Summary
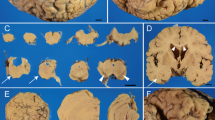
Clinico—pathological report of two sporadic cases of spongy degeneration of the CNS of non-Jewish origin with onset of clinical symptoms at the age of 5 years and protracted course up to late adolescence. The morphological findings of this “juvenile type” of the disorder, including diffuse spongy vacuolation of both the white and grey matter of the neuraxis, with diffuse and severe demyelination and astroglial hyperplasia, were consistent with those of other protracted infantile cases. In addition to spongy degeneration, axonal dystrophy and hyperpigmentation of the pallido-nigral system and axonal spheroids in the spongy cerebellar white matter were present in both cases. The significance of axonal dystrophy in these protracted forms of spongy degeneration is discussed.
Zusammenfassung
Klinisch-morphologischer Bericht über zwei sporadische Fälle von spongiöser Dystrophie des ZNS nicht-jüdischer Abstammung mit Beginn der klinischen Symptomatik im 5. Lebensjahr und protrahiertem Verlauf mit Tod in 21. bzw. 17. Lebensjahr. Die Gehirnveränderungen dieses „juvenilen Typs” der Erkrankung umfaßten diffuse spongiöse Veränderungen der weißen und grauen Substanz des gesamten ZNS mit schwerer diffuser Entmarkung und diffuser Astrogliareaktion. Sie entsprachen damit weitgehend den Befunden bei protrahierten infantilen Fällen. Beide Fälle boten daneben neuroaxonale Dystrophie und Hyperpigmentation des Pallidum und der roten Nigrazone sowie Axonschollen im spongiösen Kleinhirnmark. Die Bedeutung der axonalen Dystrophie bei den protrahierten Formen der spongiösen Dystrophie wird erörtert.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adachi, M., andB. W. Volk: Protracted form of spongy degeneration of the central nervous system (van Bogaert and Bertrand type). Neurology (Minneap.)18, 1084 to 1092 (1968).
—,B. J. Wallace, L. Schneck, andB. W. Volk: Fine structure of spongy degeneration of the central nervous system (van Bogaer and Bertrand type). J. Neuropath. exp. Neurol.25, 598–616 (1966).
Banker, B. Q., J. T. Robertson, andM. Victor: Spongy degeneration of the nervous system in infancy. Neurology (Minneap.)14, 981–1001 (1964).
Bogaert, L. van, andI. Bertrand: Spongy degeneration of the brain in infancy. Amsterdam: North-Holland Publ. Comp. 1967.
Brucher, J. M., R. Dom etA. Robin: Dégénérescence spongieuse juvénile du système nerveux central. Ses rapports avec la maladie d'Hallervorden-Spatz et les dystrophies neuro-axonales. Rev. neurol.119, 425–444 (1968).
Buchanan, D. S., andR. L. Davis: Spongy degeneration of the nervous system. A report of four cases with a review of the literature. Neurology (Minneap.)15, 207–222 (1965).
Feigin, I., C. E. Pena, andG. Budzilovich: The infantile spongy degenerations. Neurology (Minneap.)18, 153–167 (1968).
Gambetti, P., W. J. Mellmann, andN. K. Gonatas: Familial spongy degeneration of the central nervous system (Van Bogaert-Bertrand disease). An ultrastructural study. Acta neuropath. (Berl.)12, 103–115 (1969).
Hogan, G. R., andE. P. Richardson, Jr.: Spongy degeneration of the nervous system (Canavan's disease). Report of a case in an Irish-American family. Pediatrics35, 284–294 (1965).
Jellinger, K.: Neuroaxonale Dystrophien. Verh. dtsch. Ges. Path.52, 92–126 (1968).
Kamoshita, S., G. B. Reed, Jr., andM. J. Aguilar: Axonal dystrophy in a case of Canavan's spongy degeneration. Neurology (Minneap.)17, 895–898 (1967).
—,I. Rapin, K. Suzuki, andK. Suzuki: Spongy degeneration of the brain: A chemical study of two cases including isolation and characterization of myelin. Neurology (Minneap.)18, 975–985 (1968).
Kolkmann, F.-W., u.E. Völzke: Über die spongiösen Dystrophien des Nervensystems im frühen Kindesalter. I. Die diffuse Form — Typ Canavan. Z. Kinderheilk.97, 222–239 (1966).
Seitelberger, F., u.K. Jellinger: Spongiöser Typ der Leukodystrophie. In:Gerlach, J., H.-P. Jensen, W. Koos u.H. Kraus: Pädiatrische Neurochirurgie, S 845 bis 846, Stuttgart: G. Thieme 1967.
—, u.K. Weingarten: Zur Beteiligung des Nervus opticus bei einigen degenerativen Hirnprozessen. J. Génét. hum.15, 284–301 (1966).
Zu Rhein, G., P. L. Eickmann, andF. Puletti: Familial idiocy with spongy degeneration of the central nervous system of van Bogaert-Bertrand type. Neurology (Minneap.)10, 998–1006 (1960).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jellinger, K., Seitelberger, F. Juvenile form of spongy degeneration of the CNS. Acta Neuropathol 13, 276–281 (1969). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00690647
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00690647