Abstract
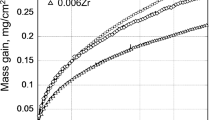
The oxidation behavior of Fe-C alloys in the temperature range 600–850°C has been studied. CO 2 evolved during oxidation was measured using an infrared gas analyzer. The presence of C lowers the oxidation rate relative to that of pure Fe and this has been related to the rejection of carbon at the alloy-scale interface causing poor contact between scale and alloy. As a result, the scale contains a higher proportion of magnetite, which reduces its overall growth rate. Very little carbon is lost to the atmosphere. The ease with which the rejected carbon is incorporated into the alloy depends on the alloy structure.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
E. Portevin, E. Pretet, and H. Jolivet,Rev. Metall. 31, 101, 186, 219 (1934).
C. Upthegrove and D. Murphy,Trans. Amer. Soc. Steel Treat. 21, 73 (1933).
C. A. Siebert,Trans. Amer. Soc. Met. 27, 75 (1939).
D. J. McAdam and G. W. Geil,J. Res. Nat. Bur. Stand. 23, 63 (1939).
H. J. Engel and F. K. Peters,Arch. Eisenhuttenwes. 28, 567 (1957).
K. Bohenkamp and H. J. Engel,Arch. Eisenhuttenwes. 32, 359 (1962).
K. Bohenkamp and H. J. Engel,Proceedings of the 1st International Congress on Metallic Corrosion, (Butterworths, London, 1962), p. 125.
J. Manenc, M. Bojic, and J. Benard,C.R. Acad. Sci. Paris 264, 1573 (1967).
J. P. Plumensi, A. Kohn, G. Vagnard, and J. Manenc,Corros. Sci. 9, 309 (1969).
J. Manenc and G. Vagnard,Corros. Sci. 9, 857 (1969).
J. Baud, J. P. Plumensi, and J. Manenc,Werkst. Korros,23, 876 (1972).
J. Baud, A. Ferrier, J. Manenc, and J. Benard,Oxid. Met. 9, 69 (1975).
H. Meurer and H. Schmalzried,Arch. Eisenhuttenwes. 42, 87 (1971).
D. Caplan, G. I. Sproule, R. J. Hussey, and M. J. Graham,Oxid. Met. 13, 255 (1979).
D. Caplan, G. I. Sproule, R. J. Hussey, and M. J. Graham,Oxid. Met. 12, 67 (1978).
W. W. Smeltzer and D. J. Young,Prog. Solid State Chem. 17 (1975).
G. J. Yurek, J. P. Hirth, and R. A. Rapp,Oxid. Met. 8, 265 (1974).
J. Paidassi,Rev. Metall. 54, 569 (1957).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Malik, A.U., Whittle, D.P. Oxidation of Fe-C alloys in the temperature range 600–850°C. Oxid Met 16, 339–353 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00611348
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00611348