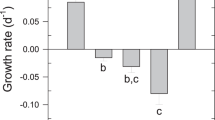
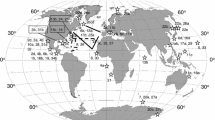
Abstract
A dual-isotope method was developed to measure grazing rates and food preferences of individual species of heterotrophic dinoflagellates from natural populations, collected from the Slope, Gulf Stream, and Sargasso Sea and from a transect from Iceland to New England, in 1983. The isotope method measures the grazing rates of microzooplankton which cannot be separated in natural populations on the basis of size. Tritiated-thymidine and 14C-bicarbonate were used to label natural heterotrophic and autotrophic food, respectively. Nine oceanic dinoflagellate species in the genera Protoperidinium, Podolampas, and Diplopsalis fed on both heterotrophic and autotrophic food particles with clearance rates of 0.4 to 8.0 μl cell-1 h-1, based on 3H incorporation, and 0.0 to 28.3 μl cell-1 h-1, based on 14C incorporation. Two dinoflagellate species, Protoperidinium ovatum and Podolampas palmipes, fed only on 3H-labelled food particles. Several species of dinoflagellates fed on bacteria (<1 μm) which had been prelabelled with 3H-thymidine. The clearance rates of heterotrophic dinoflagellates and ciliates were similar and within the range of tintinnid ciliate clearance rates reported in the literature. As heterotrophic dinoflagellates and ciliates can have comparable abundances in oceanic waters, we conclude that heterotrophic dinoflagellates may have an equally important impact as microheterotrophic grazers of phytoplankton and bacteria in oceanic waters.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
Anraku, M.: Influence of the Cape Cod Canal on the hydrography and on the copepods in Buzzards Bay and Cape Cod Bay, Massachusetts. II. Respiration and feeding. Limnol. Oceanogr. 9, 195–206 (1964)
Barker, H. A.: The culture and physiology of the marine dinoflagellates. Arch. Mikrobiol. 6, 157–181 (1935)
Beers, J. R., F. M. H. Reid and G. L. Stewart: Seasonal abundance of the microplankton population in the North Pacific Central Gyre. Deep-Sea Res. 29, 227–245 (1982)
Biecheler, B.: Recherches sur les Peridiniens. Bull. biol. Fr. Belg. 36 (Suppl.), 1–149 (1952)
Blackbourn, D. J.: The feeding biology of tintinnid Protozoa and some other inshore microzooplankton, 224 pp. Ph.D. thesis, University of British Columbia 1974
Bursa, A. S.: The annual oceanographic cycle at Igloolik in the Canadian Arctic. II. The phytoplankton. J. Fish. Res. Bd Can. 18, 563–615 (1961)
Cachon, P. J. et M. Cachon: Le système stomatopharyngien de Kofoidinium Pavillard. Comparisons avec celui divers Peridiniens libres et parasites. Protistologica 10, 217–222 (1974)
Capriulo, G. M.: Feeding of field collected tintinnid micro-zooplankton on natural food. Mar. Biol. 71, 73–86 (1982)
Capriulo, G. M. and E. J. Carpenter: Grazing by the 35 to 202 μm micro-zooplankton in Long Island Sound. Mar. Biol. 56, 319–326 (1980)
Capriulo, G. M. and D. V. Ninivaggi: A comparison of the feeding activities of field collected tintinnids and copepods fed identical natural particle assemblages. Annls Inst. océanogr., Paris (N.S.) 58 (Suppl.), 325–334 (1982)
Conover, R. J.: Oceanography of Long Island Sound, 1952–1954. VI. Biology of Acartia tonsa and A. clausii. Bull. Bingham oceanogr. Coll. 15, 156–233 (1956)
Conover, R. J.: Feeding interactions of the pelagic zone. Rapp. P. v. Réun. Cons. perm. int. Explor. Mer 173, 66–76 (1978)
