Summary
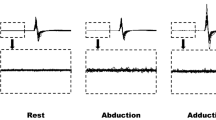
Cortical potentials associated with unilateral and bilateral simultaneous thumb opposition were studied in 9 healthy subjects. The P1 component, “pre-motion positivity”, was recognized in 5 out of 9 subjects on unilateral thumb movement. In all subjects in whom P1 was recognized, P1 was dominant over the cerebral hemisphere ipsilateral to the contracting muscles. On bilateral simultaneous thumb movement, however, P1 was not discerned in any subject. This is compatible with the assumption that P1 is related to an inhibition of imitative movement of the opposite hand (mirror movement). The N2 component had its onset after the start of muscle contraction in most cases, suggesting that N2 might not reflect activation of the corticospinal pathways.
Zusammenfassung
Corticale Potentiale, assoziiert mit unilateralen und bilateralen gleichzeitigen Daumenoppositionen, wurden bei 9 gesunden Männern studiert. Die P1-Komponente, „prämotorische Positivierung“, wurde an der unilateralen Daumenbewegung bei 5 der 9 Versuchspersonen beobachtet. Bei allen Versuchspersonen, bei welchen P1 gesehen wurde, war P1 dominant über der homolateralen Hemisphäre. Bei bilateraler gleichzeitiger Daumenbewegung wurde P1 bei keiner Versuchsperson gefunden. Dieser Befund ist kompatibel mit der Annahme, daß P1 in Beziehung mit einer Hemmung der imitatorischen Bewegung der gegenseitigen Hand (mirror movement) steht. Die N2-Komponente begann in den meisten Fällen nach dem Beginn der Muskelkontraktion. Dieser Befund läßt vermuten, daß N2 nicht die Aktivierung der corticospinalen Bahnen reflektiert.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Becker, W., Hoehne, O., Iwase, K., Kornhuber, H. H.: Bereitschaftspotential, prämotorische Positivierung und andere Hirnpotentiale bei sakkadischen Augenbewegungen. Vis. Res.12, 421–436 (1972)
Brodal, A.: Neurological anatomy, 2nd ed., 159 p. London: Oxford University Press 1969
Deecke, L., Scheid, P., Kornhuber, H. H.: Distribution of readiness potential, pre-motion positivity, and motor potential of the human cerebral cortex preceding voluntary finger movements. Exp. Brain Res.7, 158–168 (1969)
Donchin, E., Otto, D., Gerbrandt, L. K., Pribram, K. H.: While a monkey waits: Electrocortical events recorded during the foreperiod of a reaction time study. Electroenceph. clin. Neurophysiol.31, 115–127 (1971)
Gerbrandt, L. K., Goff, W. R., Smith, D. B.: Distribution of the human average movement potential. Electroenceph. clin. Neurophysiol.34, 461–474 (1973)
Gilden, L., Vaughan, H. G., Jr., Costa, L. D.: Summated human EEG potentials with voluntary movement. Electroenceph. clin. Neurophysiol.20, 433–438 (1966)
Green, J. B.: An electromyographic study of mirror movements. Neurology (Minneap.)17, 91–94 (1967)
Järvilehto, T., Fruhstorfer, H.: Differentiation between slow cortical potentials associated with motor and mental acts in man. Exp. Brain Res.11, 309–317 (1970)
Karlin, L., Marty, M. J., Brauth, S. E., Mordkoff, A. M.: Auditory evoked potentials, motor potentials and reaction time. Electroenceph. clin. Neurophysiol.31, 129–136 (1971)
Kornhuber, H. H., Deecke, L.: Hirnpotentialänderungen bei Willkürbewegungen und passiven Bewegungen des Menschen: Bereitschaftspotential und reafferente Potentiale. Pflügers Arch. ges. Physiol.284, 1–17 (1965)
McAdam, D. W., Rubin, E. H.: Readiness potential, vertex positive wave, contingent negative variation and accuracy of perception. Electroenceph. clin. Neurophysiol.30, 511–517 (1971)
Oikawa, T., Fujitani, Y., Uematsu, S.: Cerebral motor potentials accompanying voluntary and reactive movements. Electroenceph. clin. Neurophysiol.32, 204 (1972)
Rosenfeld, J. P., Fox, S. S.: Movement-related macropotentials in cat cortex. Electroenceph. clin. Neurophysiol.32, 75–80 (1972)
Vaughan, H. G., Jr., Costa, L. D., Gilden, L., Schimmel, H.: Identification of sensory and motor components of cerebral activity in simple reaction time tasks. Proc. 73rd Conv. Amer. Psychol. Assoc.1, 179–180 (1965)
Vaughan, H. G., Jr., Costa, L. D., Ritter, W.: Topography of the human motor potential. Electroenceph. clin. Neurophysiol.25, 1–10 (1968)
Vaughan, H. G., Jr., Gross, E. G., Bossom, J.: Cortical motor potential in monkeys before and after upper limb deafferentation. Exp. Neurol.26, 253–262 (1970)
Walshe, F. M. R.: On the role of the pyramidal system in willed movements. Brain70, 329–354 (1947)
Wilke, J. T., Lansing, R. W.: Variations in the motor potential with force exerted during voluntary arm movements in man. Electroenceph. clin. Neurophysiol.35, 259–265 (1973)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shibasaki, H., Kato, M. Movement-associated cortical potentials with unilateral and bilateral simultaneous hand movement. J. Neurol 208, 191–199 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00630632
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00630632