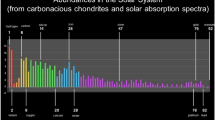
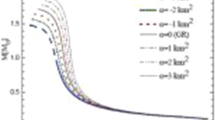
Abstract
A model of the galaxy is constructed and evolved in which the integrated influence of stellar and supernova nucleosynthesis on the composition of the interstellar gas is traced numerically. Our detailed assumptions concerning the character of the matter released from evolving stars and supernovae are guided by the results of recent stellar evolutionary calculations and hydrodynamic studies of supernova events. Stars of main sequence mass in the range 4≤M≤8M ⊙ are assumed to give rise to supernova events, leaving remnants we identify with neutron stars and pulsars and forming both the carbon-to-iron nuclei and ther-process heavy elements in the explosive ejection of the core material. For more massive stars, we assume the core implosion will result in the formation of a Schwarzschild singularity, that is, a black hole or ‘collapsar’. The straightforward assumptions (1) that the gas content of the galaxy decreases exponentially with time to its present level of ∼5% and (2) that the luminosity function characteristic of young clusters and the solar neighborhood is appropriate throughout galactic history, lead to the prediction that ≈ 20% of the unevolved stars of approximately one solar mass (M ⊙) in the galaxy today should have metal compositionsZ≲0.1Z ⊙. As Schmidt has argued from similar reasoning, this is quite inconsistent with current observations; an early generation dominated by more massive stars—which would by now have evolved—is suggested by this difficulty. Many of these massive stars, according to our assumptions, will end their lives as collapsed black hole remnants. It is difficult to visualize an epoch of massive star formation in the collapsing gas cloud which formed our galaxy which would enrich the gas rapidly enough to account for the level of heavy element abundances in halo population stars; we have therefore proposed a stage of star formation which is entirely pregalactic in character. We suggest that the Jeans' length-sized initial condensations in the expanding universe discussed by Peebles and Dicke may provide the appropriate setting for this first generation of stars. Guided by these considerations, and by the need for a substantial quantity of ‘unseen’ mass to bind our local group of galaxies, we have constructed a model of the galaxy in which this violent early phase of massive star formation produces both (1) approximately 25% of the level of heavy elements observed in the solar system and (2) an enormous unseen mass in the form of black holes. The implications of our model for other features of the galaxy, including supernova nucleosynthesis, the cosmic ray production of the light elements, and cosmochronology, are discussed in detail.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander, E. C. Jr., Lewis, R. S. Reynolds, J. H. and Michel, M. C.: 1971, ‘Plutonium-244: Confirmation as an Extinct Radioactivity’, preprint.
Arnett, W. D.: 1967,Can. J. Phys. 45, 1621.
Arnett, W. D.: 1969a,Astrophys. Space Sci. 5, 180.
Arnett, W. D.: 1969b,Astrophys. J. 157, 1369.
Arnett, W. D., Truran, J. W., and Woosley, S. E.: 1971,Astrophys. J. 165, 87.
Barkat, Z.: 1971,Astrophys. J. 163, 433.
Barkat, Z., Buchler, J.-R. and Wheeler, J. C.: 1971, ‘Beta-Processes in Exploding Stars’, preprint.
Bodenheimer, P.: 1966,Astrophys. J. 144, 103.
Burbidge, E. M.and Burbidge, G. R.: 1971, ‘The Masses of Galaxies, inStars and Stellar Systems, Vol. IX, Galaxies and the Universe(eds. A. Sandage and M. Sandage), University of Chicago Press, Chicago, to be published.
Burbidge, E. M., Burbidge, G. R., Fowler, W. A., and Hoyle, F.: 1957,Rev. Mod. Phys. 29, 547.
Buchler, J.-R.,Wheeler, J. C., and Barkat, Z.: 1971, ‘Thermonuclear Detonations in Evolved Stellar Cores’, preprint.
Cameron, A.G.W.: 1957, Chalk River Rept. CRL-41.
Cameron, A. G. W.: 1968, inOrigin and Distribution of the Elements (ed. L. H. Ahrens), Pergamon Press, Oxford.
Cameron, A. G. W.: 1970,Ann. Rev. Astron.Astrophys. 8, 179.
Cameron, A. G. W., Delano, M. D.,and Truran, J. W.: 1970, inProceedings of the International Conference on the Properties of Nuclei far from the Valley of Beta-Stability, Vol. 2, CERN.