Cuhel, R. and J. Waterbury: Biochemical composition and shortterm nutrient incorporation patterns in a unicellular marine cyanobacterium, Synechococcus (WH 7803). Limnol. Oceanogr. 29, 370–373 (1984)
Daro, M. H.: A simplified 14C method for grazing measurements on natural plankton populations. Helgoländer wiss. Meeresunters. 31, 241–248 (1978)
Davis, P. G.: Bacterivorous flagellates in marine waters, 164 pp. Ph.D. thesis, University of Rhode Island 1982
Davis, P. G. and J. McN. Sieburth: Differentiation of phototrophic and heterotrophic nanoplankton populations in marine waters by epifluorescence microscopy. Annls Inst. océanogr., Paris (N.S.) 58 (Suppl.), 249–260 (1982)
Davis, P. G. and J. McN. Sieburth: Estuarine and oceanic microflagellate predation of actively growing bacteria: estimation by frequency of dividing-divided bacteria. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 19, 237–246 (1984)
Deevey, G. B. and A. L. Brooks: Copepods of the Sargasso Sea off Bermuda: species composition, and vertical and seasonal distribution between the surface and 2 000 m. Bull. mar. Sci. 27, 256–291 (1977)
Dodge, J. D. and R. M. Crawford: The morphology and fine structure of Ceratium hirundinella (Dinophyceae). J. Phycol. 6, 137–149 (1970)
Dodge, J. D. and B. Hart-Jones: The vertical and seasonal distribution of dinoflagellates in the North Sea. Botanica mar. 17, 113–117 (1974)
Donaghay, P. L. and L. F. Small: Food selection capabilities of the estuarine copepod Acartia clausi. Mar. Biol. 52, 137–146 (1979)
Droop, M. R.: Phagotrophy in Oxyrrhis marina. Nature, Lond. 172, 250–252 (1953)
Elbrächter, M.: On the taxonomy of unarmored dinophytes (Dinophyta) from the Northwest African upwelling region. “Meteor” ForschErgebn. (Ser. D) 30, 1–22 (1979)
Fenchel, T.: Suspension feeding in ciliated Protozoa: functional response and particle size selection. Microb. Ecol. 6, 1–11 (1980a)
Fenchel, T.: Relation between particle size selection and clearance in suspension feeding ciliates. Limnol. Oceanogr. 25, 735–740 (1980b)
Fenchel, T.: Ecology of heterotrophic microflagellates. II. Bioenergetics and growth. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 8, 225–231 (1982)
Frey, L. C. and E. F. Stoermer: Dinoflagellate phagotrophy in the upper Great Lakes. Trans. Am. microsc. Soc. 99, 439–444 (1980)
Frost, B. W.: Effects of size and concentration of food particles on the feeding behavior of the marine planktonic copepod Calanus pacificus. Limnol. Oceanogr. 17, 805–815 (1972)
Fuhrman, J. A.: Influence of method on the apparent size distribution of bacterioplankton cells: epifluorescence microscopy compared to scanning electron microscopy. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 5, 103–106 (1982)
Fuhrman, J. A. and F. Azam: Thymidine incorporation as a measure of heterotrophic bacterioplankton production in marine surface waters: evaluation and field results. Mar. Biol. 66, 109–120 (1982)
Gaines, G. and F. J. R. Taylor: Extracellular digestion in marine dinoflagellates. J. Plankton Res. 6, 1057–1061 (1984)
Hargis, J. R.: Comparison of techniques for measuring zooplankton filtration rates. Limnol. Oceanogr. 22, 942–944 (1977)
Heinbokel, J. F.: Studies on the functional role of tintinnids in the Southern California Bight. I. Grazing and growth rates in laboratory cultures. Mar. Biol. 47, 177–189 (1978)
Hollibaugh, J. T., J. A. Fuhrman and F. Azam: Radioactive labelling of natural assemblages of bacterioplankton for use in trophic studies. Limnol. Oceanogr. 25, 172–181 (1980)
