Abstract
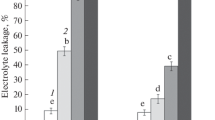
Exposure of spinach plants to high temperature (35° C) increased the heat resistance of the leaves by about 3° C. This hardening process occurred within 4 to 6 h, whereas dehardening at 20°/15° C required 1 to 2 days. At 5° C dehardening did not take place. Hardening and dehardening occurred in both the dark and the light. The hardiness was tested by exposure of the leaves to heat stress and subsequent measurements of chlorophyll fluorescence induction and light-induced absorbance changes at 535 nm on the leaves and of the photosynthetic electron transport in thylakoids isolated after heat treatment. Heat-induced damage to both heat-hardened and non-hardened leaves seemed to consist primarily in a breakdown of the membrane potential of the thylakoids accompanied by partial inactivation of electron transport through photosystem II. The increase in heat resistance was not due to temperature-induced changes in lipid content and fatty acid composition of the thylakoids, and no conspicuous changes in the polypeptide composition of the membranes were observed. Prolonged heat treatment at 35° C up to 3 days significantly decreased the total lipid content and the degree of unsaturation of the fatty acids of membrane lipids without further increase in the thermostability of the leaves. Intact chloroplasts isolated from heat-hardened leaves retained increased heat resistance. When the stroma of the chloroplasts was removed, the thermostability of the thylakoids was decreased and was comparable to the heat resistance of chloroplast membranes obtained from non-hardened control plants. Compartmentation studies demonstrated that the content of soluble sugars within the chloroplasts and the whole leaf tissue decreased as heat hardiness increased. This indicated that in spinach leaves, sugars play no protective role in heat hardiness. The results suggest that changes in the ultrastructure of thylakoids in connection with a stabilizing effect of soluble non-sugar stroma compounds are responsible for acclimatization of the photosynthetic apparatus to high temperature conditions. Changes in the chemical composition of the chloroplast membranes did not appear to play a role in the acclimatization.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DGDG:
-
digalactosyl diglyceride
- MGDG:
-
monogalactosyl diglyceride
- PG:
-
phosphatidyl glycerol
- PGA:
-
3-phosphoglyceric acid
References
Ageeva, O.G., Lutova, M.I.: The influence of heat hardening of peas Pisum sativum L. on photosynthesis and photochemical reactions. Bot. Zh. (Leningrad) 56, 1365–1373 (1971)
Alexandrov, V.Y.: Cells, molecules and temperature. Conformational flexibility of macromolecules and ecological adaptation. In: Ecological Studies, vol. 21. Berlin, Heidelberg, New York: Springer 1977
Appelqvist, L.-A.: Lipids in Cruciferae IX. The effect of growth temperature and stage of development on the fatty acid composition of leaves, siliques and seeds of “zeroerucic-acid” breeding lines of Brassica napus. Physiol. Plant. 25, 493–502 (1971)
Armond, P.A., Schreiber, U., Björkman, O.: Photosynthetic acclimation to temperature in the desert shrub, Larrea divaricata. II. Light-harvesting efficiency and electron transport. Plant Physiol. 61, 411–415 (1978)
Arnon, D.I.: Copper enzymes in isolated chloroplasts. Polyphenoloxidase in Beta vulgaris. Plant Physiol. 24, 1–15 (1949)
Berger, L., Slein, M.W., Colowick, S.P., Cori, C.F.: Isolation of hexokinase from baker's yeast. J. Gen. Physiol. 29, 379–391 (1946)
Bergmeyer, H.U. (ed.): Methoden der enzymatischen Analyse, 3rd Ed. Weinheim/Bergstr.: Verlag Chemie 1974
Berry, J.A., Fork, D.C., Garrison, S.: Mechanistic studies of thermal damage to leaves. Carnegie Inst. Year Book 74, 751–759 (1975)
Björkman, O.: Thermal stability of the photosynthetic apparatus in intact leaves. Carnegie Inst. Year Book 74, 748–751 (1975)
Björkman, O., Boynton, J., Berry, J.: Comparison of the heat stability of photosynthesis, chloroplast membrane reactions, photosynthetic enzymes, and soluble protein in leaves of heat adapted and cold-adapted C4 species. Carnegie Inst. Year Book 75, 400–407 (1976)
