Abstract
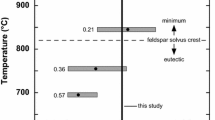
The sequence of crystallization in a biotite-granite from the Bohus batholith of Norway and Sweden, deduced from its texture, was magnetite, plagioclase, microcline, quartz, and finally biotite. Several sequences of crystallization were determined experimentally at 2 kb in the presence of varying only for H2O contents below 1.2% by weight. The rock was fused to a homogeneous glass, and each experiment included samples of finely crushed rock and glass. The samples were reacted in Ag-Pd capsules with measured H2O content in coldseal pressure vessels with NNO buffer. With excess H2O (more than 6.5%) the crystallization interval extends from 865° C to 705° C. In the H2O-deficient region, the solidus temperature remains unchanged as long as a trace of vapor is present, but the liquidus temperature increases as H2O content decreases; with 0.8 % H2O the liquidus temperature is 1125° C, the crystallization interval is 420° C, and a separate aqueous vapor phase is evolved only a few degrees above the solidus at 705° C. The biotite phase boundary increases slightly from 845° C with excess H2O to 875° C with 1% H2O, and it intersects the steep phase boundaries for quartz and feldspars; the sequence of crystallization changes at each intersection point. Similar diagrams at various pressures for related rock compositions involving muscovite, biotite and amphibole will provide grids useful in defining limits for the water content of granitic and dioritic magmas. Applications are considered for the Bohus batholith, other granitic rocks, and rhyolites. The Bohus magma could have been formed by crustal anatexis as a mobile assemblage of H2O-undersaturated liquid and residual crystals with initial total H2O content less than 1.2%, or it could have been derived by fractionation of a more basic parent with low H2O content from mantle or subduction zone, but it could not have been derived from a primary andesite generated from mantle peridotite. We consider it unlikely that the H2O content of large granitic magma bodies exceeds about 1.5% H2O; these magmas are H2O-undersaturated through most of their histories. Uprise and progressive crystallization of magma bodies produces H2O-saturation around margins and in the upper regions of magma chambers. H2O-saturated rhyolitic and dacitic magmas with phenocrysts can be tapped from the upper parts of the magma chambers.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, A.T.: The before-eruption water content of some high-alumina magmas. Bull. Volcan. 37, 530–552 (1973)
Aramaki, S.: Hydrothermal determination of temperature and water pressure of the magma of Aira Caldera, Japan. Am. Mineralogist 56, 1760–1768 (1971)
Barker, F., Wones, D.R., Sharp, W.N., Desborough, G.A.: The Pikes Peak batholith, Colorado Front Range, and a model for the origin of the gabbro-anorthosite-syenite-potassic granite suite. Precambrian Research 2, 97–160 (1975)
Brown, G.C., Fyfe, W.S.: The production of granitic melts during ultrametamorphism. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 28, 310–318 (1970)
Buddington, A.F., Lindsley, D.H.: Iron-titanium oxide minerals and synthetic equivalents. J. Petrol. 5, 310–357 (1964)
Burnham, C.W.: Hydrothermal fluids at the magmatic stage. In: Geochemistry of hydrothermal ore deposits. (H.L. Barnes ed.), p. 34–76. New York: Holt, Rinehart and Winston 1967
Burnham, C.W., Davis, N.F.: The role of H2O in silicate melts: I, P-V-T relations in the system NaAlSi3O8-H2O to 10 kilobars and 1000° C. Am. J. Sci. 270, 54–79 (1971)
Burnham, C.W., Davis, N.F.: The role of H2O in silicate melts: II. Thermodynamic and phase relations in the system NaAlSi3O8-H2O to 10 kilobars, 700 to 1100° C. Am. J. Sci. 274, 902–940 (1974)
Carmichael, I.S.E., Turner, F.J., Verhoogen, J.: Igneous petrology. 739 p. New York: McGraw-Hill 1974
Eggler, D.H.: Water-saturated and undersaturated melting relations in a Paricutin andesite and an estimate of water content in the natural magma. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 34, 261–271 (1972)
Eggler, D.H., Burnham, C.W.: Crystallization and fractionation trends in the system andesite-H2O-CO2-O2 at pressures to 10 kb. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 84, 2517–2532 (1973)
Eugster, H.P.: Heterogeneous reactions involving oxidation and reduction at high pressures and temperatures. J. Chem. Physics 26, 1160 (1957)
