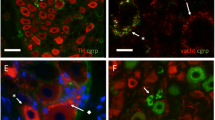
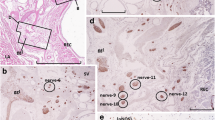
Abstract
Autonomic innervation of the prostate gland supplies the acini, and non-vascular and vascular smooth muscle. The activity of each of these tissues is enhanced by sympathetic outflow, whereas the role of the parasympathetic nervous system in this organ is unclear. In the present study, a range of methods was applied in rats to determine the location of autonomic neurons supplying this gland, the immunohistochemical properties of these neurons, the spinal connections made with the postganglionic pathways and the distribution of various axon types within the gland. Injection of the retrograde tracer, FluoroGold, into the ventral gland visualised neurons within the major pelvic ganglion and sympathetic chain. Fluorescence immunohistochemical studies on the labelled pelvic neurons showed that most were noradrenergic (also containing neuropeptide Y, NPY), the others being non-noradrenergic and containing either vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) or NPY. Sympathetic dyelabelled neurons were identified by the presence of varicose nerve terminals stained for synaptophysin on their somata following lesion of sacral inputs. Parasympathetic innervation of dye-labelled neurons was identified by continued innervation after hypogastric nerve lesion. Most noradrenergic prostate-projecting neurons were sympathetic, as were many of the non-noradrenergic VIP neurons. Parasympathetic prostate-projecting neurons were largely non-noradrenergic and contained either VIP or NPY. All substances found in retrogradely labelled somata were located in axons within the prostate gland but had slightly different patterns of distribution. The studies have shown that there are a significant number of non-noradrenergic sympathetic prostate-projecting neurons, which contain VIP.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arver S, Sjöstrand NO (1982) Functions of adrenergic and cholinergic nerves in canine effectors of seminal emission. Acta Physiol Scand 115:67–77
Baron R, Jänig W (1991) Afferent and sympathetic neurons projecting into the lumbar visceral nerves of the male rat. J Comp Neurol 314:429–436
Baumgarten HG, Falck B, Holstein AF, Owman C, Owman T (1968) Adrenergic innervation of the human testis, epididymis, ductus deferens and prostate: a fluorescence microscopic and fluorimetric study. Z Zellforsch 90:81–95
Bruschini H, Schmidt RA, Tanagho EA (1978) Neurologic control of prostatic secretion in the dog. Invest Urol 15:288–290
Cohen ML, Drey K (1989) Contractile responses in bladder body, bladder neck and prostate from rat, guinea pig and cat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 248:1063–1068
Dail WG (1993) Autonomic innervation of male genitalia. In: Maggi CA (ed) Nervous control of the urogenital system. Harwood, Chur, Switzerland, pp 69–102
Dail WG, Manzanares K, Moll MA, Minorsky N (1985) The hypogastric nerve innervates a population of penile neurons in the pelvic plexus. Neuroscience 16:1041–1046
Dail WG, Minorsky N, Moll MA, Manzanares K (1986) The hypogastric nerve pathway to penile erectile tissue: histochemical evidence supporting a vasodilator role. J Auton Nerv Syst 15:341–349
Dail WG, Trujillo D, Rosa D de la, Walton G (1989) Autonomic innervation of reproductive organs: analysis of the neurons whose axons project in the main penile nerve in the pelvic plexus of the rat. Anat Rec 224:94–101
Ding YQ, Wang YQ, Qi BZ, Li JS (1993) The major pelvic ganglion is the main source of nitric oxide-containing nerve fibres in penile erectile tissue of the rat. Neurosci Letts 164:187–189
Eckhard C (1896) Untersuchungen über die Erection des Penis beim Hunde. Beitr Anat Physiol 3:123–150
Farnsworth WE, Lawrence MH (1965) Regulation of prostate secretion in the rat. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 119:373–376
Farrell JI, Lyman Y (1937) A study of the secretory nerves of, and the action of certain drugs on the prostate gland. Am J Physiol 118:64–70
Gosling JA (1983) Autonomic innervation of the prostate. In: Hinman F (ed) Benign prostatic hypertrophy. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg, pp 349–360
Jänig W, McLachlan EM (1987) Organization of the lumbar spinal outflow to distal colon and pelvic organs. Physiol Rev 67:1332–1404
Jahn B, Schiebler W, Ouitmet C, Greengard P (1985) A 38 000-dalton membrane protein (P38) present in synaptic vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82:4137–4141
