Summary
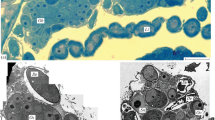
In endoplasm close to the posterior pole of the egg ofPimpla one finds conglomerated oosome material, rich in RNA. Investigations after various operations in the oosome region (10% of egg length), before cleavage were intended to show whether pole cells develop, how many segments form and if gonads contain primordial germ cells.
Oosome material was squashed with a blunt glass needle. The uninjured part of the egg in front of the oosome region develops blastoderm but no pole cells. It gives rise to a fully segmentated larva with germ cells in the gonads.
After ligation of up to 15% of egg length complete embryos with germ cells can develop. The smaller the anterior isolates, the more abdominal segments are missing.
By ligation and invagination of the hindpole of eggs with a blunt glass needle, anteriorly material from the oosome region is combined with ooplasm situated more. Translocation of only a small amount of ooplasm results in the same number of abdominal segments in the anterior isolate as in ordinary ligated eggs. Translocation of much ooplasm yields a significantly greater number of abdominal segments. It is immaterial for the metameric segmentation of the embryo whether the oosome is situated before or behind the ligature or is destroyed. But the depth of the invagination and how many segments result do not seem to be correlated.
A completely segmentated embryo can develop also after extirpation of the oosome provided care is taken not to injure the hindpole-plasm. No pole-cells result when the complete oosome is missing and the hindpole-plasm is present; loss of part of the oosome results in the development of only a few pole-cells. Thus oosome material is a necessary and quantitative condition for pole-cell differentiation. In one favourable case pole-cells developed in the extraovate because the oosome was followed after some hours by endoplasm and cleavage nuclei.
Functions of the oosome are discussed: together with cleavage nuclei it is responsible for pole-cell development. As pole-cells are not invariable precursors of germ-cells, the oosome cannot contain determinants for them. Possibly it includes postembryonic growth modifiers or it could be active in gametogenesis later on. As an egg without oosome-region is able to develop an embryo, this region does not or exclusively contain an activation-center (e. g.Platycnemis), or special hind-pole factors (e. g.Euscelis). In any case the oosome itself does not include these factors. A greater number of segments in the anterior isolate after translocation of ooplasm could be due to its special quality, as inEuscelis andBruchidius whose metameric organisations originate from a bipolar ooplasmic reaction system. Also it could depend only on the increase of ooplasm competent for differentiation-factors in the middle and anterior egg parts.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Bantock, C. R.: Experiments on chromosome elimination in the gall midge,Mayetiola destructor. J. Embryol. exp. Morph.24, 257–286 (1970).
Bier, K.: Über den Saisondimorphismus der Oogenese vonFormica rufa rufopratensis minor Gößw. und dessen Bedeutung für die Kastendetermination. Biol. Zbl.73, 170–190 (1954).
Bronskill, J. F.: Embryology ofPimpla turiondlae L. (Hymenoptera: Ichneumonidae). Canad. J. Zool.37, 655–688 (1959).
Counce, S. J., Ede, D. A.: The effect on embryogenesis of a sex-linked female-sterility factor inDrosophila melanogaster. J. Embryol. exp. Morph.5, 404–421 (1957).
Geyer-Duszyńska, I.: Experimental research on chromosome elimination in Cecidomyidae (Dipt.). J. exp. Zool.141, 391–48 (1959).
—: Genetic factors in oögenesis and spermatogenesis in Cecidomyiidae. Chromosomes Today1, 174–178 (1966).
Günther, J.: Entwicklungsfähigkeit, Geschlechtsverhältnis und Fertilität vonPimpla turionellae L. (Hymenoptera, Ichneumonidae) nach Röntgenbestrahlung oder Abschnürung des Eihinterpols. Zool. Jb. Anatomie68, 1–46 (1971).
Heinig, S.: Die Abänderung embryonaler Differenzierungsprozesse durch totale Röntgenbestrahlung im Ei vonGryllus domesticus. Zool Jb. Abt. Anat. u. Ontog.84, 425–492 (1967).
Jazdowska-Zagrodzińska, B.: Experimental studies on the role of „polar granules” in the segregation of pole cells inDrosophila melanogaster. J. Embryol. exp. Morph.16, 391–399 (1966).
Jung, E.: Untersuchungen am Ei des SpeisebohnenkäfersBruchidius obtectus SAY (Coleoptera). I. Mitteilung: Entwicklungsgeschichtliche Ergebnisse zur Kennzeichnung des Eitypus. Z. Morph. Ökol. Tiere56, 444–480 (1966a).
—: Untersuchungen am Ei des SpeisebohnenkäfersBruchidius obtectus SAY (Coleoptera). II. Mitteilung: Entwicklungsphysiologische Ergebnisse der Schnürungsexperimente. Wilhelm Roux' Arch. Entwickl.-Mech. Org.157, 320–392 (1966b).
—, Krause, G.: Experimente mit Verlagerung polnahen Eimaterials zur Analyse der Bedingungen für die metamere Gliederung des Embryos vonBruchidiue (Coleoptera). Wilhelm Roux' Arch. Entwickl.-Mech. Org.159, 89–126 (1967).
Krause, G.: Die Eitypen der Insekten. Biol. Zbl.59, 495–536 (1939).
—, Sander, K.: Ooplasmic reaction systems in insect embryogenesis. Advanc. Morphogenes.2, 259–303 (1962).
