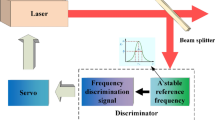
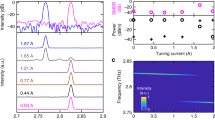
Abstract
Three promising methods of improving temporal coherence in semiconductor lasers are reviewed. They are the development of novel laser devices, a technique of optical feedback and a technique of electrical feedback. The main discussion in this paper is focused on the technique of electrical feedback. The theoretical limit of frequency stability and recent experimental results are presented with respect to the following five subjects which are indispensable in the realization of highly coherent lasers: (a) frequency stabilization; (b) improvements in frequency reproducibility; (c) linewidth reduction; (d) frequency tracking; and (e) stable, accurate and wideband frequency sweep.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Ohtsu, ‘Lasers and Atomic Clocks’ (Ohm-sha Publishing, Tokyo, 1986) (in Japanese).
M. Ohtsu, S. Katsuragi andT. Tako, ‘Performances of a Frequency Offset Locked He-Xe Laser System at 3.51μm’,IEEE J. Quantum Electron. QE-17 (1981) 1100.
A. Brillet andP. Cerez, ‘Laser Frequency Stabilization by Saturated Absorption’,J. de Physique 42 (1981) 73.
Y. Yamamoto, ‘Receiver Performance Evaluation of Various Digital Optical Modulation-Demodulation Systems in the 0.5–10μm Wavelength Region’,IEEE J. Quantum Electron. QE-16 (1980) 1251.
T. Okoshi andK. Kikuchi, ‘Heterodyne-Type Optical Fibre Communications’,J. Opt. Commun. 2 (1981) 82.
Y. Yamamoto, S. Saito andT. Mukai, ‘AM and FM Quantum Noise in Semiconductor Lasers Part II: Comparison of Theoretical and Experimental Results for AlGaAs Lasers’,IEEE J. Quantum Electron. QE-19 (1983) 47.
M. Ohtsu, H. Fukada, T. Tako andH. Tsuchida, ‘Estimation of the Ultimate Frequency Stability of Semiconductor Lasers’,Jpn J. Appl. Phys. 22 (1983) 1157.
D. W. Allan, ‘Statistics of Atomic Frequency Standards’,Proc. IEEE 54 (1966) 221.
M. Ohtsu, M. Hashimoto andH. Ozawa, ‘A Highly Stabilized Semiconductor Laser and its Application to Optically Pumped Rb Atomic Clock’,Proc. 39th A. Symp. Frequency Control, Philadelphia, 1985, p. 43.
S. Kobayashi, Y. Yamamoto, M. Ito andT. Kimura, ‘Direct Frequency Modulation in AlGaAs Semiconductor Lasers’,IEEE J. Quantum Electron. QE-18 (1982) 582.
G. Jacobsen, H. Olesen andF. Birkedahl, ‘Current/frequency-modulation Characteristics for Directly Optical Frequency-Modulated Injection Laser at 830 nm and 1.3μm’,Electron. Lett. 18 (1982) 874.
Y. Yamamoto, O. Nilsson andS. Saito, ‘Theory of a Negative Frequency Feedback Semiconductor Laser’,IEEE J. Quantum Electron. QE-21 (1985) 1919.
M. Ohtsu andN. Tabuchi, ‘Electrical Feedback and its Network Analysis for Linewidth Reduction of a Semiconductor Laser’,J. Lightwave Technol. 6 (1988) 357.
M. Ohtsu, H. Kotani andH. Tagawa, ‘Spectral Measurements of NH3 and H2O for Pollutant Gas Monitoring by 1.5μm InGaAsP/InP Lasers’,Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 22 (1983) 1553.
K. Fukuoka, M. Ohtsu andT. Tako, ‘Accurate Wavelength Measurement of the Absorption Lines in H2O Vapour by a 0.8μm AlGaAs Laser’,Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 23 (1984) L117.
V. Pevtschin andS. Ezekiel, ‘Investigation of Absolute Stability of Water-vapour-stabilized Semiconductor Laser’,Optics Lett. 12 (1987) 172.
T. Yabuzaki, A. Ibaragi, H. Hori, M. Kitano andT. Ogawa, ‘Frequency-Locking of a GaAlAs Laser to a Doppler-free Spectrum of the Cs-D2 Line’,Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 20 (1981) L451.
H. Tsuchida, M. Ohtsu, T. Tako, N. Kuramochi andM. Oura, ‘Frequency Stabilization of AlGaAs Semiconductor Laser Based on the85Rb-D2 Line’,Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 21 (1982) L561.
