Abstract
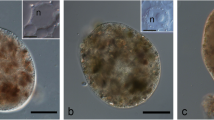
Morphological characteristics of two Pedomicrobium-like budding bacteria are described. A structured surface layer was regularly observed on strain 868. Ruthenium red- and Alcian blue-staining polymers were found on both strains.
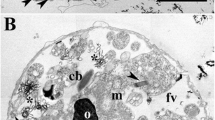
When either strain was grown in the presence of iron or manganese, the corresponding oxides accumulated on their surfaces. In thin sections iron oxides appeared as fine threads, arrays of particles or dense coatings, depending on the source of iron. Manganese oxides appeared as branching filaments or convoluted ribbons. Both metal oxides stained with ruthenium red. Extraction of the oxides followed by ruthenium red staining revealed that polyanionic polymers previously deposited on the cells were associated with the metals.
Treatment of cultures with glutaraldehyde, HgCl2, or heat, inhibited manganese but not iron deposition, suggesting that iron oxides accumulated by passive, non-biological processes. Manganese oxides apparently accumulated under control of a biological manganese-oxidizing factor. Incomplete inhibition of manganese deposition observed in cell suspensions suggested that, if the oxidizing factor was an enzyme, it was unusually stable.
Based on these results, possible mechanisms of iron and manganese deposition in association with extracellular polymers are suggested.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander, M.: Microbial ecology. New York: John Wiley and Sons, Inc. 1970
Altmann, H. J.: Bestimmung von Wasser-gelöstem Sauerstoff mit Leucoberbelinblau. I. Eine schnelle Winklermethode. Z. Anal. Chem. 262, 97–99 (1972)
Aristovskaya, T. V.: Accumulation of iron in the breakdown of organo-mineral humus complexes by micro-organisms. Dokl. Akad. Nauk. SSSR 136, 111–114 (1961) (Engl. transl.)
Bayer, M. E.: Areas of adhesion between wall and membrane of Escherichia coli. J. Gen. Microbiol. 53, 395–404 (1968)
Bayer, M. E., Thurow, H.: Polysaccharide capsule of Escherichia coli. Microscope study of its size, structure and sites of synthesis. J. Bacteriol. 130, 911–936 (1977)
Costerton, J. W., Geesey, G. G., Cheng, K. J.: How bacteria stick. Sci. Amer. 238, 86–95 (1978)
Cullimore, D. R., McCann, A. E.: The identification cultivation and control of iron bacteria in ground water. In: Aquatic microbiology (F. A. Skinner and J. M. Shewan, eds.). Soc. Appl. Bacteriol. Sympos. No. 6, pp. 219–261 London: Academic Press, Inc. 1977
Fletcher, M., Floodgate, G. D.: The adhesion of bacteria to solid surfaces. In: Microbial ultrastructure (R. Fuller and D. W. Lovelock, eds.), pp. 101–107 London: Academic Press 1976
Gebers, R., Hirsch, P.: Isolation and investigation of Pedomicrobium spp., heavy-metal depositing bacteria from soil habitats. In: Environmental biogeochemistry and geomicrobiology. Vol. 3. Methods, metals and assessment (W. E. Krumbein, ed.), pp. 901–922. Ann Arbor, Michigan: Ann Arbor Science, Inc. 1978
Ghiorse, W. C., Hirsch, P.: Iron and manganese deposition by budding bacteria. In: Environmental biogeochemistry and geomicrobiology. Vol. 3. Methods, metals and assessment (W. E. Krumbein, ed.), pp. 897–909. Ann Arbor, Michigan: Ann Arbor Science, Inc. 1978
Hayat, M. A.: Positive staining for electron microscopy. New York: Van Nostrand Reinhold Co. 1975
Hirsch, P.: Biology of budding bacteria. IV. Epicellular deposition of iron by aquatic budding bacteria. Arch. Mikrobiol. 60, 201–216 (1968)
Johnson, H. H., Stokes, J. C.: Manganese oxidation by Sphaerotilus discophorus. J. Bacteriol. 91, 1543–1547 (1966)
Khak-Mun, T.: Iron- and manganese-oxidizing microorganisms in soils of south Sakhalin. Microbiology 36, 337–344 (1967) (Engl. transl.)
MacRae, I. C., Edwards, J. F.: Adsorption of colloidal iron by bacteria. Appl. Microbiol. 24, 819–823 (1972)
Mulder, E. C.: Le cycle biologique tellurique du fer et du manganèse. Rev. Écol. Biol. Sol. 9, 321–348 (1972)
Rytér, A., Kellenberger, E., Birch-Andersen, A., Maløe, O.: Étude au microscope électronique de plasmas contenant de l'acide deoxyribonucléique. I. Les nucléotides des bactéries en croissance active. Z. Naturforsch. 13b, 597–605 (1958)
Schweisfurth, R.: Manganoxydierende Mikroorganismen in Trinkwasserversorgungsanlagen. Gaswasserfach — Wasser/Abwasser 113, 562–572 (1972)
Shah, R. G., Bhat, J. V.: Occurrence of Hyphomicrobium and Caulobacter spp. in bore-well water. Curr. Sci., 37, 571–573 (1968)
Spurr, A. R.: A low viscosity epoxy resin embedding medium for electron microscopy. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 26, 31–43 (1969)
Staley, J.-T.: Prosthecomicrobium and Ancalomicrobium. New prosthecate freshwater bacteria. J. Bacteriol. 95, 1921–1942 (1968)
Stumm, W., Morgan, J. J.: Aquatic chemistry. New York: Wiley-Interscience 1970
Tyler, P. A., Marshall, K. C.: Microbial oxidation of manganese in hydro-electric pipelines. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek. J. Microbiol. Serol. 33, 171–183 (1967)
van Ert, M., Staley, J. T.: Gas-vacuolated strains of Microcyclus aquaticus. J. Bacteriol. 108, 236–240 (1971)
van Veen, W. L., Mulder, E. G., Deinema, M. H.: The Sphaerotilus-Leptothrix group of bacteria. Microbiol. Rev. 42, 329–356 (1978)
Venable, J. H., Coggeshall, R.: A simplified lead citrate stain for use in electron microscopy. J. Cell Biol. 25, 407–408 (1965)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ghiorse, W.C., Hirsch, P. An ultrastructural study of iron and manganese deposition associated with extracellular polymers of pedomicrobium-like budding bacteria. Arch. Microbiol. 123, 213–226 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00406653
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00406653