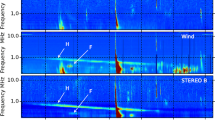
Abstract
Until the ULYSSES spacecraft reached high latitude, the only means for measuring the solar wind velocity in the polar regions was from radio scattering observations (IPS), and these remain the only way to measure the velocity near the sun. However, IPS, like many remote sensing observations, is a “line-of-sight” integrated measurement. This integration is particularly troublesome when the line-of-sight passes through a fast stream but that stream does not occupy the entire scattering region. Observations from the HELIOS spacecraft have shown that the solar wind has a bimodal character which becomes more pronounced near the sun. Recent observations from ULYSSES have confirmed that this structure is clear at high latitudes even at relatively large solar distances. We have developed a method of separating the fast and slow contributions to an IPS observation which takes advantage of this bimodal structure. In this paper I will describe the technique and its application to IPS observations made using the receiving antennas of the EISCAT incoherent backscatter radar observatory in northern Scandinavia.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Axford, W. I., this volume, 1995.
Axford, W. I. and J. F. McKenzie, in preparation, 1995.
Armstrong, J. W., W. A. Coles, M. Kojima and B. J. Rickett, Solar wind observations near the sun inThe Sun and the Heliosphere in Three-Dimensions, ed. R. G. Marsden (North Holland: Reidel) 1986.
Bourgois, G., W. A. Coles, G. Daigne, J. Silen, T. Turunen and P. J. Williams, Measurements of the solar wind velocity with EISCAT,Astron. Astrophys. 144, 452–462, 1985.
Bourgois, G. and Coles, W. A., Solar cycle changes in the turbulence level of the polar stream near the sun, In em Solar Wind Seven, ed. E. Marsch and R. Schwenn, Pergamon: Oxford, p 158, 1992.
Coles, W. A. and S. Maagoe, Solar wind velocity from IPS observations,J. Geophys. Res. (Lett.), 77, 5622, 1972.
Coles, W. A., R. Esser, U.-P. Løvhaug, and J. Markkanen, Comparison of solar wind velocity measurements with a theoretical acceleration model,J. Geophys. Res., 96, 13849, 1991.
Coles, W. A., R. R. Grall, M. T. Klinglesmith and G. Bourgois,J. Geophys. Res., submitted, 1995.
Dennison, P. A. and Hewish, A., The solar wind outside the plane of the ecliptic,Nature 213, 343–346, 1967.
Ekers, R. D. and L. T. Little, The motion of the solar wind close to the sun,Astron. Astrophys. 10, 310–316, 1971.
Hewish, A. and M. D. Symonds, Radio investigation of the solar plasma,Planet. Space Sci. 17, 313, 1969.
Kojima, K., Y. Ishida, K. Maruyama and T. Kakinuma, An observation system of interplanetary scintillation at UHF,Proc. Res. Inst. Atmospherics of Nagoya Univ. 29, 61, 1982.
Manoharan, P. K., Three-dimensional structure of the solar wind: variation of density with the solar cycle,Solar Phys. 148, 153–167, 1993.
Marsch, E. and C.-Y. Tu, Spectral and spatial evolution of compressive turbulence in the inner solar wind,J. Geophys. Res. 95, 11945, 1990.
Phillips, J. L., A. Balogh, S. J. Bame, B. E. Goldstein J. T. Gosling, J. T. Hoeksema, D. J. McComas, M. Neugebauer, N. R. Sheeley, Jr., and Y.-M. Wang, ULYSSES at 50o south: Constant immersion in the high-speed solar wind,Geophys. Res. Lett., in press, 1994.
Schwenn, R., The large scale structure of the interplanetary medium, InPhysics, of the Inner Heliosphere, 1: eds. R. Schwenn and E. Marsch (Springer-Verlag, Heidelberg), 99–181, 1990.
Scott, S. L., W. A. Coles, and G. Bourgois, Solar wind observations near the Sun using interplanetary scintillation,Astron. Astrophys. 123, 207, 1983.
Vitkevitch V. V. and V. I. Vlasov, Radio astronomical investigation of the drift of the inhomogeneous interplanetary plasma,Sov. Astron. A. J. 13, 669–676, 1970.
Watanabe, T., T. Kakinuma, M. Kojima and K. Shibasaki, Solar wind disturbance detected by the interplanetary scintillation of radio sources in early August 1972,J. Geophys. Res. 78, 8364–8366, 1973.
Wilcox J. M. and A. J. Hundhausen Comparison of heliospheric current sheet structure obtained from potential magnetic field computations and from observed polarized coronal brightness,J. Geophys. Res. 88, 8095, 1983.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Coles, W.A. A bimodal model of the solar wind speed. Astrophys Space Sci 243, 87–96 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00644037
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00644037