S. Yamaguchi andM. Suzuki, ‘Frequency Stabilization of a Diode Laser by use of the Optogalvanic Effect’,Appl. Phys. Lett.,41 (1982) 597.
T. Yanagawa, S. Saito andY. Yamamoto, ‘Frequency Stabilization of 1.5μm InGaAsP Distributed Feedback Laser to NH3 Absorption Lines’Appl. Phys. Lett.,45 (1984) 826.
A. Sollberger, A. Heinamaki andH. Melchior, ‘Frequency Stabilization of Semiconductor Lasers for Applications in Coherent Communication System’J. Lightwave Technol. LT-5 (1987) 485.
F. Favre andD. Le Guen, Emission Frequency Stability in Single-mode-fibre Optical Feedback Controlled Semiconductor Lasers’,Electron. Lett. 19 (1983) 663.
R. Wyatt andW. J. Devlin, ‘10 kHz Linewidth 1.5μm InGaAsP External Cavity Laser with 55 nm Tuning Range’,Electron. Lett. 19 (1983) 110.
F. Favre, D. Le Guen andJ. C. Simon, ‘Optical Feedback Effects upon Laser Diode Oscillation Field Spectrum’,IEEE J. Quantum Electron. QE-18 (1982) 1712.
R. Lang andK. Kobayashi, 'External Optical Feedback Effects on Semiconductor Injection Laser Properties,IEEE J. Quantum Electron. QE-16 (1980) 347.
D. Lentra, B. H. Verbeek andA. J. Den Boef, ‘Coherence Collapse in Single-Mode Semiconductor Lasers Due to Optical Feedback’,IEEE J. Quantum Electron. QE-21 (1985) 674.
M. Ohtsu andS. Kotajima, ‘Linewidth Reduction of a 1.5μm InGaAsP Laser by Electrical Feedback’,Jpn J. Appl. Phys. 24 (1985) L256.
M. Ohtsu, ‘Linewidth Reduction of a Semiconductor Laser by Electrical Feedback’,Dig. Tech. Papers, Conf. Lasers and Electro-Optics, Baltimore, 1985, Postdeadline Paper THZ5.
M. Ohtsu andS. Kotajima, ‘Linewidth Reduction of a Semiconductor Laser by Electrical Feedback’,IEEE J. Quantum Electron. QE-21 (1985) 1905.
S. Saito, O. Nilsson andY. Yamamoto, ‘Frequency Modulation Noise and Linewidth Reduction in a Semiconductor Laser by Means of Negative Frequency Feedback Technique’,Appl. Phys. Lett. 46 (1985) 3.
M. Ohtsu, ‘Demonstration and Application of Frequency Stabilization and Linewidth Reduction in Semiconductor Lasers’,Dig. Tech. Papers, Conf. Lasers and Electro-Optics, San Francisco, 1986, p. 154.
D. Welford andA. Mooradian, ‘Output Power and Temperature Dependence of the Linewidth of Single-frequency CW (GaAl)As Diode Laser’,Appl. Phys. Lett. 40 (1982) 865.
M. Osinski andJ. Buus, ‘Linewidth Broadening Factor in Semiconductor Lasers — An Overview’,IEEE J. Quantum Electron. QE-23 (1987) 9.
D. Hornbuckle, ‘GaAs IC Direct-Coupled Amplifiers’,IEEE MTT-S Int. Microwave Symp. Dig., Washington, DC, 1980, p. 387.
M. Ohtsu andS. Araki, ‘Using a 1.5μm DFB InGaAsP Laser in a Passive Ring Cavity-type Fibre Gyroscope’,Appl. Optics,26 (1987) 464.
S. Kobayashi andT. Kimura, ‘Injection Locking in AlGaAs Semiconductor Laser’,IEEE J. Quantum Electron. QE-17 (1981) 681.
K. Kuboki andM. Ohtsu, ‘Frequency Offset Locking of AlGaAs Semiconductor Lasers’,IEEE J. Quantum Electron. QE-23 (1987) 388.
K. Emura, M. Shikada, S. Fujita, I. Mito, H. Honmou andK. Minemura, ‘Novel Optical FSK Heterodyne Single Filter Detection System Using a Directly Modulated DFB-laser Diode”,Electron. Lett. 20 (1984) 1022.