Kimor, B.: The role of phagotrophic dinoflagellates in marine ecosystems. Kieler Meeresforsch. (Sondbd) 5, 164–173 (1981)
Kofoid, C. A. and O. Swezy: The free-living unarmoured dinoflagellata. Mem. Univ. Calif. 5, 1–538 (1921)
Lee, R. E.: Saprophytic and phagocytic isolates of the colorless heterotrophic dinoflagellate Gyrodinium lebouriae Herdman. J. mar. biol. Ass. U.K. 57, 303–315 (1977)
Lefèvre, J. and J. R. Grall: On the relationship of Noctiluca swarming off the western coast of Brittany with hydrological features and plankton characteristics of the environment. J. exp. mar. Biol. Ecol. 4, 287–306 (1970)
Lessard, E. J.: Oceanic heterotrophic dinoflagellates: distribution, abundance, and role as microzooplankton, 146 pp. Ph.D. dissertation, University of Rhode Island 1984
Marlowe, C. J. and C. B. Miller: Patterns of vertical distribution and migration of zooplankton at Ocean Station “P”. Limnol. Oceanogr. 20, 824–844 (1975)
Morey-Gaines, G. and M. Elbrächter: Heterotrophic nutrition. In: The biology of dinoflagellates. Ed. by F. J. R. Taylor. Oxford: Blackwell Scientific. (In press)
Morey-Gaines, G. and R. Ruse: Encystment and reproduction of the predatory dinoflagellate, Polykrikos kofoidi Chatton (Gymnodiniales). Phycologia 19, 230–236 (1980)
Mullin, M.: Some factors affecting the feeding of marine copepods of the genera Calanus. Limnol. Oceanogr. 8, 239–250 (1963)
Norris, D. R.: Possible phagotrophic feeding in Ceratium lunula Schimper. Limnol. Oceanogr. 14, 448–449 (1969)
Paasche, E. and S. Kristiansen: Ammonium regeneration by microzooplankton in the Oslofjord. Mar. Biol. 69, 55–63 (1982)
Rivkin, R. and H. Seliger: Liquid scintillation counting for 14C uptake of single cells isolated from natural samples. Limnol. Oceanogr. 26, 780–784 (1981)
Roman, M. R. and P. A. Rublee: A method to determine in situ zooplankton grazing rates on natural particle assemblages. Mar. Biol. 65, 303–309 (1981)
Runge, J. A.: Effect of hunger and season on the feeding behaviour of Calanus pacificus. Limnol. Oceanogr. 25, 134–145 (1980)
Schütt, F.: Die Peridineen der Plankton-Expedition. I. Teil, Studien über die Zellen der Peridineen, Ergebn. Atlant. Ozean Planktonexped. Humboldt-Stift. 4, 1–170 (1895)
Smetacek, V.: The annual cycle of protozooplankton in the Kiel Bight. Mar. Biol. 63, 1–11 (1981)
Spero, H. J.: Phagotrophy in Gymnodinium fungiforme (Pyrrophya): the peduncle as an organelle of ingestion. J. Phycol. 18, 356–360 (1982)
Spero, H. J. and M. D. Montescue: Phagotrophic feeding and its importance to the life cycle of the holozoic dinoflagellate, Gymnodinium fungiforme. J. Phycol. 17, 43–51 (1981)
Spittler, P.: Feeding experiments with tintinnids. Oikos (Suppl.) 15, 128–132 (1973)
Stoecker, D., R. R. L. Guillard and R. M. Kavee: Selective predation by Favella ehrenbergii (Tintinnia) on and among dinoflagellates. Biol. Bull. mar. biol. Lab., Woods Hole 160, 136–145 (1981)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by J. M. Lawrence, Tampa
Partially supported by a grant from the National Science Foundation, OCE-81-17744
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lessard, E.J., Swift, E. Species-specific grazing rates of heterotrophic dinoflagellates in oceanic waters, measured with a dual-label radioisotope technique. Mar. Biol. 87, 289–296 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00397808
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00397808