Abstract
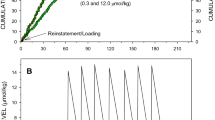
Cocaine, methylphenidate and secobarbital were compared on a drug maintained progressive-ratio procedure in baboon subjects. Trials, scheduled throughout the day, occurred at a minimum interval of 3 hrs after completion of the preceding trial. A ratio response requirement on the “initiate” lever was required during each trial which terminated in a single intravenous infusion of drug. A drug was introduced on the progressive-ratio procedure with a low ratio requirement in order to obtain a baseline performance of a high stable frequency of trial completion. The ratio requirement was systematically increased every 7 days until the “breaking point” when the rate of completing trials fell below a criterion level. Within-subject comparison revealed that cocaine produced higher breaking points than methylphenidate at the same absolute dose, 0.4 mg/kg. At the range of doses studied, manipulation of doses of methylphenidate (0.1–0.8 mg/kg) and cocaine (0.4–1.6 mg/kg) had little effect on breaking point. In contrast, increasing doses of secobarbital (6.0 and 12.0 mg/kg) produce higher breaking points within the same subjects.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Deneau, G. A., Yanagita, T., Seevers, M. H.: Self-administration of psychoactive substances by the monkey. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 16, 30 (1969)
Findley, J. D., Robinson, W. W., Gilliam, W.: A restraint system for chronic study of the baboon. J. exp. Anal. Behav. 15, 69 (1971)
Findley, J. D., Robinson, W. W., Peregrino, L.: Addiction to secobarbital and chlordiazepoxide in the Rhesus monkey by means of a self-infusion preference procedure. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 26, 93 (1972)
Hodos, W.: Progressive ratio as a measure of reward strength. Science 134, 943 (1961)
Hodos, W.: Motivational properties of long durations of rewarding brain stimulation. J. comp. physiol. Psychol. 59, 219 (1965)
Hodos, W., Kalman, J.: Effects of increment size and reinforcer volume on progressive-ratio performance. J. exp. Anal. Behav. 6, 387 (1963)
Keesey, R. E., Goldstein, M. D.: Use of progressive fixed-ratio procedures in the assessment of intracranial reinforcement. J. exp. Anal. Behav. 11, 293 (1968)
Yanagita, T.: An experimental framework for evaluation of dependence liability of various types of drugs in monkeys. Bull. Narcot. 25, 57 (1973)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Griffiths, R.R., Findley, J.D., Brady, J.V. et al. Comparison of progressive-ratio performance maintained by cocaine, methylphenidate and secobarbital. Psychopharmacologia 43, 81–83 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00437619
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00437619