Summary
-
1.
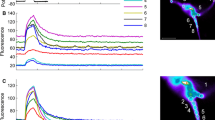
Segments from the nonspiking peripheral dendrites of a crustacean coxal receptor (T fiber) were studied using the voltage clamp technique. The peripheral endings of the T fiber are sensitive to stretch applied to a specialized receptor muscle by rotation of the coxa. The intraganglionary portion of the T fiber is presynaptic to the motor neurons innervating the coxal muscle.
-
2.
Depolarizing commands activated three separate fast channels: (i) a transient inward sodium current,INa, which is blocked by tetrodotoxin (TTX); (ii) a transient outward current,Io1, having the same voltage-dependent characteristics asINa; and (iii) a second, longer-lasting, outward current,Io2.
-
3.
BothINa andIo1 were inactivated when segments were clamped at voltages more positive than -50 mV, whereasIo2 could be activated at voltages more positive than -50 mV.
-
4.
Io1 andIo2 were blocked by 4-aminopyridine (4-AP) and by tetraethylammonium (TEA), althoughIo2 shows a greater sensitivity to TEA thanIo1.
-
5.
It is suggested thatIo1 may be a factor in determining the nonspiking behavior of the dendrites and thatIo2 may limit the stretch-induced depolarization in the dendrite to a value more negative than that at which the maximum rate of transmitter release occurs.
-
6.
In addition to the three fast currents, the presence of a slow inward and slow outward current could also be demonstrated. The effects of the slow currents were longer in segments cut from the proximal part of the dendrites.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams, D. J., Smith, S. J., and Thompson, S. H. (1980). Ionic currents in molluscan soma.Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 3141–167.
Aldrich, R. W., Getting, P. A., and Thompson, S. H. (1979). Inactivation of delayed outward current in molluscan neurone somata.J. Physiol. (Lond.) 291507–530.
Alexandrowicz, J. S., and Whitear, M. (1957). Receptor elements in the coxal region ofDecapoda crustacea.J. Mar. Biol. Ass. U.K. 36603–628.
Blight, A. R., and Llinas, R. (1980). The non-impulsive stretch receptor complex of the crab. A study of depolarization release coupling at a tonic sensorimotor synapse.Phil. Trans. Roy. Soc. B 290219–247.
Bush, B. M. H. (1980). Non-impulsive stretch receptors in crustaceans.Soc. Exp. Biol. Semin. Ser. 6147–176.
Bush, B. M. H., and Roberts, A. (1971). Coxal muscle receptors in the crab: the receptor potentials of the S and T fibers in response to ramp stretches.J. Exp. Biol. 55813–832.
Bush, B. M. H., Godden, D. H., and McDonald, G. A. (1975). Voltage clamping of non-impulsive afferent of the crab thoracico-coxal muscle receptor.J. Physiol. (Lond.) 2453–5(P).
Connor, J. A. (1975). Neural repetitive firing: A comparative study of membrane properties of crustacean walking leg axons.J. Neurophysiol. 38922–932.
Connor, J. A. (1978). Slow repetitive activity from fast conductance changes in neurons.Fed. Proc. 372139–2145.
Connor, J. A., and Stevens, F. C. (1971). Inward and delayed outward membrane currents in isolated neural somata under voltage clamp.J. Physiol. (Lond.) 2131–19.
DiCaprio, R. A., and Clarac, F. (1981). Reversal of a walking leg reflex elicited by a muscle receptor.J. Exp. Biol. 90197–203.
Edginton, D. R., and Stuart, A. E. (1979). Calcium channels in the high resistivity axonal membrane of photoreceptors of the giant barnacle.J. Physiol. (Lond.) 294433–445.
Hermann, A., and Gorman, A. L. F. (1981a). Effects of 4-aminopyridine on potassium currents in a molluscan neuron.J. Gen. Physiol. 7863–86.
Hermann, A., and Gorman, A. L. F. (1981b). Effects of tetraethylammonium on potassium current in a molluscan neuron.J. Gen. Physiol. 7887–110.
Krauhs, J. M., and Mirolli, M. (1975). Morphological changes associated with stretch in a mechanoreceptor.J. Neurocytol. 4231–246.
Lowe, D. A., Bush, B. M. H., and Ripley, S. H. (1978). Pharmacological evidence for “fast” sodium channels in nonspiking neurons.Nature 274289–290.
Marmor, M. F. (1971). The effects of temperature and ions on the current-voltage relation and electrical characteristics of a molluscan neuron.J. Physiol. (Lond.) 218573–598.
Marmor, M. F. (1975). The membrane of giant molluscan neurons: Electrophysiologic properties and the origin of resting potential. InProgress in Neurobiology, Pergamon Press, London, pp. 176–195.
Mirolli, M. (1979). The electrical properties of a crustacean sensory dendrite.J. Exp. Biol. 781–27.
Mirolli, M. (1981). Fast inward and outward current channels in a non-spiking neurone.Nature 292251–253.
Narahashi, T. (1974). Chemicals as tools in the study of excitable membranes. Physiol. Rev.54813–889.
Paul, D. H. (1976). Role of proprioceptive feedback from nonspiking mechanosensory cells in the sand crab,Emerita analoga.J. Exp. Biol. 65243–258.
Pepose, J. S., and Lisman, J. E. (1978). Voltage-sensitive potassium channels inLimulus ventral photoreceptors.J. Gen. Physiol. 71101–120.
Ripley, S. H., Bush, B. M. H., and Roberts, A. (1968). Crab muscle receptor which responds without impulses.Nature Lond. 2181170–1171.
Roberts, A., and Bush, B. M. H. (1971). Coxal muscle receptors in the crab: The receptor current and some properties of the receptor nerve fibers.J. Exp. Biol. 54515–524.
Thomas, M. V. (1977). Microelectrode amplifier with improved method of input-capacitance neutralisation.Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 15450–454.
Thompson, S. H. (1977). Three pharmacologically distinct potassium channels in molluscan neurons.J. Physiol. (Lond.) 265465–488.
Whitear, M. (1965). The fine structure of crustacean proprioceptors. II. The thoracico-coxal organs inCarcinus, Pagurus andAstacus.Phil. Trans. Roy. Soc. Lond. B 248437–456.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mirolli, M. Inward and outward currents in isolated dendrites of crustacea coxal receptors. Cell Mol Neurobiol 3, 355–370 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00734716
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00734716