Rao, K., Panda, T. Release of periplasmic penicillin amidase from Escherichia coli by chloroform shock. Bioprocess Engineering 14, 101–103 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00387964
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00387964