Cameron, A. G. W. and Fowler, W. A.: 1971,Astrophys. J. 164, 111.
Cameron, A. G. W. and Truran, J. W.: 1971,J. Roy. Astron. Soc. Can. 65, 1.
Caughlan, G. R. and Fowler, W. A.: 1962,Astrophys. J. 136, 453.
Chandrasekhar, S.: 1939,An Introduction to the Study of Stellar Structure, University of Chicago Press, Chicago.
Clifford, F. E. and Taylor, R. J.: 1965,Mem. Roy. Astron. Soc. 69, 21.
Colgate, S. A.: 1971,Astrophys. J. 163, 221.
Colgate, S. A. and White, R. H.: 1966,Astrophys. J. 143, 626.
Deutsch, A. J.: 1969, inMass Loss from Stars (ed. M. Hack), D. Reidel Publ. Co., Dordrecht, Holland.
Dicke, R. H.: 1969,Astrophys. J. 155, 123.
Ezer, D. and Cameron, A. G. W.: 1967,Can. J. Phys. 45, 3429.
Ezer, D. and Cameron, A.G.W.: 1971, ‘The Evolution of Hydrogen-Helium Stars’, preprint.
Fowler, W. A.: 1971, ‘New Observations and Old Nucleocosmochronologies’,preprint.
Fowler, W. A., Burbidge, G. R., and Burbidge, E. M.: 1955,Astrophys. J.Suppl. 2, 167.
Fowler, W. A., Greenstein, J. L., and Hoyle, F.: 1962,Geophys. J. 6, 148.
Gunn, J. E., and Ostriker, J. P.: 1970,Astrophys. J. 160, 979.
Hansen, C. J. and Wheeler, J. C.: 1969,Astrophys. Space Sci. 3, 464.
Hayashi, C., Hoshi, R., and Sugimoto, D.: 1962,Prog. Theor. Phys.Suppl. 22, 1.
Henyey, L. G., LeLevier, R.,and Levee, R. D.: 1959,Astrophys. J. 129, 2.
Hirasawa, T.: 1971, ‘Formation of Protogalaxies and Molecular Processes in Hydrogen Gas’, preprint.
Hohenberg, C. M.: 1969,Science 166, 212.
Iben, I., Jr: 1965,Astrophys. J. 142, 1447.
Iben, I., Jr.:1966a,Astrophys. J. 143, 483.
Iben, I., Jr.:1966b,Astrophys. J. 143, 505.
Iben, I., Jr.:1966c,Astrophys. J. 143, 516.
Iben, I., Jr.:1967a,Astrophys. J. 147, 624.
Iben, I., Jr.: 1967b,Astrophys. J. 147, 650.
Iben, I. and Rood, R. D.: 1970,Astrophys. J. 161, 587.
Kodaira, K., Greenstein, J. L., and Oke, J. B.: 1970,Astrophys. J. 159, 485.
King, I. R.: 1967, Draft Report I.A.U., p. 846.
King, I. R.: 1968,Astron. J. 71, 276.
Kuhi, L. R.: 1966,Astrophys. J. 143, 991.
Larson, R. B. and Starrfield, S.: 1971, ‘On the Formation of Massive Stars and the Upper Limit of Stellar Masses’, preprint.
LeBlanc, J. M. and Wilson, J. R.: 1970,Astrophys. J. 161, 541.
Limber, D. N.: 1960,Astrophys. J. 131, 168.
McClure, R. D. and van den Bergh, S.: 1968,Astron. J. 73, 313.
Mitler, H. E.: 1967, inHigh Energy Reactions in Astrophysics (ed. B.S.P. Shen), W. J. Benjamin, Inc., New York.
Mitler, H. E.: 1970, Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory, Special Report No. 330.
Oort, J. H.: 1970,Astron. Astrophys. 7, 381.
Paczynski, B.: 1970,Acta Astron. 20, 47.
Page, T.: 1965, Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory,Special Report No. 195.
Pagel, B. E. J.: 1968, inOrigin and Distribution of the Elements (ed. L. H. Ahrens), Pergamon Press, Oxford.
Partridge, R. B. and Peebles, P. J. E.: 1967,Astrophys. J. 148, 377.
Peebles, P.J.E.: 1969,Astrophys. J. 155, 393.
Peebles, P. J. E.: 1971,Astron. Astrophys. 11, 377.
