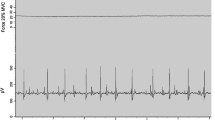
Summary
Slow (m.soleus) and fast (m.tibialis anterior) muscles of the rabbit were subjected to indirect long-term intermittent stimulation (3 weeks, 8 hrs daily) with a frequency pattern of 10 imp/sec. Whereas no changes were observed in case of the slow muscle, stimulation induced profound changes in the fast tibialis anterior muscle. These consisted in a rearrangement of the enzyme activity pattern of energy-supplying metabolism,e.g. decrease in glycogenolytic and glycolytic enzyme activities and severalfold increase in key enzymes of aerobic endoxidation of substrates in β-oxidation and the citric acid cycle. Concomitant with the increase in aerobic oxidative capacity, there was an increased resistance to fatigue. Histochemical studies revealed a strong increase in mitochondria of all fibres. The bimodal distribution of fibre cross-sectional area in the normal tibialis anterior muscle was changed by stimulation into a more homogeneous population of fibres with a smaller cross-sectional area. Despite a 50% increase in time to peak of isometric twitch contraction no changes were observed in the fibre population with regard to myofibrillar ATPase reaction in quantitative evaluation of whole cross-sections of the muscles. The percentage of fibres histochemically classified as slow amounted to 2.8% and 3.1% in control and stimulated tibialis anterior muscle. Nevertheless the data suggest a transformation of the fibre population under the influence of long-term intermittent stimulation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baldwin, K. M., Winder, W. W., Terjung, R. L., Holloszy, J. O.: Glycolytic enzymes in different types of skeletal muscle: adaptation to exercise. Amer. J. Physiol.225, 962–966 (1973)
Bass, A., Brdiczka, D., Eyer, P., Hofer, S., Pette, D.: Metabolic differentiation of distinct muscle types at the level of enzymatic organization. Europ. J. Biochem.10, 198–206 (1969)
Brdiczka, D., Pette, D., Brunner, G., Miller, F.: Kompartmentierte Verteilung von Enzymen in Rattenlebermitochondrien. Europ. J. Biochem.5, 294–304 (1968)
Brown, M. D., Cotter, M., Hudlicka, O., Smith, M. E., Vrbová, G.: The effect of long-term stimulation of fast muscles on their ability to withstand fatigue. J. Physiol. (Lond.)238, 47–48P (1973)
Bücher, T., Luh, W., Pette, D.: Einfache und zusammengesetzte optische Tests mit Pyridinnucleotiden. In: Handbuch der physiologisch- und pathologisch-chemischen Analyse. Hoppe-Seyler/Thierfelder, eds., Vol. VI/A, pp. 292–339. Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer 1964
Burke, R. E., Levine, D. N., Tsairis, P., Zajac, F. E. III: Physiological types and histochemical profiles in motor units of the cat gastrocnemius. J. Physiol. (Lond.)234, 723–748 (1973)
Burke, R. E., Levine, D. N., Zajac, F. E. III, Tsairis, P., Engel, W. K.: Mammalian motor units: physiological-histochemical correlation in three types in cat gastrocnemius. Science174, 709–712 (1971)
Close, R. I.: Dynamic properties of mammalian skeletal muscles. Physiol. Rev.52, 129–197 (1972)
Cotter, M., Hudlicka, O., Pette, D., Staudte, H. W., Brbová, G.: Changes of capillary density and enzyme pattern in fast rabbit muscles during long-term stimulation. J. Physiol. (Lond.)230, 34P (1973)
Edström, L., Kugelberg, E.: Histochemical composition, distribution of fibres and fatiguability of single motor units. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiat.31, 424–433 (1968)
Exner, G. U., Staudte, H. W., Pette, D.: Isometric training of rats —effects upon fast and slow muscle and modification by an anabolic hormone )Nandrolone Decanoate). Pflügers Arch.345, 1–14 (1973)
Guth, L.: Fact and artifact in the histochemical procedure for myofibrillar ATPase. Exp. Neurol.41, 440–450 (1973)
Gutmann, E., Hajek, J.: Differential reaction of muscle to excessive use in compensatory hypertrophy and increased phasic activity. Physiol. bohemoslov.20, 205–212 (1971)
Kugelberg, E., Edström, L.: Differential histochemical effects of muscle contractions on phosphorylase and glycogen in various types of fibres: relation to fatigue. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiat.31, 415–423 (1968)
Melichna, J., Gutmann, E.: Stimulation and immobilization effects on contractile and histochemical properties of denervated muscle. Pflügers Arch.352, 165–178 (1974)
Müller, W.: Temporal progress of muscle adaption to endurance training in hind limb muscles of young rats. Cell Tiss. Res.156, 61–87 (1974)
Nolte, J., Pette, D.: Microphotometric determination of enzyme activity in single cells in cryostat sections. I. Application of the gel film technique to microphotometry and studies on the intralobular distribution of succinate dehydrogenase and lactate dehydrogenase activities in rat liver. J. Histochem. Cytochem.20, 567–576 (1972)
Padykula, H. A., Herman, E.: The specificity of the histochemical method for adenosine triphosphatase. J. Histochem. Cytochem.3, 170–183 (1955)
Pette, D., Leisner, E., Müller, W., Vrbová, G.: Pflügers Arch., submitted for publication
Pette, D., Staudte, H. W., Vrbová, G.: Physiological and biochemical changes induced by long-term stimulation of fast muscle. Naturwissenschaften59, 469–470 (1972)
Pette, D., Smith, M. E., Staudte, H. W., Vrbová, G.: Effects of long-term electrical stimulation on some contractile and metabolic characteristics of fast rabbit muscles. Pflügers Arch.338, 257–272 (1973)
Riley, D. A., Allin, E. F.: The effects of inactivity, programmed stimulation, and denervation on the histochemistry of skeletal muscle fibre types. Exp. Neurol.40, 391–413 (1973)
Salmons, S., Vrbová, G.: The influence of activity on some contractile characteristics of mammalian fast and slow muscles. J. Physiol. (Lond.)210, 535–549 (1969)
Samaha, F. J., Yunis, E. J.: Quantitative and histochemical demonstration of a calcium activated mitochondrial ATPase in skeletal muscle. Exp. Neurol.41, 431–439 (1973)
Staudte, H. W., Exner, G. U., Pette, D.: Effects of short-term, high intensity (sprint) training on some contractile and metabolic characteristics of fast and slow muscle of the rat. Pflügers Arch.344, 159–168 (1973)
Syrový, I., Gutmann, E., Melichna, J.: Effect of exercise on skeletal muscle myosin ATPase activity. Physiol. bohemoslov.21, 633–638 (1972)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This study was supported by Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft, Sonderforschungsbereich 138 „Biologische Grenzflächen und Spezifität” and by grants from Deutscher Sportbund. B.U.R. obtained a fellowship from Deutscher Akademischer Austauschdienst. G.U.E. and R.S. were fellows of Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pette, D., Ramirez, B.U., Müller, W. et al. Influence of intermittent long-term stimulation on contractile, histochemical and metabolic properties of fibre populations in fast and slow rabbit muscles. Pflugers Arch. 361, 1–7 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00587333
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00587333