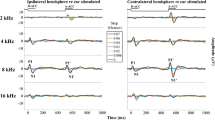
Summary
The first part of this paper is concerned with the acoustically evoked responses for a frequency of 1 kHz, obtained in eleven, normal hearing, adult subjects. Amplitudes as well as latencies were different in the adapted and non-adapted states of the auditory system. The second part deals with the effects of sedative agents and psychotropic drugs (Atosil, Valium and Mandrax) upon ERA latencies. In a group of four normal hearing adults, latencies were first assessed prior to medication. In contrast to amplitudes, latencies were independent of the time the measurement was being taken, even for SPLs near the threshold of hearing. Latencies were then reassessed at various times after medication. In that case, they were not only prolonged, but also showed wider variations, especially near the threshold of hearing. It was only upon Atosil-sedation that results were satisfactory within the first 2 h after medication.
Zusammenfassung
Im ersten Teil werden die akustischen Reizantworten und Latenzen von 11 normalhörenden Erwachsenen bei einer Testfrequenz von I kHz gezeigt: wie die Amplituden weisen auch die Latenzen Unterschiede für den adaptierten und nicht-adaptierten Zustand des akustischen Sinnesorgans auf. Der zweite Teil zeigt den Einfluß von Atosil, Valium und Mandrax auf die ERA-Latenzen in Abhängigkeit von der Zeit nach der Medikation. 4 normalhörende Erwachsene mit und zur Kontrolle ohne Sedierung werden untersucht. Die Latenzen beim nichtsedierten Erwachsenen sind im Gegensatz zu den Amplituden unabhängig vom Meß-zeitpunkt, d. h. die Latenzen sind zeitlich konstant, sogar in Nähe der Hörschwelle. Die Latenzen unter Sedierung sind im allgemeinen nicht nur verlängert, sondern schwanken auch so stark in Hörschwellennähe, daß ohne ihre Berücksichtigung genaue Schwellenbestimmungen und verwertbare Ergebnisse nicht immer möglich sind, die allerdings mit Atosil-Sedierung etwa innerhalb der ersten 2 Std nach Medikation erreicht werden können.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Keidel, W. D.: Anatomic und Elektrophysiologie der zentralen akustischen Bahnen. In: HNO-Heilk., ein kurzgefaßtes Handbuch in 3 Bänden, Bd. III/3, S. 2013 bis 2098. Stuttgart: Thieme 1966.
Kollar, A.: Die Beziehungen zwischen Lautstärke, Latenzzeit und Amplitude in der EEG-Audiometrie. Mschr. Ohrenheilk. 105, 101–106 (1971).
Moore, E. J., Rose, D. E.: Variability of latency and amplitude of acoustically evoked responses to pure tones of moderate to high intensity. Int. Audiol. 8, 172–181 (1969).
Morgan, A., Charachon, R., Gérin, P.: Electro-encephalographic audiometry for young children. Arch. klin. exp. Ohr.-, Nas- u. Kehlk.-Heilk. 198, 144–150 (1971).
Müller, G., Stange, G.: The input-output function of the slow auditory evoked potential in contralateral, ipsilateral and vertex recordings. Arch. klin. exp. Ohr.-, Nas.- u. Kehlk.-Heilk. 198, 116–126 (1971).
Pirsig, W.: Die Verwendbarkeit von Dehydrobenzperidol als Sedativum bei audiometrischen Untersuchungen. HNO (Berl.) 19, 89–93 (1971).
Spoor, A., F. Timmer, D. W. Odenthal: The evoked auditory response to intensity modulated and frequency modulated tones and tonebursts. Int. Audiol. 8, 410–415 (1969).
Spreng, M.: Über die Messung der Frequenzgruppe und der Integrationszeit des menschlichen Gehörs durch vom Schall abhängigen Hirnspannungen Tangs der Kopfhaut. Dissertation, T.H. Stuttgart 1967.
Spreng, M.: Detection of influence of latency variability upon the averaged evoked responses. Int. Audiol. 9, 304–308 (1970).
Stange, G.: The relation between functional parameters of subjective and objective audiometry. Arch. klin. exp. Ohr.-, Nas.- u. Kehlk.-Heilk. 198, 85–101 (1971).
—The effect of sedative agents and psychotropic drugs on the electrical response audiometry (ERA). Arch. klin. exp. Ohr.-, Nas.- u. Kehlk.-Heilk. 201 (1972) (in preparation).
Wilkinson, R. T., Morlock, H. C.: Auditory evoked responses and reaction time. Electroenceph. clin. Neurophysiol. 23, 50–56 (1967).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
With financial assistance of “SFB 70” (Sonderforschungsbereich für Hirnforschung und Sinnesphysiologie der Deutschen Forschungsgemeinschaft) und “Stiftung Volkswagenwerk”.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karnahl, T., Benning, C.D. Effect of sedation upon evoked response audiometry: Amplitude and latency vs sound pressure level. Arch. klin. exp. Ohr.-, Nas.- u. Kehlk.Heilk. 201, 181–188 (1972). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00398001
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00398001