Abstract
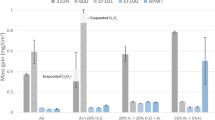
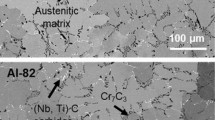
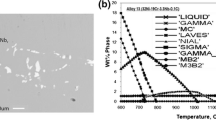
A systematic study is presented of the oxidation of pure iron-chromium-aluminum alloys at 800°C, in pure oxygen, at a pressure of 200 Torr. Oxidation characteristics are described with reference to kinetic measurements, scale topographies and morphologies, and also possible growth mechanisms. An oxide map is used to show that alloys may be classified into four categories depending on the external scale that forms: Fe2O3, Cr2O3, Al2O3, or Al2O3 with iron-oxide nodules. Alloys containing less than 2–2.5 wt. % aluminum formed either Fe2O3 or Cr2O3 as an external scale, depending on the chromium content, and internal, rod-like protrusions of Al2O3. At higher aluminum concentrations, Al2O3 was always present as an external scale, although this was interspersed by iron-oxide nodules at chromium concentrations of less than 5 wt. %. A model based on Wagner's secondary getter concept is proposed for eliminating nodule nucleation. Evidence is also present that indicates that at 800°C, alumina scale decohesion occurs prior to void formation and that voids are the result of thermal etching beneath lifted scales.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
O. Kubaschewski and B. E. Hopkins,Oxidation of Metals and Alloys (Butterworths, London, 1962), p. 237.
S. L. Case and K. R. Van Horn,Aluminum in Iron and Steel (Wiley, New York, 1953), p. 265.
I. G. Wright, MCIC Report 72-07, Columbus, Ohio (1972).
P. Tomaszewicz and G. R. Wallwork,Rev. High Temp. Mat. 4(1), 75 (1978).
E. A. Gulbransen and K. F. Andrew,J. Electrochem. Soc. 106(4), 294 (1959).
W. C. Hagel,Corrosion 21(11), 316 (1965).
C. S. Wukusick and J. F. Collins,Mat. Res. Stand. 4, 637 (1964).
I. Pfeiffer,Z. Metallkd. 53, 309 (1962).
H. Krainer, L. Wetternick, and E. Carius,Arch. Eisenhuttenw. 22, 103 (1951).
J. K. Tien and F. S. Pettit,Met. Trans. 3(6), 1587 (1972).
F. H. Stott, G. C. Wood, and F. A. Golightly,Corros. Sci. 19, 869 (1979).
T. Amano, S. Yajima, and Y. Saito,Trans. Jpn. Inst. Met. 20(8), 431 (1979).
F. H. Stott, G. C. Wood, and M. G. Hobby,Oxid. Met. 3(2), 103 (1971).
F. A. Golightly, F. H. Stott, and G. C. Wood,Oxid. Met. 10(3), 163 (1976).
I. Zaplatynsky, NASA TN D-8462 (1977).
E. A. Gulbransen and K. F. Andrew,Trans. Metall. Soc. AIME 221(12), 1247 (1961).
M. Lambertin, A. Stoklosa, and W. W. Smeltzer,Oxid. Met. 15(3/4), 335 (1981).
N. Iwamoto, Y. Tsunawaki, and S. Matsuda, Trans. JWRI4(2), 45 (1975).
H. Ike and H. Okabe,Trans. Jpn. Inst. Met. 20(4), 186 (1979).
H. Nagai, T. Murai, and H. Nitani,Trans. Jpn. Inst. Met. 20(8), 442 (1979).
I. Kvernes, M. Oliveira, and P. Kofstad,Corros. Sci. 17, 237 (1977).
E. Scheit and E. H. Schulz,Arch. Eisenhuttenw. 6, 155 (1932).
P. Tomaszewicz and G. R. Wallwork,Oxid. Met. 19(5/6), 165 (1983).
P. Tomas, Doctoral dissertation, University of New South Wales, Sydney, Australia (1982).
G. R. Wallwork,Rep. Prog. Phys. 39(5), 401 (1976).
A. U. Seybolt,J. Electrochem. Soc. 107(10), 369 (1952).
C. Wagner,J. Electronchem. Soc. 99(10), 369 (1952).
C. Wagner,J. Electrochem. Soc. 103(11), 627 (1956).
C. Wagner,Z. Elektrochem. 63(7), 772 (1959).
C. Wagner,Corros. Sci. 5, 751 (1965).
C. S. Giggins, E. J. Felten, and F. S. Pettit,Stress Effects and the Oxidation of Metals, J. V. Cathcart, ed. (Metallurgical Society of AIME, New York, 1975), p. 245.
J. D. Kuenzly and D. L. Douglass,Oxid. Met. 8(3), 139 (1974).
E. D. Hondros and A. J. W. Moore,Acta Metall. 8, 647 (1960).
G. E. Rhead and H. Mykura,Acta Metall. 10, 578 (1962).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tomaszewicz, P., Wallwork, G.R. The oxidation of high-purity iron-chromium-aluminum alloys at 800°C. Oxid Met 20, 75–109 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00662042
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00662042