Abstract
The predictability of maximum oxygen uptake (\(\dot V_{O_2 }\)max) was tested on 78 male subjects taken from four different age-groups (ages: 9 to 10, 13 to 14, 17 to 18, 20 to 52). \(\dot V_{O_2 }\)max and W170 were measured during the same experiment, both with stepwise respectively continuously increasing loads on the bicycle ergometer. Oxygen uptake and heart rate were measured at submaximal and maximal workloads.
We examined the predictability of \(\dot V_{O_2 }\)max by following the methods described by åstrand and Ryhming (1954), Margaria et al. (1965), and Rutenfranz (1971). We also examined the W170-test which gives a direct information on submaximal criteria and requires no further extrapolation and the equation given by Müller (1961 a, b), which allows to compare results of the LPI-method for assessing the endurance limit at submaximal work with the method of I. åstrand (1960) to determine the endurance limit as percentage of maximal aerobic power.
When we used the methods mentioned above we observed a considerable underestimation of the measured \(\dot V_{O_2 }\)max. The results obtained by Müller's equation, however, deviated unsystematically from measured \(\dot V_{O_2 }\)max.
By means of age-correcting factors according to I. åstrand (1960) respectively to von Döbeln et al. (1967) it is possible to adjust the prediction of \(\dot V_{O_2 }\)max without inquiring into the sources of the observed deviations.
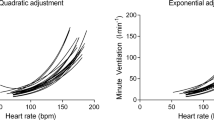
By means of special factors to correct extrapolation we were, however, able to avoid an error that is typical of all methods which determine \(\dot V_{O_2 }\)max based on the linear relationship between pulse frequency and oxygen uptake during work by extrapolation to maximal heart rate. This error is due to an underestimation of \(\dot V_{O_2 }\)max as there is no linear relationship between heart rate and O2-consumption in the upper performance section. In this section O2-consumption increases more with increasing workload than heart rate.
In order to compare the above mentioned procedures we transformed the original formulas and adapted them to the conditions we met in our own experiments.
The coefficients of validity with the exception of those calculated according to Müller show that there do not exist any striking differences.
The cardio-vascular performance capacity was estimated equally well by means of W170.
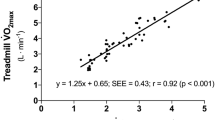
In predicting \(\dot V_{O_2 }\)max the standard deviation was 7 to 10,5%. The mean error of a single determination was 4 to 7%, whether \(\dot V_{O_2 }\)max was measured or predicted.
Zusammenfassung
An 78 mÄnnlichen Personen im Alter von 9 bis 25 Jahren, aufgeteilt in vier Altersgruppen (9 bis 10, 13 bis 14, 17 bis 18, 20 bis 25 Jahre), wurden Bestimmungen der W170 und maximale Arbeitsversuche sowohl bei stufenweise als auch bei kontinuierlich ansteigender Leistung durchgeführt. Gemessen wurden die O2-Aufnahme und die Pulsfrequenz bei submaximalen und maximalen Belastungen.
Die Verfahren zur indirekten Bestimmung der maximalen O2-Aufnahme (\(\dot V_{O_2 }\)max) nach åstrand u. Ryhming (1954), Margaria et al. (1965) und Rutenfranz (1971) sowie die Bestimmung der W170 wurden eingehend untersucht. Au\erdem wurde die Umrechnungsformel mit in die Betrachtung einbezogen, welche von Müller (1961 a, b) angegeben wurde, um die Bestimmung der DauerleistungsfÄhigkeit mit Hilfe des LPI mit der Bestimmung der DauerleistungsfÄhigkeit nach I. åstrand (1960) in ProzentsÄtzen der maximalen O2-Aufnahme zu vergleichen.
Bei der Anwendung der indirekten Verfahren ergab sich mit Ausnahme des Verfahrens nach Müller, für das unsystematische Abweichungen resultierten, eine deutliche UnterschÄtzung der gemessenen \(\dot V_{O_2 }\)max.
