Abstract
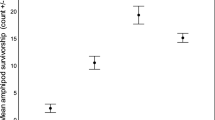
The amphipod species consumed by Lagodon rhomboides represented only a small subset of the amphipod assemblage available at three seagrass habitats in Apalachee Bay, Florida (USA). Predatory preferences were related most closely to the microhabitat of prey species and were unrelated to amphipod abundances. Important prey species were all epifaunal types. Consumption of preferred amphipod species was non-selective at a site with sparse macrophyte cover, but selectivity increased with macrophyte biomass. The amphipod species that were preferentially selected as prey by pinfish correspond with those that have been suggested as being limited by fish predators. It was suggested that mediation of predator behavior by physical structure in seagrass meadows may play an important role in the regulation of species richness and abundances. Species-specific identification of prey is recommended for food-habit studies.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
Adams, S.M.: The ecology of eelgrass, Zostera marina (L.), fish communities. I. Structural analysis. J. exp. mar. Biol. Ecol. 22, 269–291 (1976a)
—: Feeding ecology of eelgrass fish communities. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 105, 514–519 (1976b)
Brooks, J.L.: The effects of prey size selection by lake planktivores. Syst. Zool. 17, 272–291 (1968)
—: Predation, body size and composition of plankton. Science, N.Y. 150, 29–35 (1965)
Caldwell, D.K.: The biology of the pinfish, Lagodon rhomboides (Linnaeus). Bull. Fla St. Mus. biol. Sci. 2, 77–173 (1957)
Carr, W.E.S. and C.A. Adams: Food habits of juvenile marine fishes: evidence of the cleaning habit in the leatherjacket, Oligoplites saurus, and the spottail pinfish, Diplodus holbrooki. Fish. Bull. U.S. 70, 1111–1120 (1972)
——: Food habits of juvenile marine fishes occupying seagrass beds in the estuarine zone near Crystal River, Florida. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 102, 511–540 (1973)
Darnell, R.M.: Food habits of fishes and larger invertebrates of Lake Ponchartrain, Louisiana. Contr. mar. Sci. Univ. Tex. 5, 353–416 (1958)
Emlen, J.M.: The role of time and energy in food preference. Am. Nat. 100, 611–617 (1966)
—: Optimal choice in animals. Am. Nat. 102, 385–390 (1968)
Estabrook, G.F. and A.E. Dunham: Optimal diet as a function of absolute abundance, relative abundance, and relative value of available prey. Am. Nat. 110, 401–413 (1976)
Galbraith, M.G.: Size selective predation on Daphnia by rainbow trout and yellow perch. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 96, 1–10 (1967)
Hansen, D.: Food, growth, migration, reproduction and abundance of pinfish and Atlantic croaker near Pensacola, Florida. Fishery Bull. Fish Wildl. Serv. U.S. 68, 135–146 (1969)
Hoese, H.D. and R.S. Jones: Seasonality of larger animals of a Texas turtle grass community. Contr. mar. Sci. Univ. Tex. 9, 37–47 (1963)
Hughes, R.N.: Optimal diets under the energy maximization premise: the effects of recognition time and learning. Am. Nat. 113, 209–221 (1979)
Ivlev, V.S.: Experimental ecology of the feeding of fishes, 302 pp. New Haven: Yale University Press 1961
Keast, A.: Food specializations and bioenergetic interrelations in the fish faunas of some small Ontario waterways. In: Marine food chains, pp 377–411. Ed. by J.H. Steele Berkeley: University of California Press 1970
Kilby, J.D.: The fishes of two Gulf coastal marsh areas. Tulane Stud. Zool. 2, 175–247 (1955)
Kislalioglu, M. and R.N. Gibson: The feeding relationship of shallow water fishes in a Scottish sea loch. J. Fish Biol. 11, 257–266 (1977)
Levins, R. and R.H. MacArthur: An hypothesis to explain the incidence of monophagy. Ecology 50, 910–911 (1969)
MacArthur, R.H. and E. Pianka: On optimal use of a patchy environment. Am. Nat. 100, 603–609 (1966)
Nelson, W.G.: Organization of a subtidal seagrass amphipod guild: the roles of predation, competition, and physical stress, Ph.D. dissertation, Duke University, Durham 1978
