Abstract
Functionally isolated segments of rat colon and rectum were perfused in situ in a closed loop system. Rectum was defined as the lower 25–35% of the length of large intestine (cecum excluded). Perfusion conditions were optimized at 0.5 ml·min−1 and 3 cm H2O luminal pressure.
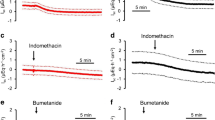
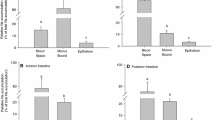
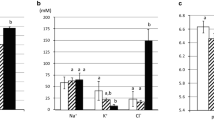
Variation of perfusion rate between 0.2 and 2 ml·min−1 did not influence net volume transport (J nv ). Luminal distension following elevation of hydrostatic pressure to 18 cm H2O reversibly increasedJ nv . Under control conditionsJ nv and Na+-transport rates (J nNa ) of colon were 2–3 times higher than those of rectum. In colon transepithelial electrical potential difference ψms was time independent −12 mV (lumen negative) whereas rectal ψms increased with time from −6 mV, reaching a plateau of −67 mV within 6h. Amiloride 10−4 mol·l−1 had no effect on ψms,J nv , andJ nNa in colon but did slightly depress K+-secretion in colon descendens. In contrast, ψms in rectum was dosedependently depressed, being reversed to +7 mV at 10−4 mol·l−1.J nv andJ nNa were decreased by half. Acetazolamide in addition to amiloride lowered the positive post-amiloride rectal ψms by half. Adrenalectomy had no effect on colonic ψms, but abolished ψms of the rectum. A single dose of 40 μg·kg−1 b.w. aldosterone during the experiment restored the typical time course of rectal ψms, but did not affect ψms in colon. It is concluded that aldosterone induces an amiloride-sensitive Na+-pathway only in rectum, but not in colon, and that colon and rectum differ basically in their transport properties, quantitatively as well as qualitatively, as do the kidney distal convoluted tubule and the cortical collecting duct.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Archampong, E. Q., Harris, J., Clark, C. G.: The absorption and secretion of water and electrolytes across the healthy and the diseased human colonic mucosa measured in vitro. Gut13, 880–886 (1972)
Barratt, L. J.: The effect of amiloride on the transepithelial potential difference of the distal tubule of the rat kidney. Pflügers Arch.361, 251–254 (1976)
Barry, R. J. C., Eggenton, J.: Electrical activity of the intestine. Biomembranes, 4B, intestinal absorption (D. H. Smyth, ed.), pp. 917–960. London-New York: Plenum Press 1974
Bastl, Ch., Binder, H. J., Hayslett, J. P.: The mammalian colon — a model of distal tubule function. Fed. Proc.35, 464 (1976)
Behar, J.: Magnesium absorption by the rat ileum and colon. Am. J. Physiol.327, 334–340 (1974)
Bright-Asare, P., Binder, H. J.: Stimulation of colonic secretion of water and electrolytes by hydroxy fatty acids. Gastroenterology64, 81–88 (1973)
Chosniak, I., Munck, B. G., Skadhauge, E.: Sodium chloride transport across the chicken coprodeum. Basic characteristics and dependence on sodium chloride intake. J. Physiol. (Lond.)271, 489–504 (1977)
Cortney, M. A.: Renal tubular transfer of water and electrolytes in adrenalectomized rats. Am. J. Physiol.216, 589–598 (1969)
Cummings, J. H.: The colon: Absorptive, secretory and metabolic functions. Digestion13, 232–240 (1975)
Curran, P. F., Schwartz, G. F.: Na, Cl and H2O transport by rat colon. J. Gen. Physiol.43, 555–571 (1960)
David, H. A., Hartley, H. O., Pearson, E. S.: The distribution of the ratio, in a single normal sample, of range to standard deviation. Biometrika41, 482–493 (1954)
Dolman, D., Edmonds, C. J.: The effect of aldosterone and the renin-angiotensin system on sodium, potassium and chloride transport by proximal and distal rat colon in vivo. J. Physiol. (Lond.)250, 597–611 (1975)
