Abstract
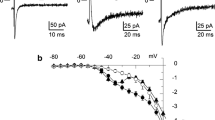
Using the patch-clamp technique, we have characterised the inward current from enzymatically dispersed rabbit pulmonary arterial cells, and investigated the effects of the vasodilator, nitroprusside (NP), on these and other membrane currents. With Cs+-filled pipettes, inward currents were recorded during brief depolarizing voltage steps in both physiological Ca2+ and 10 mM Ba2+. The threshold for current activation was positive to -40 mV and the current peaked at 0 mV for Ca2+ and +10mV for Ba2+. During the first few minutes of recording, inward currents increased or “ran-up”. This could not be attributed to blockade of outward current or the inclusion of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) in the patch pipette. Experiments revealed that all the inward current was carried through a single type of voltage-activated Ca2+ channel, namely the high-threshold, dihydropyridine-sensitive channel. It was unaffected by tetrodotoxin but was abolished at all potentials by low concentrations of Cd2+ (100 μM) or nifedipine (1–2μM). NP (1 μM) suppressed peak inward Ba2+ current at +10 mV by approximately 45%. Higher concentrations (50 μM) did not produce further blockade of the current. This decrease was associated with increased inactivation of the current, and both effects required the presence of ATP in the patch pipette. In physiological Ca2+, using K+-filled pipettes, NP was found to induce spontaneous bursts of outward currents, which are probably activated by the release of Ca2+ from Ca2+-overloaded stores. These results are consistent with NP lowering cytosolic Ca2+, and hence causing vasodilation, by inhibiting Ca2+ influx through voltage-gated Ca2+ channels and by promoting Ca2+ uptake into the sarcoplasmic reticulum.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akaike N, Kanaide H, Kuga T, Nakamura M, Sadoshima J, Tomoike H (1989) Low-voltage-activated calcium current in rat aorta smooth muscle cells in primary culture. J Physiol (Lond) 416:141–160
Bean BP (1989) Classes of calcium channels in vertebrate cells. Annu Rev Physiol 51:367–384
Bean BP, Sturek M, Puga A, Hermsmeyer K (1986) Calcium channels in muscle cells isolated from rat mesenteric arteries: modulation by dihydropyridine drugs. Circ Res 59:229–235
Benham CD, Bolton TB (1986) Spontaneous transient outward currents in single visceral and vascular smooth muscle cells. J Physiol (Lond) 381:385–406
Benham CD, Hess P, Tsien RW (1987) Two types of calcium channels in single smooth muscle cells from rabbit ear artery studied with whole-cell and single-channel recordings. Circ Res 61 [Suppl I]:10–16
Chad JE, Eckert R (1986) An enzymatic mechanism for calcium current inactivation in dialysed Helix neurones. J Physiol (Lond) 378:31–51
Clapp LH, Gurney AM (1989) Multiple effects of nitroprusside on membrane currents in smooth muscle cells from rabbit pulmonary artery (Abstract). J Physiol (Lond) 418:19P
Clapp LH, Gurney AM (1991) Outward currents in rabbit pulmonary artery cells dissociated with a new technique. Experimental Physiol. In press
Collins P, Griffith TM, Henderson AH, Lewis MJ (1986) Endothelium-derived relaxing factor alters calcium fluxes in rabbit aorta: a cyclic guanosine monophosphate-mediated effect. J Physiol (Lond) 381:427–437
Désilets M, Driska SP, Baumgarten CM (1989) Current fluctuations and oscillations in smooth muscle cells from the hog carotid artery: role of the sarcoplasmic reticulum. Circ Res 65:708–722
Fabiato A (1985) Rapid ionic modifications during the aequorin-detected calcium transient in a skinned canine cardiac purkinje cell. J Gen Physiol 85:189–246
