Abstract
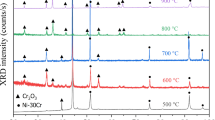
Yttrium ions of 150 keV energy were implanted into the alloys Ni-20Cr, Ni-4Cr, and into nickel. The microstructures were then characterized using transmission electron microscopy, selected area channeling patterns and back-scattered electron images. Low yttrium fluences between 1×1014 and 5× 1015 Y+/cm2 did not alter the microstructures of Ni-20Cr. However, fluences of 1×1016, 5×1016, and 7.5×1016 caused the crystalline structures of the alloy to be replaced by an amorphous phase. Fluences of 7.5×1016 Y+/cm2 also rendered Ni-4Cr and nickel amorphous. Self-ion implantation experiments on Ni-20Cr did not cause the amorphous phase to form. The depth distribution of elements in Ni-20Cr following yttrium ion implantation (7.5× 1016 Y+/cm2) was determined by Auger electron spectroscopy. This showed in addition to the added yttrium a surface depletion in nickel concentration and a simultaneous enrichment in chromium concentration. At approximately 500 Å, the chromium concentration is approximately 32 at.%. This depletion/enrichment zone extends throughout the implanted layer. Annealing the Ni-20Cr implanted with 7.5×1016 Y+/cm2 in vacuum for one hour at 600°C resulted in the recrystallization of Ni-Cr solid solution and the formation of very fine grains of Y2O3. Annealing at 800°C for 5 minutes showed recrystallized Ni-Cr, Y2O3, and an additional phase or phases.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. P. Whittle and J. Stringer,Phil. Trans. Roy. Soc. Lond. A295, 309 (1980).
J. C. Pivin, C. Roques-Carmes, J. Chaumont, and H. Bernas,Corros. Sci. 20, 947 (1980).
F. H. Stott, J. S. Punni, G. C. Wood, and G. Dearnaley, inIon Implantation into Metals, V. Ashworthet al., eds. (Pergamon Press, NY, 1982), p. 245.
D. Loison, J. C. Pivin, and J. Chaumont, inIon Implantation into Metals, V. Ashworthet al., eds. (Pergamon Press, NY, 1982), p. 255.
C. H. Yang, G. E. Welsch, and T. E. Mitchell,Mater. Sci. Eng. 69, 351 (1985).
C. H. Yang, G. Welsch, and T. E. Mitchell,J. Mater. Sci. 25, 1724 (1990).
W. E. King, K. S. Grabowski, D. F. Mitchell, and P. M. Baldo,Oxid. Met. 31, 181 (1989).
P. Y. Hou and J. Stringer,Oxid. Met. 29, 45 (1988).
K. Przybylski, Proc. 10th Int. Symp. on Reactivity of Solids, Dijon, France, Aug. 27–Sept. 1, 1984, inMaterials Science Monographs, Vol. 28, P. Barret and L. C. Dufour, eds. (Elsevier, The Netherlands, 1985), p. 78.
K. Przybylski and G. J. Yurek, The reactive element effect on high temperature oxidation — After fifty years,Materials Science Forum, Vol. 43, W. E. King, ed. (Trans. Tech. Publications, Switzerland, 1989), p. 1.
W. E. King and K. S. Grabowski, inEnvironmental Degradation of Ion and Laser Beam Treated Surfaces, G. S. Was and K. S. Grabowski, eds. (TMS, Pennsylvania, 1989), p. 277.
C. S. Giggins and F. S. Pettit,Trans. TMS-AIME 245, 2509 (1969).
D. I. Potter, M. Ahmed, and S. Lamond,J. Met. 35, 17 (1982).
B. E. Warren,X-Ray Diffraction, Chap. 10 (Addison-Wesley, Reading, Massachusetts, 1969).
M. Ahmed and D. I. Potter,Acta Met. 33, 2221 (1985).
M. Saqib and D. I. Potter,Mater. Sci. Eng. 90, 81 (1987).
J. P. Biersack and L. G. Haggmark,Nucl. Instr. Meth. 174, 257 (1980).
G. R. Booker, inModern Diffraction and Imaging Techniques in Materials Science, S. Amelinckx, R. Gevers, G. Remaut, and J. Van Landuyt, eds. (North-Holland Publishing Company, Amsterdam, 1970), p. 613.
M. Ahmed and D. I. Potter,Acta Met. 35, 2341 (1987).
J. M. Hampikian, O. F. Devereux, and D. I. Potter,Mater. Sci. Eng. A116, 119 (1989).
V. Goerlach, P. Ziemann, and W. Buckel,Nucl. Inst. Meth. 209/210, 235 (1983).
D. I. Potter,Defect Diffusion Forum,61, 13 (1988).
C. S. Giggins and F. S. Pettit,Trans. TMS-AIME 245, 2495 (1969).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hampikian, J.M., Potter, D.I. The effects of yttrium ion implantation on the oxidation of nickel-chromium alloys. I. The microstructures of yttrium implanted nickel-chromium alloys. Oxid Met 38, 125–138 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00665048
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00665048