Peebles, P. J. E. and Dicke, R.: 1968,Astrophys. J. 154, 891.
Podosek, F. A.: 1970,Earth Planet, Sci. Letters 8,183.
Reeves, H., Fowler, W. A., and Hoyle, F.: 1969,Nature 226, 727.
Rose, W. K.: 1966,Astrophys. J. 146, 838.
Rose, W. K.: 1967,Astrophys. J. 150, 193.
Rose, W. K.: 1969,Astrophys. J. 155, 491.
Salpeter, E. E.: 1955,Astrophys. J. 121, 161.
Salpeter, E. E.: 1959,Astrophys. J. 129, 608.
Sandage, A. R.: 1957,Astrophys. J. 125, 422.
Sanders, R. H.: 1967,Astrophys. J. 150, 971.
Schmidt, M.: 1959,Astrophys. J. 129, 243.
Schmidt, M.: 1963,Astrophys. J. 137, 758.
Schramm, D. N. and Wasserburg, G. R.: 1970,Astrophys. J. 162, 57.
Schwarzschild, M. and Harm, R.: 1958,Astrophys. J. 128, 348.
Schwarzschild, M. and Harm, R.: 1965,Astrophys. J. 142, 855.
Schwarzschild, M. and Harm, R.: 1967,Astrophys. J. 150, 961.
Schwarzschild, M. and Spitzer, L.: 1953,Observatory 73, 77.
Seeger, P. A.: 1970, inProceedings of the International Conference on the Properties of Nuclei far from the Valley of Beta-Stability, Vol. 1, CERN.
Seeger, P. A., Fowler, W. A. and Clayton, D. D.: 1965,Astrophys. J. Suppl. 97, 121.
Seeger, P. A., and Schramm, D. N.: 1970,Astrophys. J. 160, L157.
Shklovsky, I. S.: 1968,Supernovae, Wiley and Sons, London.
Simoda, M. and Kimura, H.: 1968,Astrophys. J. 151, 133.
Spinrad, H.: 1966,Publ. Astron. Soc. Pacific 78, 367.
Spinrad, H., Greenstein, J. L., Taylor, B. J., and King, I. R.: 1970,Astrophys. J. 162, 891.
Spinrad, H., and Taylor, B. J.: 1969,Astrophys.J. 157, 1279.
Tammann, G. A.: 1970,Astron. Astrophys. 8, 458.
Truran, J. W. and Arnett, W. D.: 1970,Astrophys. J. 160, 181.
Truran, J. W., Arnett, W. D. and Cameron, A. G. W.: 1967,Can. J. Phys. 45, 2315.
Truran, J. W. and Cameron, A. G. W.: 1970,Nature 225, 710.
Truran, J. W., Cameron, A. G. W., and Hilf, E.: 1970, inProceedings of the International Conference on the Properties of Nuclei far from the Valley of Beta-Stability, Vol. 1, CERN.
Truran, J. W., Hansen, C. J., and Cameron, A. G. W.: 1965,Can. J. Phys. 43, 1616.
Van den Bergh, S.: 1957,Astrophys. J. 125, 445.
Wagoner, R. V., Fowler, W. A. and Hoyle, F.: 1967,Astrophys. J. 148, 3.
Wallerstein, G., Greenstein, J.L., Parker, R., Helper, H. L.,and Aller, L. H.: 1963,Astrophys. J. 137, 280.
Wasserburg, G. J., Huneke, J. C., and Burnett, D. S.: 1969,J. Geophys. Res. 74, 4221.
Wasserburg, G. J., Schramm, D. N., and Huneke, J. C.: 1969,Astrophys. J. 157,L91.
Weigert, A.: 1966,Z. Astrophys. 64, 395.
Wheeler, J. C., Barkat, Z. and Buchler, J.-R.: 1970,Astrophys. J. Letters 162, L129.
Wheeler, J. C. and Hansen, C. J.: 1971,Astrophys. Space Sci. 11, 373.
Wilson, J. R.: 1971,Astrophys. J. 163, 209.
Wyller, A. A.: 1970,Astrophys. J. 160, 443.
Ziebarth, K.: 1970,Astrophys. J. 162, 947.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Truran, J.W., Cameron, A.G.W. Evolutionary models of nucleosynthesis in the galaxy. Astrophys Space Sci 14, 179–222 (1971). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00649203
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00649203