Durch „Alterskorrekturfaktoren“ in Anlehnung an I. åstrand (1960) bzw. an von Döbeln et al. (1967) konnte die Berechnung der \(\dot V_{O_2 }\)max optimiert werden. Diese Faktoren stellen jedoch nur eine pauschale Korrektur für verschiedene Fehlerquellen dar.
Demgegenüber lÄ\t sich durch Extrapolationskorrektur ein systematischer Fehler gezielt ausschalten, der in allen Verfahren zu finden ist, die von der linearen Beziehung zwischen Arbeitspuls und O2-Mehrverbrauch ausgehend über die Extrapolation auf die maximale Herzfrequenz die \(\dot V_{O_2 }\)max ermitteln.
Um die genannten Verfahren besser miteinander vergleichen zu können, nahmen wir eine Umformung der Gleichungen vor und pa\ten sie den vorgefundenen VerhÄltnissen an. Die ValiditÄtskoeffizienten zeigten, da\ mit Ausnahme der Umrechnungsformel nach Müller alle diese Verfahren bezüglich der Vorhersagegenauigkeit der \(\dot V_{O_2 }\)max gleichwertig sind. Die SchÄtzung der kardiovasculÄren LeistungsfÄhigkeit mit Hilfe der W170, die keine Korrekturen erfordert, erwies sich als nicht weniger verlÄ\lich.
Der Standardfehler bei der Vorhersage der \(\dot V_{O_2 }\)max betrug 7 bis 10,5%. Der mittlere Fehler einer Einzelbestimmung lag für die direkte und die indirekte Bestimmung der \(\dot V_{O_2 }\)max zwischen 4 und 7%.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Allen, J. G.: Aerobic capacity and physiological fitness of Australian men. Ergonomics 9, 485 (1966)
Anderson, T. W., Shephard, R. J.: Physical training and exercise diffusing capacity. Int. Z. angew. Physiol. 25, 198 (1968)
åstrand, I.: Aerobic work capacity in men and women with special reference to age. Acta physiol. scand. 49, Suppl. 169 (1960)
åstrand, P.-O.: Kommentar zu Wyndham, C. H.: Submaximal tests for estimating maximum oxygen intake. Canad. med. Ass. J. 96, 736 (1967)
åstrand, P.-O., Rodahl K.: Textbook of work physiology. New York: McGraw-Hill 1970
åstrand, P.-O., Ryhming, I: A nomogram for calculation of aerobic capacity (physical fitness) from pulse rate during submaximal work. J. appl. Physiol. 7, 218 (1954)
Bates, D. V.: Kommentar zu Holmgren, A., Cardiorespiratory determinants of cardiovascular fitness. Canad. med. Ass. J. 96, 697 (1967)
Cumming, G. R., Friesen, W.: Bicycle ergometer measurement of maximal oxygen uptake in children. Canad. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 45, 937 (1967)
Davies, C. T. M.: Maximum oxygen uptake: prediction from cardiac frequency during submaximal exercise. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 189, 77 P. (1967)
Davies, C. T. M.: Limitations to the prediction of maximum oxygen intake from cardiac frequency measurements. J. appl. Physiol. 24, 700 (1968)
Döbeln, W. von, åstrand, I., Bergström, A.: An analysis of age and other factors related to maximal oxygen uptake. J. appl. Physiol. 22, 934 (1967)
Ehrenstein, W., Müller-Limmroth, W.: über die ZuverlÄssigkeit des Leistungspulsindex (LPI) nach E. A. Müller als Kriterium der körperlichen LeistungsfÄhigkeit. Int. Z. angew. Physiol. 26, 189 (1968)
Eichhorn, J.: Die maximale aerobe LeistungsfÄhigkeit untrainierter junger MÄnner und ihre Sauerstoffmangel-Belastungstoleranz. Deutsche Luft- und Raumfahrt. Forsch.ber. 67-39 DVL-Bericht. Porz-Wahn: Zentr. Wiss. Berichtswesen der DVL 1967