F. Favre andD. Le Guen, ‘Spectral Narrowing by Optical Feedback’,Proc. Int. Conf. Lasers, San Francisco, 1983, p. 79.
F. M. Gardner, ‘Phaselock Technique’ (John Wiley & Sons, New York, 1979).
M. Ohtsu, ‘Ultrahigh Coherence in Semiconductor Lasers’,Tech. Dig. Optical Fibre Communication Conf./ Sixth Int. Conf. on Integrated Optics and Optical Fibre Communication, Reno, 1987, Paper TUC5, p. 52.
K. H. Cameron, M. R. Matthews, T. G. Hodgkinson andW. J. Devlin, ‘Frequency-Stable Packaged 20-kHz Linewidth 1.5μm InGaAsP External Cavity Laser Used in an Experimental Heterodyne Optical Fibre System’,Tech. Dig. Conf. Lasers and Electro-Optics, Baltimore, 1985, PaperTUC5.
B. Broberg, F. Koyama, Y. Tohmori andY. Suematsu, ‘1.53μm DFB Lasers by Mass Transport’,Electron. Lett. 20 (1984) 692.
Y. Suematsu, ‘Semiconductor Lasers and Optical Integrated Circuits’ (Ohm-sha Publishing, Tokyo, 1984) (in Japanese).
Y. Arakawa andA. Yariv, ‘Enhanced Modulation Performance and Reduced Quantum Noise in Quantum Well Lasers’,Tech. Dig. Conf. Lasers and Electro-Optics, Baltimore, 1985, PaperWH5, p. 90.
T. Fujita, J. Ohya, K. Matsuda, M. Ishino, H. Sato andH. Serizawa, ‘Narrow Spectral Linewidth Characteristics of Monolithic Integrated-passive-cavity InGaAsP/InP Semiconductor Lasers’,Electron. Lett. 21 (1985) 374.
S. Murata, S. Yamazaki, I. Mito andK. Kobayashi, ‘Spectral Characteristics for 1.3μm Monolithic External Cavity DFB Lasers’,Electron. Lett. 22 (1986) 1197.
T. Tohmori, Y. Suematsu, H. Tsushima andS. Arai, ‘Wavelength Tuning of GaInAsP/InP Integrated Lasers with Butt-jointed Built-in Distributed Bragg Reflector”,Electron. Lett. 19 (1983) 656.
L. D. Westbrook, A. W. Nelson, P. J. Fiddyment andJ. V. Collins, ‘Monolithic 1.5μm Hybrid DFB/ DBR Lasers with 5 nm Tunining Range’,Electron. Lett. 20 (1984) 957.
Y. Yamazaki, K. Emura, M. Shikada, M. Yamaguchi andI. Mito, ‘Realization of Flat FM Response by Directly Modulating a Phase Tunable DFB Laser Diode’,Electron. Lett. 21 (1985) 283.
Y. Yoshikuni andG. Motosugi, ‘Multielectrode Distributed Feedback Laser for Pure Frequency Modulation and Chirping Suppressed Amplitude Modulation’,J. Lightwave Technol. LT-5 (1987) 516.
J. L. Hall, D. Hills, C. Salomon andM. Rayman, ‘Stable Lasers: Progress and Applications’,Tech. Dig. Conf. Lasers and Electro-Optics, Baltimore, 1985, PaperFM3, p. 294.
K. Iga andB. I. Miller, ‘GaInAsP/InP Laser with Monolithically Integrated Monitoring Detector’,Electron. Lett. 16 (1980) 342.
V. W. S. Chan, ‘Space Coherent Optical Communication Systems — An Introduction’,J. Lightwave Technol. LT-5 (1987) 633.
F. Durnst, A. Melling andJ. H. Whitelaw, ‘Principle and Practice of Laser-Doppler Anemometry’ (Academic Press, New York, 1976).
T. G. Giallorenzi, J. A. Bucaro, A. Dandridge, G. J. Sigel, Jr, J. H. Cole, S. C. Rashleigh andR. C. Priest, ‘Optical Fiber Sensor Technology’,IEEE J. Quantum Electron. QE-18 (1982) 626.
N. Takeuchi, H. Baba, K. Sakurai andT. Ueno, ‘Diode-laser random-modulation cw lidar’,Appl. Opt. 25 (1986) 63.
M. Hashimoto andM. Ohtsu, ‘Experiments on a Semiconductor Laser Pumped Rubidium Atomic Clock’,IEEE J. Quantum Electron. QE-23 (1987) 446.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ohtsu, M. Frequency stabilization in semiconductor lasers. Opt Quant Electron 20, 283–300 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00620246
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00620246