Conclusions
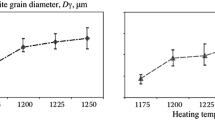
The main reasons for the low plasticity and ductility of maraging steel 00N18K9M5T in large sections are the coarse-grained structure resulting from heating for hot working and the precipitation of carbides or titanium carbonitrides in the form of a network in the grain boundaries.
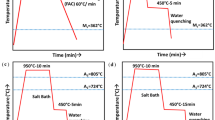
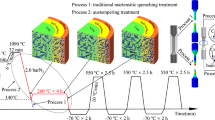
2.To eliminate the carbide and titanium carbonitride precipitates in the form of networks and agglomerates and also to refine the grains it is necessary to use a special heat treatment to dissolve the carbonitride precipitates at 1200° and higher, with rapid cooling from this temperature (in water), followed by triple recrystallization at 900–970° with cooling in water (or oil or fused salts). Such heat treatment substantially increases the plasticity and ductility of the steel and also the resistance to repeated static loading.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
V. D. Sadovskii et al., Transformations During Heating of Steel [in Russian], Metallurgizdat, Moscow (1959).
V. D. Sadovskii et al., Metal. i Term. Obrabotka Metal., No. 4 (1969).
Additional information
All-Union Scientific-Research Institute of Aviation Materials. Translated from Metallovedenie i Termicheskaya Obrabotka Metallov, No. 4, pp. 18–21, April, 1971.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Revyakina, O.K., Belyakov, L.N., Nikol'skaya, V.L. et al. Heat treatment of large forged and pressed bars of steel 00N18K9M5T. Met Sci Heat Treat 13, 285–288 (1971). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00661337
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00661337