Summary
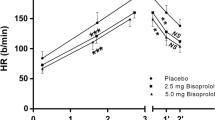
The effect of verapamil (240 mg) on exercise capacity was studied during a short graded and a single-level endurance exercise test in 12 normal volunteers; it was compared to the effects of atenolol (100 mg × day−1). Intake of verapamil, atenolol and placebo, administered according to a randomized, double-blind cross-over design, was started 3 days before the exercise tests. Compared to placebo, verapamil did not affect peak oxygen uptake in the graded test or exercise duration in the endurance test. Heart rate, systolic blood pressure, rating of perceived exertion and respiratory data at submaximal and peak exercise were unaffected in either test. On the other hand atenolol reduced maximal oxygen uptake by 5% (p<0.001) and endurance exercise duration by 17% (p<0.05). Besides marked decreases in heart rate and systolic blood pressure during the two types of exercise, atenolol also reduced oxygen uptake at submaximal exercise levels and it increased the rating of perceived exertion (p<0.05), the latter only during the endurance exerice test.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ambrosioni E, Costa FV, Montebugnoli L, Bassein L, Marchesini B, Magnani B (1983) Comparison of antihypertensive efficacy of atenolol, oxprenolol and pindolol at rest and during exercise. Drugs [Suppl 25] 2:30–36
Belz GG, Spies G (1985) A controlled study of slow-release verapamil in anihypertensive therapy. Z Kardiol 74:453–459
Fellenius E (1983) Muscle fatigue andβ-blockers —A review. Int J Sports Med 4:1–8
Franciosa J, Wilen M (1984) Nitrendipine effects on exercise and hemodynamics in hypertension. Clin Pharmacol Ther 35:241
Franz I-W, Wiewel D (1984) Antihypertensive effects on blood pressure at rest and during exercise of calicum antagonists,β-receptor blockers, and their combination in hypertensive patients. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol [Suppl 7] 6:S1037-S1042
Frishman WH, Klein NA, Klein P et al. (1982) Comparison of oral propranolol and verapamil for combined systemic hypertension and angina pectoris. Am J Cardiol 50:1164–1172
Galbo H, Christensen NJ, Holst JJ (1977) glucose-induced decrease in glucagon and epinephrine responses to exercise in man. J Appl Physiol 42:525–530
Hespel P, Lijnen P, Vanhees L, Fagard R, Fiocchi R, Moerman E, Amery A (1986) Differentiation of exercise-induced metabolic responses during selectiveβ 1- andβ 2-antagonism. Med Sci Sports Exerc 18:186–191
Ishizaki T, Oyama Y (1983) Atenolol dose-finding studies. Drugs [Suppl 25] 2:42–49
Kaiser P (1984) Physical performance and muscle metabolism duringβ-adrenergic blockade in man. Acta Physiol Scand 84, supp 536:1–53
Kindermann W, Schnitt W, Stengele E (1985) Influence of calcium antagonists on physical capacity and metabolism. Dtsch Med Wochenschr 110:1657–1661
Klein M, Weiner D, Kellett M (1986) Regular formation and sustained-release verapamil therapy in normotension and in mild to moderate hypertension. Am J Cardiol 57:69D-73D
Leenen FHH, Coener CHM, Zondersland M, Maas AHJ (1980) Effects of cardioselective and non-selectiveβ-blockade on dynamic exercise performance in mildly hypertensive men. Clin Pharmacol Ther 28:12–21
Leonetti G, Cuspidi C, Sampieru L, Terzoli L, Zanchetti A (1982) Comparison of cardiovascular, renal, and humoral effects of acute administration of two calcium channel blockers in normotensive and hypertensive subjects. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 4:S319-S324
Lundborg P, Åstrom H, Bengtsson C, Fellenius E, Von Schenck H, Svensson L, Smith U (1981) Effect ofβ-adrenoceptor blockade on exercise performance and metabolism. Clin Sci 61:299–305
Lund-Johansen P (1985) Hemodynamic effects of calcium channel blockers at rest and during exercise in essential hypertension. Am J Med [Suppl 79] 4A:11–18
Mooy J, Böhm R, Petri H, Van Kemenade J, Rahn KH (1986) The effects of verapamil and propranolol on exercise tolerance in hypertensive patients. In prepartion
Pearson SB, Banks DC, Patrick JM (1979) The effect ofβ-adrenoceptor blockade on factors affecting exercise tolerance in normal man. Br J Pharmacol 8:143–148
Petri H, Arends BG, Van Baak MA (1986) The effect of verapamil on cardiovascular and metabolic responses during exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol 55:499–502
Pool PE, Seagren SC, Salel AF (1985) Effects of diltiazem on serum lipids, exercise performance and blood pressure: randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled evaluation for systemic hypertension. Am J Cardiol 56:86H-91H
Raffestin B, Denjean A, Legrand A, Derrieux C, Biollot J, Comoy E, Martre H, Lockhart A (1985) Effects of nifedipine on responses to exercise in normal subjects. J Appl Physiol 58:702–709
Reybrouck T, Amery A, Billiet L (1977) Hemodynamic response to graded exercise after chronic beta-adrenergic blockade. J Appl Physiol 42:133–138
Stein D, Lowenthal D, Porter S, Falkner B, Bravo E, Hare T (1984) Effects of nifedipine and verapamil on isometric, and dynamic exercise in normal subjects. Am J Cardiol 54:386–389
Stern HC, Matthews JH, Belz GG (1986) Intrinsic and reflex actions of verapamil and nifedipine: assessment in normal subjects by noninvasive techniques and autonomic blockade. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 29:541–547
Tesch PA, Kaiser P (1983) Effects ofβ-adrenergic blockade on O2 uptake during submaximal and maximal exercise. J Appl Physiol 54:901–905
Verstappen FTJ, Van Baak MA (1987) Exercise capacity, energy metabolism, and beta-adrenoceptor blockade. Eur J Appl Physiol 56:712–718
Yamakado T, Oonishi N, Kondo S, Noziri A, Nakano T, Takezowa H (1983) Effects of diltiazem on cardiovascular responses during exercise in systemic hypertension and comparison with propranolol. Am J Cardiol 52:1023–1027
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vanhees, L., Fagard, R. & Amery, A. Effect of calcium channel blockade and beta-adrenoceptor blockade on short graded and single-level endurance exercises in normal men. Europ. J. Appl. Physiol. 58, 87–91 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00636608
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00636608