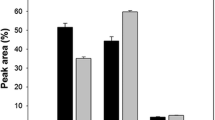
Abstract
A protein-free growth medium (W38 medium) had previously been developed for the NS0 mouse myeloma cell line which is cholesterol-auxotrophic. This paper describes the development of a protein-free growth medium for NS0 cells expressing humanised monoclonal antibody using GS (glutamine synthetase) as a selectable marker. Several GS-engineered NS0 cell lines expressing humanised monoclonal antibody grew in a modification of W38 medium which maintained GS-selection, supplemented with cholesterol, phosphatidylcholine and β-cyclodextrin. Further studies showed that additional glutamic acid, asparagine, ribonucleosides and choline chloride improved cell growth. Amino acid analysis identified a number of amino acids that were being depleted from the culture medium. NS0 cell lines 9D4 and 2H5 expressing CAMPATH-1H* were adapted to enable them to grow serum-free in the absence of cholesterol and β-cyclodextrin. Cholesterol-independent 9D4 (9D4.CF) cells grown in shake flask culture using an enriched protein-free medium (WNSD medium), supplemented with human recombinant insulin (Nucellin), reached a maximum cell density to 1.86×106 cells ml−1 producing 76.6 mg l−1 of antibody. CAMPATH-1H antibody produced using serum-free medium was found to be functionally activein vitro in the Antibody Dependant Cellular Cytotoxicity (ADCC) assay.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- C:
-
cholesterol
- CD:
-
cyclodextrin
- dhfr:
-
dihydrofolate reductase
- F68:
-
Pluronic F68
- GS:
-
glutamine synthetase
- MSX:
-
methionine sulphoximine
- P:
-
phosphatidylcholine
- PC-FBS:
-
phosphatidylcholine, cholesterol and foetal bovine serum
- RPMI:
-
RPMI 1640 medium
- ADCC:
-
Antibody-dependant cellular cytotoxicity
References
Bebbington CR, Renner G, Thomson S, King D, Abrams D and Yarranton GT (1992) High-level expression of recombinant antibody from myeloma cells using glutamine synthetase as an amplifiable selectable marker. Bio/Technology 10: 169–175.
Brown ME, Renner G, Field RP and Hassel T (1992) Process Development for the production of recombinant antibodies using the glutamine Synthetase (GS) system. Cytotechnology 9(1–3): 231–236.
Dyer MJS, Hale G, Hayhoe FGJ, and Waldmann H (1989) Effect of CAMPATH 1 antibodiesin vivo in patients with lymphoid malignancies: influence of antibody isotype. Blood 73: 1431–1439
Galfre G and Milstein (1982) Chemical typing of human kappa light chain subgroups expressed by human hybrid myelomas. Immunology 45: 125–127.
Hale G, Clark M and Waldmann H. (1985) Therapeutic potential of monoclonal antibodies: isotype specificity of antibody-dependant cell-mediated cytotoxicity with human lymphocytes. J. Immunol. 134: 3056–3061.
Hale G, Cobbold SP, Waldmann H (1988a) T-cell depletion with Campath 1H antibodies in allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. Transplantation 45: 753–759.
Hale G, Dyer MJS, Clark MR, Philips JM, Marcus R, Reichmann L, Winter G, and Waldmann H (1988b) Remision induction in non-Hodgkins lymphoma with reshaped human monoclonal antibody, CAMPATH-1H. Lancet 2: 1394–1399.
Hale G, Xia M-Q, Tighe HP, Dyer MJS, and Waldmann H (1990) The CAMPATH-1H antigen (CDw52). Tissue Antigens 35: 118–127.
Isaacs JD (1990) The antiglobulin responce to therapeutic antibodies. Semin. Immunol 2: 449–456.
Isaacs JD, Watts RA, Hazleman BL, Hale G, Keogan MT Cobbold SP and Waldmann H (1992) Humanised monoclonal antibody therapy for rheumatoid arthritis. The Lancet 340 (Sept 26): 748–752.
Keen MJ (1995A) Development of a serum-free culture medium for the large scale production of recombinant protein from Chinese hamster ovary cells. Cytotechnology 17: 153–163.
Keen MJ (1995) High density culture of rat myeloma and rat hybridoma cells in a protein-free medium. Cytotechnology 17: 193–202.
Keen MJ and Steward T (1995) Adaptation of cholesterol-requiring NS0 mouse myeloma cells to high density growth in a fully defined protein-free and cholesterol-free culture medium. Cytotechnology 17: 203–211.
Lifely MR, Hale C, Boyce S, Keen MJ and Phillips J (1995) Glycosylation and biological activity of CAMPATH-1H expressed in different cell lines and grown under different culture conditions. Glycobiology 5(8): in press.
Nacheva E, Fischer P, Karpas A, Sherrington P, Hayhoe FGJ, Manolov G, Manolova Y, Ferstl G, Haas O, and Gadner H (1987) Complex translocation t (8; 12; 14) in a cell line derived from a child with nonendemic Burkitts-type acute lymphoplastic leukemia. Cancer Genet. Cytogenet. 28: 145–153.
Sato JD Kawamoto T and Okamoto T (1987) Cholesterol requirement of P3-X63-Ag8 mouse myeloma cells for growth in vitro. J. Exp. Med. 165: 1761–1766
Stryer L (1988) Biochemistry 3rd edition, W. H. Freeman and Co. Page 290.
Page MJ and Sydenham MA (1991) High level expression of the humanised monoclonal antibody Campath 1H in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Bio/Technology 9: 64–68.
Riechman L, Clark M, Waldman H and Winter G (1988) Reshaping human antibodies for therapy. Nature 332: 323–327.
Urlaub G and Chasin LA (1980) Isolation of Chinese hamster ovary cell mutants deficient in dihydrofolate reductase activity. Pros. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 77(7): 4216–4220.
Wallace GR (1994) Monoclonal antibodies as therapeutic agents. The Pharmaceutical Journal 252: 715–718.
Winter G and Milstein C (1991). Man made antibodies. Nature 349: 293–299, 24th Jan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Keen, M.J., Hale, C. The use of serum-free medium for the production of functionally active humanised monoclonal antibody from NS0 mouse myeloma cells engineered using glutamine synthetase as a selectable marker. Cytotechnology 18, 207–217 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00767768
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00767768