Mahr, E.: Struktur und Entwicklungsfunktion des Dotter-Endoplasmasystems im Ei des Heimchens (Gryllus domesticus). Wilhelm Roux' Arch. Entwickl.-Mech. Org.152, 263–302 (1960).
Meng, C.: Strukturwandel und histochemische Befunde insbesondere am Oosom während der Oogenese und nach der Ablage des Eies vonPimpla turionellae L. (Hymenoptera, Ichneumonidae). Wilhelm Roux' Archiv161, 162–208 (1968).
—: Autoradiographische Untersuchungen am Oosom in der Oocyte vonPimpla turionellae L. (Hymenoptera). Wilhelm Roux' Archiv165, 35–52 (1970).
Müller, H.: Die Entwicklungsleistungen abgeschnürter Eiteile bei der SchlupfwespePimpla turionellae L. Zulassungsarbeit für das Lehramt an den Gymnasien. Zool. Inst. Würzburg (1963).
Sander, K.: Analyse des ooplasmatischen Reaktionssystems vonEuscelis plebejus FALL. (Cicadina) durch Isolieren und Kombinieren von Keimteilen. I. Mitteilung. Die Differenzierungsleistungen vorderer und hinterer Eiteile. Wilhelm Roux' Arch. Entwickl.-Mech. Org.151, 430–497 (1959).
—: Analyse des ooplasmatischen Reaktionssystems vonEuscelis plebejus FALL (Cicadina) durch Isolieren und Kombinieren von Keimteilen. II. Mitteilung. Die Differenzierungsleistungen nach Verlagern von Hinterpolmaterial. Wilhelm Roux' Arch. Entwickl.-Mech. Org.151, 660–707 (1960).
—: Über den Einfluß von verlagertem Hinterpolmaterial auf das metamere Organisationsmuster im Zikaden-Ei. Verh. Dtsch. Zool. Ges. 1961 in Saarbrücken. Zool. Anz., Suppl.25, 315–322 (1962).
—, Herth, W., Vollmar, H.: Abwandlungen des metameren Organisationsmusters in fragmentierten und in abnormen Insekteneiern. Verh. Zool. Ges. 1969 in Würzburg. Zool. Anz., Suppl.38, 46–52 (1970).
Sauer, G.: Die Regulationsbefähigung des Keimanlagenblastoderms vonGryllus domesticus beim Beginn der Wirkung des Differenzierungszentrums. Zool. Jb. Abt. Anat. u. Ontog.79, 149–222 (1961).
Sauer, H. W.: Zeitraffer-Mikrofilm-Analyse embryonaler Differenzierungsphasen vonGryllus domesticus. Z. Morph. Ökol. Tiere56, 143–251 (1966).
Schanz, geb. Breitenborn, G.: Entwicklungsvorgänge im Ei der LibelleIschnura elegans und Experimente zur Frage ihrer Aktivierung. Eine Mikro-Zeitraffer-Film-Analyse. Inaugural-Dissertation, 1–92 (Naturw. Fakultät d. Univ. Marburg, 1965).
Schnetter, M.: Physiologische Untersuchungen über das Differenzierungszentrum in der Embryonalentwicklung der Honigbiene. Wilhelm Roux' Arch. Entwickl.-Mech. Org.131, 285–323 (1934).
—: Die Entwicklung von Zwerglarven in geschnürten Bieneneiern. Verh. Dtsch. Zool. Ges. in Freiburg 1936. Zool. Anz., Suppl.9, 82–88 (1936).
Schnetter, W.: Experimente zur Analyse der morphogenetischen Funktion der Ooplasmabe-standteile in der Embryonalentwicklung des Kartoffelkäfers (Leptinotarsa decemlineata SAY). Wilhelm Roux' Arch. Entwickl.-Mech. Org.155, 637–692 (1965).
Seidel, F.: Untersuchungen über das Bildungsprinzip der Keimanlage im Ei der LibellePlatycnemis pennipes. Wilhelm Roux' Arch. Entwickl.-Mech. Org.119, 322–440 (1929).
—: Entwicklungsphysiologie des Insekten-Keims. Verh. Dtsch. Zool. Ges. in Freiburg 1936. Zool. Anz., Suppl.9, 291–336 (1936).
—: Analyse des Differenzierungsverlaufs im Insektenei (Gryllus) mittels UV- und Röntgenbestrahlungen. Verh. Dtsch. Zool. Ges. 1963 in München. Zool. Anz., Suppl.27, 121–143 (1964).
—: Das Eisystem der Insekten und die Dynamik seiner Aktivierung. Verh. Dtsch. Zool. Ges. 1965 in Jena. Zool. Anz., Suppl.29, 166–187 (1966).
Wolf, R.: Kinematik und Feinstruktur plasmatischer Faktorenbereiche des Eies vonWachtliella persicariae L. (Diptera). II. Teil: Das Verhalten ooplasmatischer Teilsysteme nach Zentrifugierung im 4-Kern-Stadium. Wilhelm Roux' Archiv163, 40–80 (1969).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Durchgeführt mit Leihgaben der Deutschen Forschungsgemeinschaft und mit Hilfe von Euratom (Verträge Nr. 041-65-10 BIOD und Nr. 077-69-I BIOC mit dem Heiligenberg-Institut).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Achtelig, M., Krause, G. Experimente am ungefurchten Ei vonPimpla turionellae L. (Hymenoptera) zur Funktionsanalyse des Oosombereichs. W. Roux' Archiv f. Entwicklungsmechanik 167, 164–182 (1971). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00577038
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00577038