Ewart, A., Green, D.C., Carmichael, I.S.E., Brown, F.H.: Voluminous low temperature rhyolitic magmas in New Zealand. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 33, 128–144 (1971)
Friedman, I., Lipman, P.W., Obradovich, J.D., Gleason, J.D.: Meteoric water in magmas. Science 184, 1069–1072 (1974)
Fyfe, W.S.: The generation of batholiths. Tectonophysics 17, 273–283 (1973)
Green, T.H.: Crystallization of calc-alkaline andesite under controlled high-pressure conditions. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 34, 150–166 (1972)
Holloway, J.R.: The system pargasite-H2O-CO2: a model for melting of a hydrous mineral with a mixed-volatile fluid — I. Experimental results to 8 kbar. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 37, 651–666 (1973)
Huang, W., Wyllie, P.J.: Melting relations of muscovite-granite to 35 kbar as a model for fusion of metamorphosed subducted oceanic sediments. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 42, 1–14 (1973)
Huang, W.L., Wyllie, P.J.: Melting relations of muscovite with quartz and sanidine in the K2O-Al2O3-SiO2-H2O system to 30 kilobars and an outline of paragonite melting relations. Am. J. Sci. 274, 378–395 (1974)
Huang, W.L., Robertson, J.K., Wyllie, P.J.: Melting relations of muscovite to 30 kilobars in the system KAlSi3O8-Al2O3-H2O. Am. J. Sci. 273, 415–427 (1973)
Jahns, R.H., Burnham, C.W.: Experimental studies of pegmatite genesis: I. A model for the derivation and crystallization of granitic pegmatities. Econ. Geol. 64, 843–864 (1969)
Lipman, P.W., Friedman, I.: Interaction of meteoric water with magma: an oxygen-isotope study of ash-flow sheets from Southern Nevada. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 86, 695–702 (1975)
Luth, W.C.: The systems NaAlSi3O8-SiO2 and KAlSi3O8-SiO2 to 20 kb and the relationship between H2O content, \(P_{H_2 O} \), and P total in granitic magmas. Am. J. Sci. 267-A, 325–341 (1969)
Marsh, B.D., Carmichael, I.S.E.: Benioff zone magmatism. J. Geophys. Res. 79, 1196–1206 (1974)
Merrill, R.B., Wyllie, P.J.: Hydrous upper mantle: water-excess and water-deficient melting relations of hornblende eclogite (abstract). Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 53, 552 (1972)
Merrill, R.B., Wyllie, P.J.: Kaersutite and kaersutite eclogite from Kakanui, New Zealand — Water-excess and water-deficient melting at 30 kilobars. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 86, 555–570 (1975)
Millhollen, G.L., Wyllie, P.J.: Relationship of brown hornblende mylonite to spinel peridotite mylonite at St. Paul's rocks. Abstracts with programs. Geol. Soc. Am., Denver 2, 625 (1970)
Millhollen, G., Wyllie, P.J.: Melting of brown-hornblende mylonite from St. Paul's rocks under water-saturated and water-deficient conditions to 30 kilobars. J. Geol. 82, 589–606 (1974)
Moore, J.G., Lockwood, J.P.: Origin of comb layering and orbicular structure, Sierra Nevada batholith, California. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull 84, 1–20 (1973)
Mueller, R.F.: Stability of biotite: a discussion. Am. Mineralogist 57, 300–316 (1972)
Mysen, B.O., Kushiro, I., Nicholls, I.A., Ringwood, A.E.: A possible mantle origin for andesitic magmas. Discussion of a paper by Nicholls and Ringwood. 1. Opening discussion, 2. Reply to opening discussion, 3. Comments on the reply of Nicholls and Ringwood, and 4. Final reply. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 21, 221–229 (1974)
Nicholls, I.A.: Liquids in equilibrium with peridotitic mineral assemblages at high water pressures. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 45, 289–316 (1974)
Piwinskii, A.J.: The attainment of equilibrium in hydrothermal experiments with “granitic rocks”. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2, 161–162 (1967)
Piwinskii, A.J.: Experimental studies of igneous rock series: Central Sierra Nevada batholith, California. J. Geol. 76, 548–570 (1968)
Piwinskii, A.J.: Experimental studies of granitoids from the Central and Southern Coast Ranges, California. Tschermaks Mineral. Petrogr. Mitt. 20, 107–130 (1973a)
Piwinskii, A.J.: Experimental studies of igneous rock series, central Sierra Nevada batholith, California: Part II. Neues Jahrb. Mineral. Monatsh. H. 5, 193–215 (1973b)
Piwinskii, A.J.: Experimentelle Untersuchungen an granitischen Gesteinen von den südlichen Coast-Ranges, Transverse-Ranges und der Mojave-Wüste, Kalifornien. Fortschr. Mineral. 51, 240–255 (1974)
Piwinskii, A.J.: Experimental studies of granitoid rocks near the San Andreas fault zone in the Coast and Transverse ranges and Mojave Desert, California. Tectonophysics 25, 217–231 (1975)