Duarte, C. G., Chomety, F., Giebisch, G.: Effect of amiloride, ouabain, and furosemide on distal tubular function in the rat. Am. J. Physiol.221, 632–639 (1971)
Edmonds, C. J.: The gradient of electrical potential difference and of sodium and potassium of the gut contents along the caecum and colon of normal and sodium-depleted rats. J. Physiol. (Lond.)193, 571–588 (1967)
Edmonds, C. J.: Transport of sodium and secretion of potassium and bicarbonate by the colon of normal and sodium-depleted rats. J. Physiol. (Lond.)193, 589–602 (1967)
Edmonds, C. J.: Salts and water. Biomembranes, 4B, intestinal absorption (D. H. Smyth, ed.), pp. 711–759. London-New York: Plenum Press 1974
Edmonds, C. J., Marriott, J.: The effect of aldosterone and adrenalectomy on the electrical potential difference of rat colon and on the transport of sodium, potassium, chloride, and bicarbonate. J. Endocrinol.39, 517–531 (1967)
Edmonds, C. J., Marriott, J.: Factors influencing the electrical potential across the mucosa of rat colon. J. Physiol. (Lond.)194, 457–478 (1968)
Edmonds, C. J., Marriott, J.: The effect of aldosterone on the electrical activity of rat colon. J. Endocrinol.44, 363–377 (1969)
Edmonds, C. J., Marriott, J.: Na transport and short-circuit current in rat colon in vivo and the effect of aldosterone. J. Physiol. (Lond.)210, 1021–1039 (1970)
Field, M., McColl, I.: Ion transport in rabbit ileal mucosa. III. Effects of catecholamines. Am. J. Physiol.225, 852–856 (1973)
Fisher, K. A., Binder, H. J., Hayslett, J. P.: Potassium secretion by colonic mucosal cells after potassium adaptation. Am. J. Physiol.231, 987–994 (1976)
Frizzell, R. A., Koch, M. J., Schultz, S. G.: Ion transport by rabbit colon. I. Active and passive components. J. Membr. Biol.27, 297–316 (1976)
Fromm, M., Hegel, U., techn. assistance Lüderitz, S.: Transport in large intestine of rat in vivo: Influence of perfusion rate and pressure, of amiloride and acetazolamide. Pflügers Arch.335, R 75 (1975)
Gfeller, E., Walser, M.: Stretch-induced changes in geometry and ultrastructure of transporting surfaces of toad bladder. J. Membr. Biol.4, 16–28 (1971)
Gross, J. B., Imai, M., Kokko, J. P.: A functional comparison of the cortical collecting tubule and the distal tubule. J. Clin. Invest.55, 1284–1294 (1975)
Haberich, F. J., Herzer, R., Aziz, O., Dennhardt, R.: Resorptions-und Sekretionsstudien am Darm. I. Mitteilung. Technik der extrakorporalen Perfusion beliebiger, vorübergehend funktionell isolierter Darmabschnitte an der wachen Ratte. Z. Ges. Exp. Med.148, 223–237 (1968)
Hierholzer, K., Wiederholt, M., Holzgreve, H., Giebisch, G., Klose, R. M., Windhager, E. E.: Micropuncture study of renal transtubular concentration gradients of sodium and potassium in adrenalectomized rats. Pflügers Arch.285, 193–210 (1965)
Lange, S., Veit, K., Hegel, U., Gutsche, H. U.: Die Wirkung von Amilorid auf den Elektrolyttransport des Rattencolons und ihre Abhängigkeit von Mineralocorticoiden. Endokrinologie63, 271–278 (1974)
Lennane, R. J., Peart, W. S., Shaw, J.: Adrenergic influences on the electrical potential across the colonic mucosa of the rabbit. J. Physiol. (Lond.)250, 367–372 (1975)
Leslie, B. R., Schwartz, J. H., Steinmetz, P. R.: Coupling between Cl− absorption and HCO −3 secretion in turtle urinary bladder. Am. J. Physiol.225, 610–616 (1973)
Levens, N. R., Munday, K. A., York, B.: Effect of angiotensin II on fluid transport, transmural potential difference and resistance in the rat distal colon in vivo. J. Endocrinol.67, 64–65 (1975)
Lewis, L. D., Fordtran, J. S.: Effect of perfusion rate on absorption, surface area, unstirred water layer thickness, permeability, and intraluminal pressure in the rat ileum in vivo. Gastroenterology68, 1509–1516 (1975)
Lief, P. D., Mutz, B. F., Bank, N.: Effect of stretch on passive transport in toad urinary bladder. Am. J. Physiol.230, 1722–1729 (1976)