Fox AP, Nowycky MC, Tsien RW (1987) Kinetic and pharmacological properties distinguishing three types of calcium currents in chick sensory neurones. J Physiol (London) 394:149–172
Furchgott RF, Vanhoutte PM (1989) Endothelium-derived relaxing and contracting factors. FASEB J 3:2007–2018
Ignarro LJ, Lippton H, Edwards JC, Baricos WH, Hyman AL, Kadowitz PJ, Gruetter CA (1981) Mechanism of vascular smooth muscle relaxation by organic nitrates, nitrites, nitroprusside, and nitric oxide: evidence for the involvement of S-nitrosothiols as active intermedicates. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 218:739–749
Ignarro LJ, Byrns RE, Buga GM, Wood KS (1987) Endotheliumderived relaxing factor from rabbit pulmonary artery and vein possesses pharmacological and chemical properties that are identical to those for nitric oxide radical. Circ Res 61:866–879
Karaki H, Sato K, Ozaki H, Murakami K (1988) Effects of sodium nitroprusside on cytosolic calcium level in vascular smooth muscle. Eur J Pharmacol 156:259–266
Komori S, Bolton TB (1989) Actions of guanine nucleotides and cyclic nucleotides on calcium stores in single patch-clamped smooth muscle cells from rabbit portal vein. Br J Pharmacol 97:973–982
Loirand G, Mironneau C, Mironneau J, Pacaud P (1989) Two types of calcium currents in single smooth muscle cells from rat portal vein. J Physiol (Lond) 412:333–349
Magliola L, Jones AW (1990) Sodium nitroprusside alters Ca2+ flux components and Ca2+-dependent fluxes of K+ and Cl− in rat aorta. J Physiol (Lond) 421:411–424
Morgan JP, Morgan KG (1984) Alteration of cytoplasmic ionized calcium levels in smooth muscle by vasodilators in the ferret. J Physiol (Lond) 357:539–551
Murad F (1986) Cyclic guanosine monophosphate as a mediator of vasodilation. J Clin Invest 78:1–5
Nishimura J, van Breemen C (1989) Direct regulation of smooth muscle contractile elements by second messengers. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 163:929–935
Ohya Y, Sperelakis N (1989) ATP regulation of the slow calcium channels in vascular smooth muscle cells of guinea-pig mesenteric artery. Circ Res 64:145–154
Ohya Y, Kitamura K, Kuriyama H (1987) Modulation of ionic currents in smooth muscle balls of the rabbit intestine by intracellularly perfused ATP and cyclic AMP. Pflügers Arch 408:465–473
Okabe K, Kitamura K, Kuriyama H (1988) The existence of a highly tetrodotoxin sensitive Na channel in the freshly dispersed smooth muscle cells of the rabbit main pulmonary artery. Pflügers Arch 411:423–428
Palmer RM, Ferrigo AG, Moncada S (1987) Nitric oxide release accounts for the biological activity of endothelium-derived relaxing factor. Nature 327:524–525
Raeymaekers L, Hofmann F, Casteels R (1988) Cyclic GMP-dependent protein kinase phosphorylates phospholamban in isolated sarcoplasmic reticulum from cardiac and smooth muscle. Biochem J 252:269–273
Sturek M, Hermsmeyer K (1986) Calcium and sodium channels in spontaneously contracting vascular muscle cells. Science 233:475–478
Twort CHC, van Breemen C (1988) Cyclic guanosine monophosphate-enhanced sequestration of Ca2+ by sarcoplasmic reticulum in vascular smooth muscle. Circ Res 62:961–964
Vivaudou MB, Clapp LH, Walsh JV Jr, Singer JJ (1988) Regulation of one type of Ca2+ current in smooth muscle cells by diacylglycerol and acetylcholine. FASEB J 2:2497–2504
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Clapp, L.H., Gurney, A.M. Modulation of calcium movements by nitroprusside in isolated vascular smooth muscle cells. Pflugers Arch. 418, 462–470 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00497774
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00497774