Kaleczyc J, Majewski M, Calka J, Lakomy M (1993) Adrenergic innervation of the epididymis, vas deferens, accessory genital glands and urethra in the boar. Folia Histochem Cytobiol 31:117–123
Keast JR (1991) Patterns of co-existence of peptides and differences of nerve fibre types associated with noradrenergic and non-noradrenergic (putative cholinergic) neurons in the major pelvic ganglion of the male rat. Cell Tissue Res 266:405–415
Keast JR (1992a) Location and peptide content of pelvic neurons supplying the muscle and lamina propria of the rat vas deferens. J Auton Nerv Syst 40:1–12
Keast JR (1992b) A possible neural source of nitric oxide in the rat penis. Neurosci Letts 143:69–73
Keast JR (1995) Visualization and immunohistochemical characterization of sympathetic and parasympathetic neurons in the male rat major pelvic ganglion. Neuroscience 66:655–662
Keast JR, Groat WC de (1989) Immunohistochemical characterization of pelvic neurons which project to the bladder, colon, or penis in rats. J Comp Neurol 288:387–400
Keast JR, Booth AM, Groat WC de (1989) Distribution of neurons in the major pelvic ganglion of the rat which supply the bladder, colon or penis. Cell Tissue Res 256:105–112
Kolbeck SC, Steers WD (1993) Origin of neurons supplying the vas deferens of the rat. J Urol 149:918–921
Lange W, Unger J (1990) Peptidergic innervation within the prostate gland and seminal vesicle. Urol Res 18:337–340
Langworthy OR (1965) Innervation of the pelvic organs of the rat. Invest Urol 2:491–511
Luckensmeyer GB, Keast JR (1994) Projections from the prevertebral and major pelvic ganglia to the ileum and large intestine of the rat. J Auton Nerv Syst 49:247–259
Martínez-Piñeiro L, Dahiya R, Nunes LL, Tanagho EA, Schmidt RA (1993) Pelvic plexus denervation in rats causes morphologic and functional changes of the prostate. J Urol 150:215–218
Owman C, Sjöstrand C (1965) Short adrenergic neurons and catecholamine-containing cells in vas deferens and accessory male genital glands of different mammals. Z Zellforsch 66:300–320
Potter EK (1988) Neuropeptide Y as an autonomic neurotransmitter. Pharmacol Ther 37:251–273
Properzi G, Cordeschi G, Francavilla S (1992) Postnatal development and distribution of peptide-containing nerves in the genital system of the male rat. Histochemistry 97:61–68
Purinton PT, Fletcher TF, Bradley WE (1973) Gross and light microscopic features of the pelvic plexus in the rat. Anat Rec 175:697–706
Shima M (1973) Studies on the innervation of the prostate. Jpn J Urol 64:539–554
Shimizu T, Egan-Konopka LM, Ohta Y, Dun NJ (1982) Localization of postganglionic neurons to the male genital organ in the major pelvic ganglion of the rat. Tohoku J Exp Med 136:351–352
Sjöstrand NO (1965) The adrenergic innervation of the vas deferens and the accessory male genital glands. Acta Physiol Scand [Suppl] 65:1–82
Smith ER (1968) The stimulation of canine prostate secretion by parasympathomimetic agents. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 164:312–316
Smith ER (1975) The canine prostate and its secretion. In: Thomas JA, Singhal RL (eds) Molecular mechanisms of gonadal hormone action. University Park, Baltimore, pp 167–204
Tabatabai M, Booth AM, Groat WC de (1986) Morphological and electrophysiological properties of pelvic ganglion cells in the rat. Brain Res 382:61–70
Vaalasti A, Hervonen A (1979) Innervation of the ventral prostate of the rat. Am J Anat 154:231–244
Vaalasti A, Hervonen A (1980a) Autonomic innervation of the human prostate. Invest Urol 17:293–297
Vaalasti A, Hervonen A (1980b) Nerve endings in the human prostate. Am J Anat 157:41–47
Vera PL, Nadelhaft I (1992) Afferent and sympathetic innervation of the dome and the base of the urinary bladder of the female rat. Brain Res 29:651–658
Wang J-M, McKenna KE, McVary KT, Lee C (1991) Requirement of innervation for maintenance of structural and functional integrity in the rat prostate. Biol Reprod 44:1171–1176
Watanabe H, Shima M, Kojima M, Ohe H (1988) Dynamic study on nervous control of prostatic contraction and fluid excretion in the dog. J Urol 140:1567–1570
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kepper, M., Keast, J. Immunohistochemical properties and spinal connections of pelvic autonomic neurons that innervate the rat prostate gland. Cell Tissue Res. 281, 533–542 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00417871
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00417871