Summary
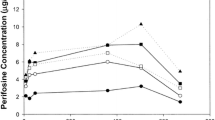
The pharmacokinetic characteristics of prednisolone and of chlorambucil and its β-oxidized metabolite, phenylacetic mustard (PAM) were studied in plasma after the oral administration of 200 mg prednimustine (Sterecyt) and a regimen consisting of 20 mg prednisolone plus 20 mg chlorambucil, respectively. A total of 12 cancer patients completed this trial. The drugs were given in a cross-over study as single doses, and serial plasma samples were collected for 32 h. Chlorambucil and PAM were assayed by a gas chromatographic/mass spectrometry method and prednisolone, by radioimmunoassay. The median relative availability of the prednisolone and chlorambucil moiety in prednimustine was 19% and 16%, respectively. Prednisolone, as well as chlorambucil and PAM, appeared later and at a significantly lower concentration in plasma after treatment with prednimustine as compared with the mixture of chlorambucil and prednisolone. We also found that the elimination phase of chlorambucil and PAM in plasma is prolonged after the administration of prednimustine as compared with chlorambucil per se. In contrast, the elimination of the prednisolone moiety of prednimustine and that following the administration of a plain prednisolone tablet did not seem to differ. The modified plasma profile of the alkylating components following prednimustine administration may be important for the clinical efficacy of prednimustine.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adair CG, Bridges JM, Desai ZR (1986) Can food affect the bioavailability of chlorambucil in patients with haematological malignancies? Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 17: 99
Ehrsson H, Wallin I, Nilsson SO, Johansson B (1983) Pharmacokinetics of chlorambucil in man after administration of the free drug and its prednisolone ester (Prednimustine, Leo 1031). Eur J Clin Pharmacol 24: 251
Ferry JJ, Horvath AM, Bekersky I, Heath EC, Ryan CF, Colburn WA (1988) Relative and absolute bioavailability of prednisone and prednisolone after separate oral and intravenous doses. J Clin Pharmacol 28: 81
Fredholm B, Gunnarsson K, Jensen G, Müntzing J (1978) Mammary tumour inhibition and subacute toxicity in rats of prednimustine and of its molecular components chlorambucil and prednisolone. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol 42: 159
Gaver RC, Deeb G, Pittman KA, Issell BF, Mittelman A, Smyth RD (1983) Disposition of orally administered [14C]-prednimustine in cancer patients. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 11: 139
Gunnarsson PO, Johansson SÅ, Svensson L (1984) Cholesterol ester formation by transesterification of chlorambucil: a novel pathway in drug metabolism. Xenobiotica 14 (7): 569
Hartley-Asp B, Gunnarsson PO, Liljekvist J (1986) Cytotoxicity and metabolism of prednimustine, chlorambucil and prednisolone in a Chinese hamster cell line. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 16: 85
Hartvig P, Simonsson B, Öberg G, Wallin I, Ehrsson H (1988) Inter- and intraindividual differences in oral chlorambucil pharmacokinetics. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 35: 551
Hiller E, Thiel E, Emmerich B, Lipp T, Herrmann R, Ho AD, Musch E, Loos U, Wellens W, Hügl E, Rüchle H, Manegold C, Schlag R, Linkesch W, Termander B, Nilsson B (1988) Randomized study comparing Sterecyt (prednimustine) and chlorambucil + prednisolone in non-Hodgkin's lymphomas of low-grade malignancy, clinical stages III–IV (abstract). Presented at the 13th ESMO Congress, Lugano, October 30 to November 2, 1988
Jakhammer T, Olsson A, Svensson L (1977) Mass fragmentographic determination of prednimustine and chlorambucil in plasma. Acta Pharm Suec 14: 485
McLean A, Woods RL, Catovsky D, Farmer P (1979) Pharmacokinetics and metabolism of chlorambucil in patients with malignant disease. Cancer Treat Rev 6: 33
Newell DR, Shepherd CR, Harrap KR (1981) The pharmacokinetics of prednimustine and chlorambucil in the rat. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 6: 85
Newell DR, Calvert AH, Harrap KR, McElwain TJ (1983) Studies on the pharmacokinetics of chlorambucil and prednimustine in man. Br J Clin Pharmacol 15: 253
Oppitz MM, Musch E, Malek M, Rüb HP, Unruh GE von, Loos U, Mühlenbruch B (1989) Studies on the pharmacokinetics of chlorambucil and prednimustine in patients using a new high-performance liquid chromatographic assay. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 23: 208
Sayed A, Hove W van, Vermeulen A (1981) Prednisolone plasma levels after oral administration of prednimustine. Oncology 38: 351
WHO (1979) Handbook for reporting results of cancer treatments. Offset Publication 48. WHO Geneva
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bastholt, L., Johansson, CJ., Pfeiffer, P. et al. A pharmacokinetic study of prednimustine as compared with prednisolone plus chlorambucil in cancer patients. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 28, 205–210 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00685510
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00685510