Eichhorn, J., Brüner, H., Klein, K. E., Wegmann, H. M.: FehleinschÄtzungen der maximalen O2-Aufnahme bei ihrer Bestimmung mit indirekten Methoden. Int. Z. angew. Physiol. 24, 275 (1967)
Ekblom, B., åstrand, P.-O., Saltin, S., Stenberg, J., Wallström, B.: Effect of training on circulatory response to exercise. J. appl. Physiol. 24, 518 (1968)
Glassford, R. G., Baycroft, G. H. Y., Sedgwick, A. W., Macnab, R. B. J.: Comparison of maximal oxygen uptake values determined by predicted and actual methods. J. appl. Physiol. 20, 509 (1965)
Hermansen, L., Lange-Andersen, K.: Aerobic capacity in young Norwegian men and women. J. appl. Physiol. 20, 425 (1965)
Hermansen, L., Oseid, S.: Direct and indirect estimation of maximal oxygen uptake in pre-pubertal boys. Acta paediat. scand. Suppl. 217, 18 (1971)
Hettinger, T., Birkhead, N. C., Horvath, J. M., Issekutz, B., Rodahl, K.: Assessment of physical work capacity. J. appl. Physiol. 16, 153 (1961)
Holmgren, A., åstrand, P.-O.: DL and the dimensions and functional capacities of the O2-transport system in humans. J. appl. Physiol. 21, 1463 (1966)
Hubač, M., Nová, M., Hubačová, L.: Die zulÄssige Belastung Jugendlicher bei körperlicher Arbeit. Ärztl. Jugendkunde 58, 204 (1967)
Karlsson, J., åstrand, P.-O., Ekblom, B.: Training of the oxygen system in man. J. appl. Physiol. 22, 1061 (1967)
Knuttgen, H. G.: Aerobic capacity of adolescents. J. appl. Physiol. 22, 655 (1967)
Larsson, Y. A., Persson, B., Sterky, G., Thorén, C.: Functional adaptation to rigorous training and prolonged exercise in diabetic and non-diabetic adolescent boys. J. appl. Physiol. 19, 629 (1964)
Lindemann, H.: Vergleichende Untersuchungen zur indirekten Bestimmung der maximalen Sauerstoffaufnahme. Inaug.-Diss., Gie\en 1972
Margaria, R., Aghemo, P., Rovelli, E.: Indirect determination of maximal O2 consumption in man. J. appl. Physiol. 20, 1070 (1965)
Maritz, J. S., Morrison, J. F., Peter, J., Strydom, N. B., Wyndham, C. H.: A practical method of estimating an individuals maximal oxygen intake. Ergonomics 4, 97 (1961)
Mocellin, R.: Bestimmungsmöglichkeiten der W170 bei Heranwachsenden. 2. Fortbildungstagung für SportÄrzte und SportpÄdagogen in Hessen (Gie\en, 28.–30. November 1969), S. 63, Der Hessische Sozialminister, Ed. Bechtold: Wiesbaden (o. J.)
Mocellin, R., Rutenfranz, J.: Methodische Untersuchungen zur Bestimmung der körperlichen LeistungsfÄhigkeit (W170) im Kindesalter. Z. Kinderheilk. 108, 61 (1970)
Mocellin, R., Rutenfranz, J., Singer, R.: Zur Frage von Normwerten der körperlichen LeistungsfÄhigkeit im Kindes -und Jugendalter. Z. Kinderheilk. 110, 140 (1971)
Müller, E. A.: Die Messung der körperlichen LeistungsfÄhigkeit mit einem einzigen Prüfverfahren. Forsch.ber. Nr. 1031 des Landes NRW. Köln-Opladen: Westdeutscher Verlag 1961a
Müller, E. A.: Die Ärztliche Beurteilung der körperlichen DauerleistungsfÄhigkeit im Beruf. Dtsch. med. Wschr. 86, 2272 (1961b)
Müller, E. A.: Der Leistungs-Puls-Index als Ma\ der körperlichen LeistungsfÄhigkeit im Beruf. Methoden des Max-Planck-Institutes für Arbeitsphysiologie Dortmund (Manuskript, 1962)
Müller, E. A., Olech, K.-H.: Eich-Kontrolle für das permanent-magnetisch gebremste Fahrradergometer nach E. A. Müller. Arbeitswissenschaft 3, 176 (1964)