Pulliam, H.R.: On the theory of optimal diet. Am. Nat. 108, 59–74 (1974)
Pyke, G.H., H.R. Pulliam and E.L. Charnov: Optimal foraging: a selective review of theory and tests. Q. Rev. Biol. 52, 137–154 (1977)
Reid, G.K., Jr.: An ecological study of the Gulf of Mexico fishes in the vicinity of Cedar Key, Florida. Bull. mar. Sci. Gulf Caribb. 4, 1–94 (1954)
Ricker, W.E.: The food and food supply of sockeye salmon (Oncorhynchus nerka Walbaum) in Cultus Lake, British Columbia. J. biol. Bd Can. 3, 450–468 (1937)
Robertson, A.I. and R.K. Howard: Diel trophic interactions between vertically-migrating zooplankton and their fish predators in an eelgrass community. Mar. Biol. 48, 207–213 (1978)
Royama, T.: Factors governing the hunting behavior and selection of food by the great tit, Parus major. J. Anim. Ecol. 39, 619–668 (1970)
Schoener, T.W.: Theory of feeding strategies. A. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 2, 369–404 (1971)
Shelbourne, J.E.: A predator-prey size relationship for plaice larvae feeding on Oikopleura. J. mar. biol. Ass. U.K. 42, 243–252 (1962)
Stein, R.A.: Selective predation, optimal foraging and the predator-prey interaction between fish and crayfish. Ecology 58, 1237–1253 (1977)
Stoner, A.W.: The macrobenthos of a seagrass meadow in Apalachee Bay, Florida, and the feeding ecology of Lagodon rhomboides (Pisces: Sparidae), 175 pp. Ph.D. dissertation, Florida State University, Tallahassee 1979
Stoner, A.W.: The role of seagrass biomass in the organization of benthic macrofaunal assemblages. Bull. mar. Sci. (In press)
Stoner, A.W.: Abundances, reproductive seasonality, and habitat preferences of amphipod Crustacea in seagrass meadows of Apalachee Bay, Florida (In preparation)
Vince, S., I. Valiela, N. Backus and J.M. Teal: Predation by the salt marsh killifish Fundulus heteroclitus (L.) in relation to prey size and habitat structure: consequences for prey distribution and abundance. J. exp. mar. Biol. Ecol. 23, 255–266 (1976)
Ware, D.M.: Predation by rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri): the influence of hunger, prey density and prey size. J. Fish. Res. Bd Can. 29, 1193–1201 (1972)
—: Risk of epibenthic prey to predation by rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri). J. Fish. Res. Bd Can. 30, 787–797 (1973)
Werner, E.E.: The fish size, prey size, and handling time relation in several sunfishes and some implications. J. Fish. Res. Bd Can. 31, 1531–1536 (1974)
—: Optimum foraging and the size selection of prey by bluegill sunfish (Lepomis macrochirus). Ecology 55, 1042–1052 (1974)
Wong, B. and F.J. Ward: Size selection of Daphnia pulicaria by young yellow perch (Perca flavescens) fry in West Blue Lake, Manitoba. J. Fish. Res. Bd Can. 29, 1761–1764 (1972)
Young, D.K., M.A. Buzas and M.W. Young: Species densities of macrobenthos associated with seagrasses: an experimental study of predation. J. mar. Res. 34, 577–592 (1976)
—: Community structure of the macrobenthos associated with seagrasses of the Indian River estuary, Floria. In: Ecology of marine benthos, pp 359–381. Ed. by B.C. Coull. Columbia: University of South Carolina Press 1977
——: Regulation of species densities of seagrass-associated macrobenthos: evidence from field experiments in the Indian River estuary, Florida. J. mar. Res. 36, 569–593 (1978)
Zaret, T.M. and W.C. Kerfoot: Fish predation on Bosmina longirostris: body-size selection versus visibility selection. Ecology 56, 232–237 (1975)
—: Competition in tropical stream fishes: support for the competitive exclusion principle. Ecology 52, 336–342 (1971)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by J.M. Pérès, Marseille
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stoner, A.W. Species-specific predation on amphipod crustacea by the pinfish Lagodon rhomboides: Mediation by macrophyte standing crop. Mar. Biol. 55, 201–207 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00396819
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00396819