Summary
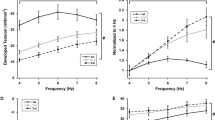
The action potential duration, tension, time to peak tension, mean rate of tension development, and ATP content of guinea pig ventricular muscle declined during 60 min of anoxic incubation. The decline in tension was closecorrelated with the decline in mean rate of tension development, whereas time to peak tension decreased in an S-shaped relationship with action potential duration decrease. When muscles were incubated under anoxic conditions for 5, 30, or 60 min then under control conditions for 30 min, the action potential duration and time to peak tension returned to control level; tension, mean rate of development, and ATP content did not recover to control level when the period of anoxia exceeded 5 min. During the first 10 min of re-oxygenation a transient overshoot of control value was noted in action potential duration and time to peak tension. The transient increase in time to peak tension was accompanied by a transient increase in tension. It was not dependent on the occurrence, or degree, of overshoot in action potential duration. Transient changes did not occur in mean rate of tension development.
It has been concluded that the anoxia-induced decrease in tension is due to a decrease in the rate of tension development as a result of a decreased ATP suppl. Time to peak tension seems related to action potential duration and both are independent oftotal muscle ATP content.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bárány, M.: ATPase activity of myosin correlated with speed of muscle shortening. J. gen. Physiol. Suppl.50, 197–217 (1967).
— Gaetjens, E., Bárány, K., Karp, E.: Comparative studies of rabbit cardiac and skeletal myosins. Arch. Biochem.106, 280–293 (1964).
Beeler, G. W., Jr., Reuter, H.: The relation between membrane potential, membrane currents, and activation of contraction in ventricular myocardial fibres. J. Physiol. (Lond.)207, 211–229 (1970).
Benson, E. S., Evans, G. T., Hallaway, B. E., Phibbs, C., Freier, E. T.: Myocardial creatine phosphate and nucleotides in anoxic cardiac arrest and recovery. Amer. J. Physiol.201, 687–693 (1961).
Bing, R. J., Gudbjarnason, S., Ischopp, H., Braasch, W.: Molecular changes in myocardial infarction in heart muscle. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci.156, 583–592 (1969).
Braasch, W., Gudbjarnason, S., Puri, P. S., Ravens, K. G., Bing, R. J.: Early changes in energy metabolism in the myocardium following acute coronary artery occlusion in anesthetized dogs. Circulat. Res.23, 429–438 (1968).
Braveny, P., Šumbera, J.: Electromechanical correlations in the mammalian heart muscle. Pflügers Arch.319, 36–48 (1970).
Buccino, R. A., Sonnenblick, E. H., Spann, J. F., Friedman, W. F., Braunwald, E.: Interactions between changes in the intensity and duration of the active state in the characterization of inotropic stimuli on heart muscle. Circulat. Res.21, 857–867 (1967).
Cingolani, H. E., Mattiazzi, A. R., Blesa, E. S., Gonzalez, N. C.: Contractility in isolated mammalian heart muscle after acid-base changes. Circulat. Res.26, 269–278 (1970).
Dettli, L., Bing, R. J.: Contractility and extractibility of heart actomyosin after death. Circulat. Res.4, 519–522 (1956).
Feinstein, M. B.: Effects of experimental congestive heart failure, ouabain, and asphyxia on the high-energy phosphate and creatine content of the guinea pig heart. Circulat. Res.10, 333–346 (1962).
Hercus, V. M., McDowall, R. J. S., Mendel, D.: Sodium exchanges in cardiac muscle. J. Physiol. (Lond.)129, 177–183 (1955).
Hunter, E., G. McDonald, T. F., MacLeod, D. P.: Metabolic depression and myocardial potassium. Submitted for publication (1971).
Jewell, B. R., Blinks, J. R.: Drugs and the mechanical properties of heart muscle. Ann. Rev. Pharmacol.8, 113–130 (1968).
Katz, A. M.: Contractile proteins of the heart. Physiol. Rev.50, 63–158 (1970).
Lindenmayer, G. E., Sordahl, L. A., Schwartz, A.: Reevaluation of oxidative phosphorylation in cardiac mitochondria from normal animals and animals in heart failure. Circulat. Res.23, 439–450 (1968).
Luchi, R. J., Kritcher, E. M.: Impaired cardiac myosin enzyme activity in acute anoxia. Circulation36, Suppl. II, 175–175 (1967).