Ouellet, Y., Poh, S. C., Becklake, M. R.: Circulatory factors limiting maximal aerobic exercise capacity. J. appl. Physiol. 27, 874 (1969)
Pirnay, F., Deroanne, R., Petit, J. M., Bottin, R., Dujardin, J.: Signification de la consommation d'oxygène correspondant à la fréquence cardiaque de 170/min. Int. Z. angew. Physiol. 29, 1 (1970)
Pirnay, F., Petit, J. M., Bottin, R., Deroanne, R., Juchmes, J., Belge, G.: Comparaison de deux méthodes de mesure de la consommation maximum d'oxygène. Int. Z. angew. Physiol. 23, 203 (1966)
Prampero, P. E. di, Cerretelli, P.: Maximal muscular power (aerobic and anaerobic) in African natives. Ergonomics 12, 51 (1969)
Rowell, L. B., Taylor, H. L., Wang, Y.: Limitations to prediction of maximal oxygen intake. J. appl. Physiol. 19, 919 (1964)
Rutenfranz, J.: Exercise tests in children and adolescents. In: Andersen, KL. Shephard, R. J., Denolin, H., Varnauskas, E., Masironi, R., Eds., Fundamentals of exercise testing. Wld. Hlth Org. 1971, 105
Rutenfranz, J., Hettinger, Th.: Untersuchungen über die AbhÄngigkeit der körperlichen LeistungsfÄhigkeit von Lebensalter, Geschlecht und körperlicher Entwicklung. Z. Kinderheilk. 83, 65 (1959)
Saltin, B., åstrand, P.-O.: Maximal oxygen intake in athletes. J. appl. Physiol. 23, 353 (1967)
Sbresny, W.: Untersuchungen zur Frage einer Bestimmung der körperlichen LeistungsfÄhigkeit mit Hilfe der W170 in verschiedenen Alters-, Leistungs- und Berufsgruppen. In Vorbereitung
Shephard, R. J.: The prediction of maximum oxygen intake from post-exercise pulse readings. Int. Z. angew. Physiol. 34, 31 (1967)
Shephard, R. J.: Endurance fitness. Toronto: University of Toronto Press 1969
Stegemann, J.: Leistungsphysiologie. Stuttgart: Thieme 1971
TerÄslinna, P., Ismail, A. H., Mac Leod, D. F.: Nomogram by åstrand and Ryhming as a predictor of maximum oxygen intake. J. appl. Physiol. 21, 513 (1966)
Vries, H. A. de, Klafs, C. E.: Prediction of maximal oxygen intake from submaximal tests. J. Sport Med. Phys. Fitness (Torino) 5, 207 (1965)
Wyndham, C. H., Cooke, H. M.: An examination of the methods of physical classification of Bantu labourers for mine work. S. Afr. med. J. 40, 275 (1966)
Wyndham, C. H., Strydom, N. B., Maritz, J. S., Morrison, J. E., Peter, J., Potgieter Z.U.: Maximum oxygen intake and maximum heart rate during strenuous work. J. appl. Physiol. 14, 927 (1959)
Wyndham, C. H., Strydom, N. B., Morrison, J. F., Peter, J., Maritz, J. S., Ward J.S.: Influence of a stable diet and regular work on body weight and capacity for exercise of African mine recruits. Ergonomics 5, 435 (1962)
Wyndham, C. H., Strydom, N. B., Morrison, J. F., Williams, C. G., Bredell, G. A. G., Peter, J., Cooke, H. M., Joffe, A.: The influence of gross body weight on oxygen consumption and physical working capacity of manual labourers. Ergonomics 6, 278 (1963)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lindemann, H., Rutenfranz, J., Mocellin, R. et al. Methodische Untersuchung zur indirekten Bestimmung der maximalen O2-Aufnahme. Europ. J. Appl. Physiol. 32, 25–53 (1973). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00422427
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00422427
Key words
- \(\dot V_{O_2 }\)max Measured
- \(\dot V_{O_2 }\)max Predicted
- Maximal Heart Rate
- W170
- Age Correcting Factor
- Factors to Correct Extrapolation.