Emmett, J.M., Walker, D.A.: Thermal uncoupling in chloroplasts. Inhibition of photophosphorylation without depression of light-induced pH change. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 157, 106–113 (1973)
Feldman, N.L.: The influence of sugars on the cell stability of some higher plants to heating and high hydrostatic pressure. Zitologia 4, 633–643 (1962)
Fork, D.C., Murata, N.: The relationship between changes of the physical phase of membrane lipids and photosynthesis in the thermophilic alga Cyanidium caldarium. In: Photosynthetic organelles Special Issue of Plant Cell Physiol. 427–436 (1977)
Gimmler, H., Kühnl, E.M., Carl, G.: Salinity dependent resistance of Dunaliella parva against extreme temperatures I. Salinity and thermoresistance. Z. Pflanzenphysiol. 90, 133–153 (1978)
Heber, U.: Conformational changes of chloroplasts induced by illumination of leaves in vivo. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 180, 302–319 (1969)
Heber, U., Krause, G.H.: Hydrogen and proton transfer across the chloroplast envelope. In: Proc. IInd Internat. Congress on Photosynthesis Research, vol. II, pp. 1023–1033, Forti, G., Avron, M., Melandri, A., eds. The Hague: W. Junk 1972
Heber, U., Pon, N.G., Heber, M.: Localization of carboxidismutase and triosephosphate dehydrogenases in chloroplasts. Plant Physiol. 38, 355–360 (1963)
Heber, U., Santarius, K.A.: Loss of adenosine triphosphate synthesis caused by freezing and its relationship to frost hardiness problems. Plant Physiol. 29, 712–719 (1964)
Heber, U., Santarius, K.A.: Direct and indirect transfer of ATP and ADP across the chloroplast envelope. Z. Naturforsch. 25b, 718–728 (1970)
Heber, U., Santarius, K.A.: Cell death by cold and heat and resistance to extreme temperatures. Mechanisms of hardening and dehardening. In: Temperature and Life, pp. 232–263, Precht, H., Christophersen, J., Hensel, H., Larcher, W., eds. Berlin, Heidelberg, New York: Springer 1973
Heber, U., Tyankova, L., Santarius, K.A.: Effects of freezing on biological membranes in vivo and in vitro. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 291, 23–37 (1973)
Heber, U., Willenbrink, J.: Sites of synthesis and transport of photosynthetic products within the leaf cell. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 82, 313–324 (1964)
Holton, R.W., Blecker, H.H., Onore, M.: Effect of growth temperature on the fatty acid composition of a blue-green alga. Phytochemistry 3, 595–602 (1964)
Jensen, R.G., Bassham, J.A.: Photosynthesis by isolated chloroplasts. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 56, 1095–1101 (1966)
Junge, W.: Membrane potentials in photosynthesis. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. 28, 503–536 (1977)
Koenig, R., Stegemann, H., Francksen, H., Paul, H.L.: Protein subunits in the potato virus x group. Determination of the molecular weights by polyacrylamide electrophoresis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 207, 184–189 (1970)
Krause, G.H.: Indirekter ATP-Transport zwischen Chloroplasten und Zytoplasma während der Photosynthese. Z. Pflanzenphysiol. 65, 13–23 (1971)
Krause, G.H.: The high-energy state of the thylakoid system as indicated by chlorophyll fluorescence and chloroplast shrinkage. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 292, 715–728 (1973)
Krause, G.H.: Changes in chlorophyll fluorescence in relation to light-dependent cation transfer across thylakoid membranes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 333, 301–313 (1974)
Krause, G.H., Santarius, K.A.: Relative thermostability of the chloroplast envelope. Planta 127, 285–299 (1975)
Levitt, J.: Responses of plants to environmental stresses. New York, London: Academic Press 1972
Lyons, J.M.: Chilling injury in plants. Annu. Rev. Plant. Physiol. 24, 445–466 (1973)
Molotkovsky, Y.G., Zheskova, I.M.: The influence of heating on the morphology and photochemical activity of isolated chloroplasts. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 20, 411–415 (1965)