Lutz, J.: Hämodynamische Eigenschaften und Gefäßreaktionen der intestinalen Strombahn. Arch. Kreislaufforsch.59, 99–152 (1968)
Lutz, J.: Druckkonstante Perfusion von Teilkreisläufen mittels einer druckgesteuerten Rollenpumpe mit analoger Durchströmungsregistrierung. Pflügers Arch.335, R89 (1972)
McKinney, T. D., Burg, M. B.: Bicarbonate secretion by rabbit cortical collecting tubules in vitro. J. Clin. Invest.61, 1421–1427 (1978)
Mirkovitch, V., Menge, H., Robinson, J. W. L.: The effect of intraluminal hydrostatic pressure on intestinal absorption in vivo. Experientia30, 912–913 (1974)
Nellans, H. N., Frizell, R., Schultz, S. G.: Coupled sodiumchloride influx across the brush border of rabbit ileum. Am. J. Physiol.225, 467–475 (1973)
Pettinger, W. A., Tanaka, K., Keeton, K., Campbell, W. B., Brooks, S. N.: Renin release, an artifact of anesthesia and its implications in rats. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med.148, 625–630 (1975)
Phillips, S. F., Schmalz, P. F.: HCO3 secretion by the rat colon: Effect of intraluminal Cl and acetazolamide. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med.135, 116–122 (1970)
Powell, D. J., Malawer, S. J.: Relationship between water and solute transport from isoosmotic solutions by rat intestine in vivo. Am. J. Physiol.215, 49–55 (1968)
Rask-Madsen, J.: Simultaneous measurement of electrical polarization and electrolyte transport by the entire normal and inflamed human colon during in vivo perfusion. Scand. J. Gastroent.8, 327–336 (1973)
Rask-Madsen, J., Hjelt, K.: Effect of amiloride on electrical activity and electrolyte transport in human colon. Scand. J. Gastroent.12, 1–6 (1977)
Schultz, S. G., Frizzell, R. A., Nellans, H. N.: Active sodium transport and the electrophysiology of rabbit colon. J. Membr. Biol.33, 351–384 (1977)
Bindslev, N., Skadhauge, E.: Sodium chloride absorption and solute-linked water flow across the epithelium of the coprodeum and large intestine in the normal and dehydrated fowl (Gallus domesticus). In vivo perfusion studies. J. Physiol. (Lond.)216, 753–768 (1971)
Stoner, L. C., Burg, M. B., Orloff, J.: Ion transport in cortical collecting tubule; effect of amiloride. Am. J. Physiol.227, 453–459 (1974)
Thomas, D. H., Skadhauge, E., Read, M. W.: Steroid effects on gut functions in birds. Biochem. Soc. Trans.3, 1164–1168 (1975)
Veit, K.: Der Einfluß von Amilorid und Mineralocorticoiden auf den Elektrolyttransport am Enddarm der Ratte. Med. Diss., Berlin 1975
Vogel, G., Meyering, E., Stoeckert, I.: Gleichgewichtskonzentrationen einiger Plasma-Solute und Na-Absorption bei Erhöhung des Na-Angebotes durch Steigerung der Na-Angebotskonzentration oder des Perfusionsvolumens/Zeit im Jejunum und Colon von Ratten. Pflügers Arch.310, 150–166 (1969)
Walser, M.: Reversible stimulation of sodium transport. J. Clin. Invest.48, 1714–1723 (1969)
Wells, H. S.: The passage of materials through the intestinal wall. I. The relation between intra-intestinal pressure and the absorption of water. Am. J. Physiol.99, 209–220 (1931)
Wright, F. S.: Increasing magnitude of electrical potential along the renal distal tubule. Am. J. Physiol.220, 624–638 (1971)
Yau, W. M., Makhlouf, G. M.: Comparison of transport mechanisms in isolated ascending and descending rat colon. Am. J. Physiol.228, 191–195 (1975)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (Wi 328).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fromm, M., Hegel, U. & Lüderitz, S. Segmental heterogeneity of epithelial transport in rat large intestine. Pflugers Arch. 378, 71–83 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00581960
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00581960