McDonald, T. F., Hunter, E. G., MacLeod, D. P.: Adenosinetriphosphate partition in cardiac muscle with respect to transmembrane electrical activity. Pflügers Arch.322, 95–108 (1971).
MacLeod, D. P., Daniel, E. E.: Influence of glucose on the transmembrane action potential of anoxic papillary muscle. J. gen. Physiol.48, 887–899 (1965).
—, Prasad, K.: Influence of glucose on the transmembrane action potential of papillary muscle. Effects of concentration, phlorizin and insulin, non-metabolizable sugars, and stimulators of glycolysis. J. gen. Physiol.53, 792–815 (1969).
Morad, M., Trautwein, W.: The effect of the duration of the action potential on contraction in the mammalian heart muscle. Pflügers Arch. ges. Physiol.299, 66–82 (1968).
Pool, P. E., Sonnenblick, E. H.: The mechanochemistry of cardiac muscle. I. The isometric contraction. J. gen. Physiol.50, 951–965 (1967).
Prasad, K., MacLeod, D. P.: Influence of glucose on the transmembrane action potential of guinea pig papillary muscle. Metabolic inhibitors, ouabain, CaCl2, and their interaction with glucose, sympathomimetic amines, and aminophylline. Circulat. Res.24, 939–950 (1969).
Rougier, O., Vassort, G., Garnier, D., Gargoülil, Y. M., Coraboeuf, E.: Existence and role of a slow inward current during the frog atrial action potential. Pflügers Arch.308, 91–100 (1969).
Sandow, A.: Skeletal muscle. Ann. Rev. Physiol.32, 87–138 (1970).
Schädler, M. H.: Proportionale Aktivierung von ATPase-Aktivität und Kontraktionsspannung durch Calciumionen in isolierten contractilen Strukturen verschiedener Muskelarten. Pflügers Arch. ges. Physiol.296, 70–90 (1967).
Scheuer, J., Stezoski, S. W.: Effects of high-energy phosphate depletion and repletion on the dynamics and electrocardiogram of isolated rat hearts. Circulat. Res.23, 519–530 (1968).
Sobel, B. E., Spann, J. F., Pool, P. E., Sonnenblick, E. H., Braunwald, E.: Normal oxidative phosphorylation in mitochondria from the failing heart. Circulat. Res.21, 355–363 (1967).
Sonnenblick, E. H.: Active state in heart muscle. Its delayed onset and modification by inotropic agents. J. gen. Physiol.50, 661–667 (1967).
Stanley, P. E., Williams, S. G.: Use of liquid scintillation spectrometer for determining adenosine triphosphate by the luciferase enzyme. Analyt. Biochem.29, 381–392 (1969).
Strehler, B. L., McElroy, W. D.: Assay of adenosine triphosphate. In: Methods of Enzymology. Vol. 3, p. 871. S. P. Colowick and N. O. Kaplan, edit. New York: Academic Press Inc. 1957.
Trautwein, W., Dudel, J.: Aktionpotential und Kontraktion des Herzmuskels im Sauerstoffmangel. Pflügers Arch. ges. Physiol.263, 23–32 (1956).
Tyberg, J.B., Parmley, W. W., Sonnenblick, E. H.: In vitro studies of myocardial asynchrony and regional hypoxia. Circulat. Res.25, 569–579 (1969).
Williamson, J. R.: Glycolytic control mechanisms. II. Kinetics of intermediate changes during the aerobic-anoxic transition in perfused rat heart. J. biol. Chem.241, 5026–5036 (1966).
Wollenberger, A., Krause, E. G.: Metabolic control characteristics of the acutely ischemic myocardium. Amer. J. Cardiol.22, 349–359 (1968).
Wood, E. H., Heppner, R.L., Weidmann, S.: Inotropic effects of electric currents. I. Positive and negative effects of constant electric currents or current current impulses applied during cardiac action potentials. II. Hypothesis: Calcium movements, excitation-contraction coupling and inotropic effects. Circulat. Res.24, 409–445 (1969).
Woodbury, J. W., Brady, A. J.: Intracellular recording from moving tissue with a flexibly mounted ultramicroelectrode. Science123, 100–101 (1956).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by grants from the Canadian and Nova Scotia Heart Foundations and the Medical Research Council of Canada.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mcdonald, T.F., MacLeod, D.P. Anoxia-recovery cycle in ventricular muscle: Action potential duration, contractility and ATP content. Pflugers Arch. 325, 305–322 (1971). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00592172
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00592172