Piwinskii, A.J., Martin, R.F.: An experimental study of equilibrium with granitic rocks at 10 kb. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 29, 1–10 (1970)
Piwinskii, A.J., Wyllie, P.J.: Experimental studies of igneous rock series: a zoned pluton in the Wallowa batholith, Oregon. J. Geol. 76, 205–234 (1968)
Piwinskii, A.J., Wyllie, P.J.: Experimental studies of igneous rock series: “Felsic Body Suite” from the Needle Point pluton, Wallowa batholith, Oregon. J. Geol. 78, 52–76 (1970)
Presnall, D.C., Bateman, P.C.: Fusion relations in the system NaAlSi3O8-CaAl2Si2O8-KAlSi3O8-SiO2-H2O and generation of granite magmas in the Sierra Nevada batholith. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 84, 3181–3202 (1973)
Putnam, G.W., Alfors, J.T.: Depth of intrusion and age of the Rocky Hill stock, Tulare County, California. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 76, 357–364 (1965)
Robertson, J.K., Wyllie, P.J.: Experimental studies on rocks from the Deboullie stock, northern Maine, including melting relations in the water-deficient environment. J. Geol. 79, 549–571 (1971a)
Robertson, J.K., Wyllie, P.J.: Rock-water systems, with special reference to the water-deficient region. Am. J. Sci. 271, 252–277 (1971b)
Shimada, M.: Melting of albite at high pressures in the presence of water. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 6, 447–450 (1969)
Steiner, J.C., Jahns, R.H., Luth, C.W.: Crystallization of alkali feldspar and quartz in the haplogranite system NaAlSi3O8-KAlSi3O8-SiO2-H2O at 4 kb. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 86, 83–98 (1975)
Stern, C.R., Wyllie, P.J.: Water-saturated and undersaturated melting relations of a granite to 35 kilobars. Earth Planet.Sci. Lett. 18, 163–167 (1973)
Stern, C.R., Huang, W.L., Wyllie, P.J.: Basalt-andesite-rhyolite-H2O: crystallization intervals with excess H2O and H2O-undersaturated liquidus surfaces to 35 kilobars, with implications for magma genesis. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. manuscript submitted
Stormer, J.C., Carmichael, I.S.E.: The Kudo-Weill plagioclase geothermometer and porphyritic acid glasses. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 28, 306–309 (1970)
Streckeisen, A.L.: Classification and nomenclature of igneous rocks. Neues Jahrb. Mineral. Abhandl. 107, 144–240 (1967)
Taylor, H.P.: The application of oxygen and hydrogen isotope studies to problems of hydrothermal alteration and ore deposition. Econ. Geol. 69, 843–883 (1974)
Tuttle, O.F., Bowen, N.L.: Origin of granite in the light of experimental studies in the system NaAlSi3O8-KAlSi3O8-SiO2-H2O. Geol. Soc. Am. Mem. 74, 153 p. (1958)
Upton, B.G.J.: The alkaline igneous complex of Kungnat Fjeld, South Greenland. Medd. Groenland 123, No. 4, 1–145 (1960)
Whitney, J.A.: The effect of reduced H2O fugacity on the buffering of oxygen fugacity in hydrothermal experiments. Am. Mineralogist 57, 1902–1908 (1974)
Whitney, J.A.: The effects of pressure, temperature and XH2O on phase assemblages in four synthetic rock compositions. J. Geol. 83, 1–31 (1975a)
Whitney, J.A.: Vapor generation in a quartz monzonite magma: a synthetic model with application to porphyry copper deposits. Econ. Geol. 70, 346–358 (1975b)
Wones, D.R.: Stability of biotite: a reply. Am. Mineralogist 57, 316–317 (1972)
Wones, D.R., Eugster, H.P.: Stability of biotite: experiment, theory, and application. Am. Mineralogist 50, 1228–1272 (1965)
Wood, B.J., Carmichael, I.S.E.: P total \(P_{H_2 O} \) and the occurrence of cummingtonite in volcanic rocks. Contrib. Mineral. Petrol. 40, 149–158 (1973)
Wyllie, P.J., Tuttle, O.F.: Experimental investigation of silicate systems containing two volatile components. Part I, Geometrical considerations. Am. J. Sci. 258, 498–517 (1960)
Yoder, H.S.: Calkalkalic andesites: experimental data bearing on the origin of their assumed characteristics. In: Proceedings of the Andesite Conference, A.R. McBirney ed. Oregon Dep. Geol. Mineral. Ind. Bull 65, 77–89 (1969)
Yoder, H.S., Kushiro, I.: Melting of a hydrous phase: phlogopite. Am. J. Sci. 267A, 558–582 (1969)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maaløe, S., Wyllie, P.J. Water content of a granite magma deduced from the sequence of crystallization determined experimentally with water-undersaturated conditions. Contr. Mineral. and Petrol. 52, 175–191 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00457293
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00457293