Müller, M., Santarius, K.A.: Changes in chloroplast membrane lipids during adaptation of barley to extreme salinity. Plant Physiol. 62, 326–329 (1978)
Mukohata, Y., Yagi, T., Higashida, M., Shinozaki, K., Matsuno, A.: Biophysical studies on subcellular particles VI. Photosynthetic activities in isolated spinach chloroplasts after transient warming. Plant Cell Physiol. 14, 111–118 (1973)
Murata, N., Troughton, J.H., Fork, D.C.: Relationships between the transition of the physical phase of membrane lipids and photosynthetic parameters in Anacystis nidulans and lettuce and spinach chloroplasts. Plant Physiol. 56, 508–517 (1975)
Nolan, W.G., Smillie, R.M.: Multi-temperature effects on Hill reaction activity of barley chloroplasts. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 440, 461–475 (1976)
Oku, T., Tomita, G.: Effect of polyethylene glycol on heat inactivation of the Hill reaction. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 44, 958–962 (1971)
Pagageorgiou, G.: Chlorophyll fluorescence: An intrinsic probe of photosynthesis. In: Bioenergetics of Photosynthesis, pp. 319–371, Govindjee, ed. New York: Academic Press 1975
Pearcy, R.W.: Effect of growth temperature on the fatty acid composition of the leaf lipids in Atriplex lentiformis (Torr.) Wats. Plant Physiol. 61, 484–486 (1978)
Pearcy, R.W., Berry, J.A., Fork, D.C.: Effects of growth on the thermal stability of the photosynthetic apparatus of Atriplex lentiformis (Torr.) Wats. Plant Physiol. 59, 873–878 (1977)
Santarius, K.A.: The effect of freezing on thylakoid membranes in the presence of organic acids. Plant Physiol. 48, 156–162 (1971)
Santarius, K.A.: The protective effect of sugars on chloroplast membranes during temperature and water stress and its relationship to frost, desiccation and heat resistance. Planta 113, 105–114 (1973)
Santarius, K.A.: Sites of heat sensitivity in chloroplasts and differential inactivation of cyclic and noncyclic photophosphorylation by heating. J. Thermal Biol. 1, 101–107 (1975)
Santarius, K.A., Heber, U.: Das Verhalten von Hill-Reaktion und Photophosphorylierung isolierter Chloroplasten in Abhängigkeit vom Wassergehalt. II. Wasserentzug über CaCl2. Planta 73, 109–137 (1967)
Santarius, K.A., Milde, H.: Sugar compartmentation in frost-hardy and partially dehardened cabbage leaf cells. Planta 136, 163–166 (1977)
Santarius, K.A., Stocking, C.R.: Intracellular localization of enzymes in leaves and chloroplast membrane permeability to compounds involved in amino acid synthesis. Z. Naturforsch. 24b, 1170–1179 (1969)
Schreiber, U.: Correlation between growth temperature and heat-induced chlorophyll fluorescence changes in Scenedesmus obliquus. Carnegie Inst. Year Book 75, 472–477 (1976)
Schreiber, U., Armond, P.A.: Heat-induced changes of chlorophyll fluorescence in isolated chloroplasts and related heat-damage at the pigment level. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 502, 138–151 (1978)
Schreiber, U., Berry, J.A.: Heat-induced changes of chlorophyll fluorescence in intact leaves correlated with damage of the photosynthetic apparatus. Planta 136, 233–238 (1977)
Shapiro, A.L., Vinuela, E., Maizel, J.V.: Molecular weight estimation of polypeptide chains by electrophoresis in SDS-polyacrylamide gels. Biochim. Biophys. Res. Commun. 28, 815–820 (1967)
Weber, K., Osborn, M.: The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J. Biol. Chem. 244, 4406–4412 (1969)
Yamashita, T., Butler, W.L.: Inhibition of chloroplasts by UV irradiation and heat treatment. Plant Physiol. 43, 2037–2040 (1968)
Yordanov, I.: Influence of high temperature on the formation and activity of the photosynthetic apparatus and spectral characteristics of the pigment-protein complexes of Phaseolus vulgaris plants. Photosynthetica 12, 344–348 (1978)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Dedicated to Professor Wilhelm Simonis, Würzburg, on the occasion of his 70th birthday
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Santarius, K.A., Müller, M. Investigations on heat resistance of spinach leaves. Planta 146, 529–538 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00388828
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00388828